L03 - UMBC
... Paths allow us to give the same name to different files located in different directories. Each running program has a current directory and all filenames are implicitly assumed to start with the name of that directory unless they begin with a slash. ...
... Paths allow us to give the same name to different files located in different directories. Each running program has a current directory and all filenames are implicitly assumed to start with the name of that directory unless they begin with a slash. ...
2.01 - SEJONG
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface ...
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface ...
Processes
... signals and other parts of the environment must be moved as well. • A process consists of three segments according to Fugetta’s framework: – Code segment is the part that contains the set of instructions that make up the program that is being executed. – Resource segment contains references to exter ...
... signals and other parts of the environment must be moved as well. • A process consists of three segments according to Fugetta’s framework: – Code segment is the part that contains the set of instructions that make up the program that is being executed. – Resource segment contains references to exter ...
Lecture-2
... Typically, a number associated with each system call System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers API converts symbolic names of services to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS ...
... Typically, a number associated with each system call System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers API converts symbolic names of services to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS ...
2K: A Component-Based Network-Centric Operating System for the
... Upon receiving an agent, a node processes its content and forwards it to the next node in the distribution network. When an application requests a new component through the ORB reflective interface, the system checks whether there is an appropriate, local version of this component. If one is not ava ...
... Upon receiving an agent, a node processes its content and forwards it to the next node in the distribution network. When an application requests a new component through the ORB reflective interface, the system checks whether there is an appropriate, local version of this component. If one is not ava ...
unit 1
... The syntax rules of a language define how we can put symbols, reserved words, and identifiers together to make a valid program The semantics of a program statement define what that statement means (its purpose or role in a program) A program that is syntactically correct is not ...
... The syntax rules of a language define how we can put symbols, reserved words, and identifiers together to make a valid program The semantics of a program statement define what that statement means (its purpose or role in a program) A program that is syntactically correct is not ...
Conventions for Arithmetic Operations in Java
... defend the omission of overloaded operators from Java on the grounds that it prevents a misguided programmer from defining operators with bizarre or misleading semantics. Presumably that’s what Flanagan5 and others in the “Java community” are worrying about. But that’s no concern for serious softwar ...
... defend the omission of overloaded operators from Java on the grounds that it prevents a misguided programmer from defining operators with bizarre or misleading semantics. Presumably that’s what Flanagan5 and others in the “Java community” are worrying about. But that’s no concern for serious softwar ...
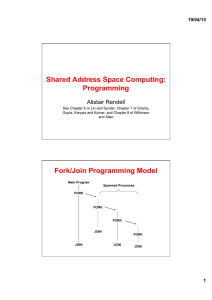
Shared Address Space Computing: Programming Fork/Join
... – What is wrong with the above? – What low level hardware support is provided to address this? ...
... – What is wrong with the above? – What low level hardware support is provided to address this? ...
1up
... – What is wrong with the above? – What low level hardware support is provided to address this? ...
... – What is wrong with the above? – What low level hardware support is provided to address this? ...
Nachos Overview - Computer and Information Science | Brooklyn
... students only need to compile a few small user programs. But if you only have Sparcstations, you need to get gcc to cross-compile to the DEC MIPS. 2. The Nachos kernel runs runs native mode while the user programs runs on the simulated CPU. This is a little weird on the SparcStation because the user ...
... students only need to compile a few small user programs. But if you only have Sparcstations, you need to get gcc to cross-compile to the DEC MIPS. 2. The Nachos kernel runs runs native mode while the user programs runs on the simulated CPU. This is a little weird on the SparcStation because the user ...
COS 217: Introduction to Programming Systems Vivek Pai
... www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr06/cos217/policies.html ...
... www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr06/cos217/policies.html ...
1) Routine is not loaded until it is called. All routines are kept on disk
... load format. The main program is loaded into memory & is executed. This type of loading is called _________ ...
... load format. The main program is loaded into memory & is executed. This type of loading is called _________ ...
A Universal Framework for (nearly) Arbitrary Dynamic Languages
... Data in the system is organized into objects, which consist primarily of some content, some instance variables, attached methods, and attributes. The content of an object is a block of arbitrary data, which is accessible by methods invoked on that object. The variables are a mapping of identifying s ...
... Data in the system is organized into objects, which consist primarily of some content, some instance variables, attached methods, and attributes. The content of an object is a block of arbitrary data, which is accessible by methods invoked on that object. The variables are a mapping of identifying s ...
chapter 1 Slides - NYU Computer Science Department
... » Java programs intended to be downloaded via the WWW and run immediately » “little applications” » requires a web browser ...
... » Java programs intended to be downloaded via the WWW and run immediately » “little applications” » requires a web browser ...
View File - UET Taxila
... Grammar: set of rules that constraint the way in which programs are written. A program that does not follow these rules has one or more syntax errors. Software Development Kit (SDK) that contains the following: Libraries: also known as Application Programming Interface (API), these files are previou ...
