Female pelvic anatomy
... uterine wall form the Myometrium (2), a myoma located in this layer is called a intramural myoma (4) The posterior surface of the uterus is completely covered by peritoneum. Anteriorly the peritoneum is reflected off the uterus at a much ...
... uterine wall form the Myometrium (2), a myoma located in this layer is called a intramural myoma (4) The posterior surface of the uterus is completely covered by peritoneum. Anteriorly the peritoneum is reflected off the uterus at a much ...
Perineum Dr. B. Mantaring Outline General Features of the
... - Secondary to straddle injury or incorrect passage of catheter into the urethra - Extravasation of urine into the superficial perineal space ...
... - Secondary to straddle injury or incorrect passage of catheter into the urethra - Extravasation of urine into the superficial perineal space ...
Biomechanics Functional Anatomy Human Female Genitalia
... subcutaneous fat. They provide an anchorage for the rectum. Because the external longitudinal muscle is absent, the circular muscle predominates and is further reinforced and thickened to form the massive sphincter ani internus muscle. The superficial (subcutaneous) perineal space also contains the ...
... subcutaneous fat. They provide an anchorage for the rectum. Because the external longitudinal muscle is absent, the circular muscle predominates and is further reinforced and thickened to form the massive sphincter ani internus muscle. The superficial (subcutaneous) perineal space also contains the ...
Chapter 28b
... cumulus oophorus - mound of granulosa cells; covers the oocyte; secures the oocyte to the follicular wall corona radiata - first layer of granulosa cells attached to the ...
... cumulus oophorus - mound of granulosa cells; covers the oocyte; secures the oocyte to the follicular wall corona radiata - first layer of granulosa cells attached to the ...
Anatomy of the genital tract The external genetalia: The external
... between the descending pubic rami and lies beneath levator ani muscles. The deep transverse perineal muscles lie between the two layers and the diaphragm is pierced by the urethra and vagina. The perineal body: This is a mass of muscular tissue lies between the anal canal and lower third of the vagi ...
... between the descending pubic rami and lies beneath levator ani muscles. The deep transverse perineal muscles lie between the two layers and the diaphragm is pierced by the urethra and vagina. The perineal body: This is a mass of muscular tissue lies between the anal canal and lower third of the vagi ...
eprint_10_28134_200
... appears flattened and lying on the vaginal floor. Penetration of the cervical lumen is very easy at this time. A large quantity of mucus is secreted and acts as a lubricant to facilitate passage of the penis or foal through the vagina. The mucus allows semen to enter the uterus. ...
... appears flattened and lying on the vaginal floor. Penetration of the cervical lumen is very easy at this time. A large quantity of mucus is secreted and acts as a lubricant to facilitate passage of the penis or foal through the vagina. The mucus allows semen to enter the uterus. ...
Pruritus vulvae
... BARTHOLIN'S CYST • Is the most common vagial vulvar tumour. Cyst may arise from the duct of the Bartholin's gland that lies in subcutaneous tissue below the lower third of labium majorum. Cysts can develop if the opening of bartholin duct becomes blocked and distended with mucoid secretion. • It pr ...
... BARTHOLIN'S CYST • Is the most common vagial vulvar tumour. Cyst may arise from the duct of the Bartholin's gland that lies in subcutaneous tissue below the lower third of labium majorum. Cysts can develop if the opening of bartholin duct becomes blocked and distended with mucoid secretion. • It pr ...
Lab 10
... • Lies external to the vagina and includes the mons pubis, labia, clitoris, and vestibular structures • Mons pubis – round, fatty area overlying the pubic symphysis • Labia majora – elongated, hair-covered, fatty skin folds homologous to the male scrotum • Labia minora – hair-free skin folds lying w ...
... • Lies external to the vagina and includes the mons pubis, labia, clitoris, and vestibular structures • Mons pubis – round, fatty area overlying the pubic symphysis • Labia majora – elongated, hair-covered, fatty skin folds homologous to the male scrotum • Labia minora – hair-free skin folds lying w ...
Other Infections of the Vulva
... is caused by the hemolytic S aureus or streptococci. The disease is autoinoculable and spreads quickly to other parts of the body, including the vulva. Thin-walled vesicles and bullae develop that display reddened edges and crusted surfaces after rupture. The disease is common in children, particula ...
... is caused by the hemolytic S aureus or streptococci. The disease is autoinoculable and spreads quickly to other parts of the body, including the vulva. Thin-walled vesicles and bullae develop that display reddened edges and crusted surfaces after rupture. The disease is common in children, particula ...