... Grammar: set of rules that constraint the way in which programs are written. A program that does not follow these rules has one or more syntax errors. Software Development Kit (SDK) that contains the following: Libraries: also known as Application Programming Interface (API), these files are previou ...
Linux+ Guide to Linux Certification
... amount of memory they need • Except for COM files, there can be any number of files in TPA at one time • Two programs can’t be run at same time • Shrinking and expanding of memory allocation during execution can be done only from programs written in either assembly language or C Understanding Operat ...
... amount of memory they need • Except for COM files, there can be any number of files in TPA at one time • Two programs can’t be run at same time • Shrinking and expanding of memory allocation during execution can be done only from programs written in either assembly language or C Understanding Operat ...
Operating System Concepts
... When multiple applications are active at the same time, it is necessary to protect the data, I/O device access, and other resource use of each application from the rest. ...
... When multiple applications are active at the same time, it is necessary to protect the data, I/O device access, and other resource use of each application from the rest. ...
Fork() system call - IT325
... Fork() system call If a program contains a call to fork( ), the execution of the program results in the execution of two processes. One process is created to start executing the program. When the fork( ) system call is executed, another process is created. The original process is called the parent p ...
... Fork() system call If a program contains a call to fork( ), the execution of the program results in the execution of two processes. One process is created to start executing the program. When the fork( ) system call is executed, another process is created. The original process is called the parent p ...
Assignment3 - Operating Systems
... Fork() system call If a program contains a call to fork( ), the execution of the program results in the execution of two processes. One process is created to start executing the program. When the fork( ) system call is executed, another process is created. The original process is called the parent p ...
... Fork() system call If a program contains a call to fork( ), the execution of the program results in the execution of two processes. One process is created to start executing the program. When the fork( ) system call is executed, another process is created. The original process is called the parent p ...
Based on the above, how many processes are created by
... Fork() system call If a program contains a call to fork( ), the execution of the program results in the execution of two processes. One process is created to start executing the program. When the fork( ) system call is executed, another process is created. The original process is called the parent p ...
... Fork() system call If a program contains a call to fork( ), the execution of the program results in the execution of two processes. One process is created to start executing the program. When the fork( ) system call is executed, another process is created. The original process is called the parent p ...
Operating Systems for Embedded Computers
... this appendix some useful C keywords and macros are explained (mostly on examples from Benu or in simplified forms). ...
... this appendix some useful C keywords and macros are explained (mostly on examples from Benu or in simplified forms). ...
Section 3A: Windows forensics
... specific physical location on the drive. Virtual Cluster Number (VCN) – When a file is saved in the NTFS, it is assigned both a logical cluster number and a virtual cluster number. The logical cluster is a physical location, while the virtual cluster consists of chained clusters. ...
... specific physical location on the drive. Virtual Cluster Number (VCN) – When a file is saved in the NTFS, it is assigned both a logical cluster number and a virtual cluster number. The logical cluster is a physical location, while the virtual cluster consists of chained clusters. ...
Library (computing)
In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often to develop software. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. In IBM's OS/360 and its successors they are referred to as partitioned data sets.In computer science, a library is a collection of implementations of behavior, written in terms of a language, that has a well-defined interface by which the behavior is invoked. This means that as long as a higher level program uses a library to make system calls, it does not need to be re-written to implement those system calls over and over again. In addition, the behavior is provided for reuse by multiple independent programs. A program invokes the library-provided behavior via a mechanism of the language. For example, in a simple imperative language such as C, the behavior in a library is invoked by using C's normal function-call. What distinguishes the call as being to a library, versus being to another function in the same program, is the way that the code is organized in the system. Library code is organized in such a way that it can be used by multiple programs that have no connection to each other, while code that is part of a program is organized to only be used within that one program. This distinction can gain a hierarchical notion when a program grows large, such as a multi-million-line program. In that case, there may be internal libraries that are reused by independent sub-portions of the large program. The distinguishing feature is that a library is organized for the purposes of being reused by independent programs or sub-programs, and the user only needs to know the interface, and not the internal details of the library.The value of a library is the reuse of the behavior. When a program invokes a library, it gains the behavior implemented inside that library without having to implement that behavior itself. Libraries encourage the sharing of code in a modular fashion, and ease the distribution of the code. The behavior implemented by a library can be connected to the invoking program at different program lifecycle phases. If the code of the library is accessed during the build of the invoking program, then the library is called a static library. An alternative is to build the executable of the invoking program and distribute that, independently from the library implementation. The library behavior is connected after the executable has been invoked to be executed, either as part of the process of starting the execution, or in the middle of execution. In this case the library is called a dynamic library. A dynamic library can be loaded and linked as part of preparing a program for execution, by the linker. Alternatively, in the middle of execution, an application may explicitly request that a module be loaded.Most compiled languages have a standard library although programmers can also create their own custom libraries. Most modern software systems provide libraries that implement the majority of system services. Such libraries have commoditized the services which a modern application requires. As such, most code used by modern applications is provided in these system libraries.