Pelvis and Contents
... • Innervation: branches of Pudendal nerve (hypogastric plexus & pelvic splanchnic nerves) • Arterial Supply: – Uterine arteries (from internal iliac) + arcuate branches of = uterus – Ovarian arteries (from abdominal aorta) + ovarian branches of uterine arteries = ovaries ...
... • Innervation: branches of Pudendal nerve (hypogastric plexus & pelvic splanchnic nerves) • Arterial Supply: – Uterine arteries (from internal iliac) + arcuate branches of = uterus – Ovarian arteries (from abdominal aorta) + ovarian branches of uterine arteries = ovaries ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy
... D. Vulva (pudendum) - external genitalia of the female, include: 1. Mons pubis - adipose CT covering the pubic symphysis 2. Labia majora - 2 thickened longitudinal skin folds that contain loose CT, adipose, smooth muscle, sweat & sebaceous glands; homologous to male scrotum 3. Labia minora - smaller ...
... D. Vulva (pudendum) - external genitalia of the female, include: 1. Mons pubis - adipose CT covering the pubic symphysis 2. Labia majora - 2 thickened longitudinal skin folds that contain loose CT, adipose, smooth muscle, sweat & sebaceous glands; homologous to male scrotum 3. Labia minora - smaller ...
The uterus
... Labia major are two fold of skin with underlying adipose Tissue. They contain sebaceous and sweat gland. Labia minor are two fold of skin lie below the labia major Anteriorly, they divide into 2 to form prepuce and frenulum of clitoris Posteriorly, they fuse to form a fold of skin called the fourche ...
... Labia major are two fold of skin with underlying adipose Tissue. They contain sebaceous and sweat gland. Labia minor are two fold of skin lie below the labia major Anteriorly, they divide into 2 to form prepuce and frenulum of clitoris Posteriorly, they fuse to form a fold of skin called the fourche ...
LICHEN SCLEROSUS Melbourne Melbourne Sexual Health Centre
... For some women, progressive LS can occur without symptoms. Also, despite resolution of itch during treatment, there can sometimes still be mild active disease. Pulsed treatment, such as weekly, has very little risk of steroid induced skin atrophy and is often recommended as the maintenance dose. ...
... For some women, progressive LS can occur without symptoms. Also, despite resolution of itch during treatment, there can sometimes still be mild active disease. Pulsed treatment, such as weekly, has very little risk of steroid induced skin atrophy and is often recommended as the maintenance dose. ...
Pelvis and Contents - Fisiokinesiterapia
... • Innervation: branches of Pudendal nerve (hypogastric plexus & pelvic splanchnic nerves) • Arterial Supply: – Uterine arteries (from internal iliac) + arcuate branches of = uterus – Ovarian arteries (from abdominal aorta) + ovarian branches of uterine arteries = ovaries ...
... • Innervation: branches of Pudendal nerve (hypogastric plexus & pelvic splanchnic nerves) • Arterial Supply: – Uterine arteries (from internal iliac) + arcuate branches of = uterus – Ovarian arteries (from abdominal aorta) + ovarian branches of uterine arteries = ovaries ...
ANATOMY OF FEMALE REPRODUCTION ORGANS
... arranged in parallel to each other thus facilitating sperm ascent. Cervical mucus contributes significantly to the normal vaginal discharge. A part forms the mucus plug which functionally closes the cervical canal and has ...
... arranged in parallel to each other thus facilitating sperm ascent. Cervical mucus contributes significantly to the normal vaginal discharge. A part forms the mucus plug which functionally closes the cervical canal and has ...
Dermatology/Vulval Conditions Clinic
... inflammation of the dermis causes a distinctive skin appearance. The cause is not known, but is likely to be autoimmune. LS can occur anywhere on the body but most commonly affects anogenital skin, especially in females. In men and boys the penis (particularly if uncircumcised) and perianal area may ...
... inflammation of the dermis causes a distinctive skin appearance. The cause is not known, but is likely to be autoimmune. LS can occur anywhere on the body but most commonly affects anogenital skin, especially in females. In men and boys the penis (particularly if uncircumcised) and perianal area may ...
Female Reproductive System
... skin, extending from the pubis to the posterior angle of the vulva • The labia minora, (singular: labium minus), two small folds of skin covered internally by a mucosa, they extend longitudinally and guard the vestibule, the place where the vagina opens. • The clitoris, is a small cylindrical mass o ...
... skin, extending from the pubis to the posterior angle of the vulva • The labia minora, (singular: labium minus), two small folds of skin covered internally by a mucosa, they extend longitudinally and guard the vestibule, the place where the vagina opens. • The clitoris, is a small cylindrical mass o ...
Anatomy of female genital organs
... The mons pubis is a rounded fatty elevation located anterior to the pubic symphysis and lower pubic region The mons pubis becomes covered with coarse pubic hairs during puberty, which also decrease after menopause. Labia Majora The labia (L. large lips) are two symmetrical folds of skin, whi ...
... The mons pubis is a rounded fatty elevation located anterior to the pubic symphysis and lower pubic region The mons pubis becomes covered with coarse pubic hairs during puberty, which also decrease after menopause. Labia Majora The labia (L. large lips) are two symmetrical folds of skin, whi ...
Document
... A cutaneous sac consisting of 2 layers: heavily pigmented skin and the closely related dartos fascia, a fat-free fascial layer including smooth muscle fibers (dartos muscle) responsible for the rugose (wrinkled) appearance of the scrotum. Because the dartos muscle attaches to the skin, its contracti ...
... A cutaneous sac consisting of 2 layers: heavily pigmented skin and the closely related dartos fascia, a fat-free fascial layer including smooth muscle fibers (dartos muscle) responsible for the rugose (wrinkled) appearance of the scrotum. Because the dartos muscle attaches to the skin, its contracti ...
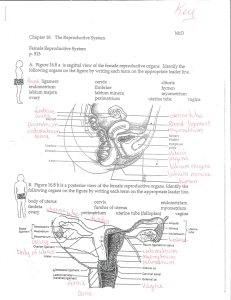
Chapter 16: The Reproductive System p. 513 c Yt(l ligament Iabium
... membrane that partially doses the vaginal canal ÿ %,x'vÿ-ÿ duct through which the ovum travels to reach the uterus v,v.ÿv ÿ_ÿ v <ÿ ÿ ÿ3C outer most layer of the wall of the uterus iDÿ'ÿVÿ ,ÿav£ vv,ÿ.ÿ'/ÿ ...
... membrane that partially doses the vaginal canal ÿ %,x'vÿ-ÿ duct through which the ovum travels to reach the uterus v,v.ÿv ÿ_ÿ v <ÿ ÿ ÿ3C outer most layer of the wall of the uterus iDÿ'ÿVÿ ,ÿav£ vv,ÿ.ÿ'/ÿ ...
Functional Anatomy of the Female Sex Organs
... on the introital opening may contribute to a sensation of genital engorgement. ...
... on the introital opening may contribute to a sensation of genital engorgement. ...
The Pelvis and Perineum
... • Comprised of three fused bones: The ilium, ischium, and pubis • Ilium: Superior region;important structures are: iliac crest, anterior/posterior superior iliac spines, anterior/posterior inferior iliac spines. • Ischium:Posteroinferior region;ischial spine, ischial tuberosity;lesser sciatic notch. ...
... • Comprised of three fused bones: The ilium, ischium, and pubis • Ilium: Superior region;important structures are: iliac crest, anterior/posterior superior iliac spines, anterior/posterior inferior iliac spines. • Ischium:Posteroinferior region;ischial spine, ischial tuberosity;lesser sciatic notch. ...
Breast and Pelvic Anatomy
... The bony pelvis consisting of bilateral iliac, ischium, and pubic bones anchored to the sacrum, results in several typical shapes. The shape most often found in adult females is the gynecoid pelvis which is of a configuration most consistent with vaginal childbirth as distinguished from the androi ...
... The bony pelvis consisting of bilateral iliac, ischium, and pubic bones anchored to the sacrum, results in several typical shapes. The shape most often found in adult females is the gynecoid pelvis which is of a configuration most consistent with vaginal childbirth as distinguished from the androi ...
Vulva

The vulva (from the Latin vulva, plural vulvae, see etymology) consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals.The vulva has many major and minor anatomical structures, including the labia majora, mons pubis, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vulval vestibule, greater and lesser vestibular glands, external urethral orifice and the opening of the vagina (introitus). Its development occurs during several phases, chiefly during the fetal and pubertal periods of time. As the outer portal of the human uterus or womb, it protects its opening by a ""double door"": the labia majora (large lips) and the labia minora (small lips). The vagina is a self-cleaning organ, sustaining healthy microbial flora that flow from the inside out; the vulva needs only simple washing to assure good vulvovaginal health, without recourse to any internal cleansing.The vulva has a sexual function; these external organs are richly innervated and provide pleasure when properly stimulated. In various branches of art, the vulva has been depicted as the organ that has the power both to ""give life"" (often associated with the womb), and to give sexual pleasure to humankind.The vulva also contains the opening of the female urethra, but apart from this has little relevance to the function of urination.