WILDERNESS AND MOUNTAIN MEDICINE
... • It runs forward on the medial wall of the orbit, continues as the anterior ethmoidal nerve through the anterior ethmoidal foramen. It then descends to enter the nasal cavity where it gives off two internal nasal branches and then continues as the external nasal nerve which supply the skin at the a ...
... • It runs forward on the medial wall of the orbit, continues as the anterior ethmoidal nerve through the anterior ethmoidal foramen. It then descends to enter the nasal cavity where it gives off two internal nasal branches and then continues as the external nasal nerve which supply the skin at the a ...
Over-the-counter vaginal preparations
... vagina due to reduced lubrication and thinning tissue. It is caused by reduced levels of oestrogen, generally following menopause. Oestrogen assists in keeping the vagina lubricated and healthy. However, when oestrogen levels drop, vaginal tissue may become thin, dry and inflamed. Atrophic vaginitis ...
... vagina due to reduced lubrication and thinning tissue. It is caused by reduced levels of oestrogen, generally following menopause. Oestrogen assists in keeping the vagina lubricated and healthy. However, when oestrogen levels drop, vaginal tissue may become thin, dry and inflamed. Atrophic vaginitis ...
Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System
... isthmus and forms the internal orifice(internal osuteri). At the extremty of the vaginal portion is the opening leading to the vagina, the external orifice (external os uteri), which is round or oval before parturition but takes the form of a transverse slit in women who have borne children. ...
... isthmus and forms the internal orifice(internal osuteri). At the extremty of the vaginal portion is the opening leading to the vagina, the external orifice (external os uteri), which is round or oval before parturition but takes the form of a transverse slit in women who have borne children. ...
Acute perineum and scrotum: Cross-sectional imaging
... diaphragm). The superficial pouch has structures common to both males and females, including the ischiocavernosus, bulbospongiosus, superficial transversus perinei muscles, the pudendal vessels, and pudendal nerves. Unique structures in the male include the root of the scrotum, bulb of the penis, an ...
... diaphragm). The superficial pouch has structures common to both males and females, including the ischiocavernosus, bulbospongiosus, superficial transversus perinei muscles, the pudendal vessels, and pudendal nerves. Unique structures in the male include the root of the scrotum, bulb of the penis, an ...
medial view, deep surface, right side
... (probe to your right) to the outside near the blunt end of the probe (on your left). It is considered a urogenital sinus. ...
... (probe to your right) to the outside near the blunt end of the probe (on your left). It is considered a urogenital sinus. ...
pelvic part
... inferior border of the pubic symphysis, inferior rami of the pubes, the rami of ischia ischial tuberosities sacrotuberous ligaments ...
... inferior border of the pubic symphysis, inferior rami of the pubes, the rami of ischia ischial tuberosities sacrotuberous ligaments ...
Perineum - Lectures - gblnetto
... and perineal membrane. The muscular layer consists of the deep transverse perineal muscles and the sphincter urethrae. The more superficial fascial layer is known as the inferior fasÂcia of the urogenital diaphragm or more commonly the perineal membrane. Through the diaphragm passes the membranous ...
... and perineal membrane. The muscular layer consists of the deep transverse perineal muscles and the sphincter urethrae. The more superficial fascial layer is known as the inferior fasÂcia of the urogenital diaphragm or more commonly the perineal membrane. Through the diaphragm passes the membranous ...
Clinical Anatomy of the Pelvis
... • The scrotum is easily distended. • In persons with large indirect inguinal hernias, for example, the intestine may enter the scrotum, making it as large as a soccer ball. • Similarly, inflammation of the testes (orchitis), associated with mumps, bleeding in the subcutaneous tissue, or chronic lymp ...
... • The scrotum is easily distended. • In persons with large indirect inguinal hernias, for example, the intestine may enter the scrotum, making it as large as a soccer ball. • Similarly, inflammation of the testes (orchitis), associated with mumps, bleeding in the subcutaneous tissue, or chronic lymp ...
Blocks of the ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric
... It divides into a genital and femoral branch at a variable distance above the inguinal ligament. (Approximately 1-1.5cm) ...
... It divides into a genital and femoral branch at a variable distance above the inguinal ligament. (Approximately 1-1.5cm) ...
pap training guideline for registered nurses
... Concurrent with endocrine changes, ovarian function diminishes during a woman's 40s, and menstrual periods begin to cease between 40 and 55 years of age although fertility may continue. Menopause is completed after 1 year of no menses. Just as menarche in the adolescent is one aspect of puberty, so ...
... Concurrent with endocrine changes, ovarian function diminishes during a woman's 40s, and menstrual periods begin to cease between 40 and 55 years of age although fertility may continue. Menopause is completed after 1 year of no menses. Just as menarche in the adolescent is one aspect of puberty, so ...
The primitive sex cords will be dissociated forming irregular cell
... 3.extrophy of the bladder: failure of mesodermal migration at the primitive streak toward the cloacal membrane. It may be associated with epispadias. 4.micropenis. 5.bifid penis (double penis). The external genitalia of the female: The short genital tubercles will form the clitoris, the unfused uret ...
... 3.extrophy of the bladder: failure of mesodermal migration at the primitive streak toward the cloacal membrane. It may be associated with epispadias. 4.micropenis. 5.bifid penis (double penis). The external genitalia of the female: The short genital tubercles will form the clitoris, the unfused uret ...
Anatomy Exam 3 Outline Lecture 16 – Pelvis and Perineum
... ii. As female continues to develop, the erectile tissue distally becomes glands of clitoris; the urethral groove forms and starts to seal together so we will break down that tissue and form a urethra. The labioscrotal folds fuse together posteriorly but remain unfused anteriorly. Growth continues an ...
... ii. As female continues to develop, the erectile tissue distally becomes glands of clitoris; the urethral groove forms and starts to seal together so we will break down that tissue and form a urethra. The labioscrotal folds fuse together posteriorly but remain unfused anteriorly. Growth continues an ...
Perenium - Dr. Krieg
... to the perineal body to anchor the anus. Just posterior to the rectum, the ischiorectal fossae from either side are continuous with each other such that an infection of the fossae can assume a horseshoe shape. The area through which the fossae connect posteriorly is between the superficial and ...
... to the perineal body to anchor the anus. Just posterior to the rectum, the ischiorectal fossae from either side are continuous with each other such that an infection of the fossae can assume a horseshoe shape. The area through which the fossae connect posteriorly is between the superficial and ...
Surface and Regional Anatomy
... Palpation - examination with the hands, touching feeling, or perceiving by the sense of touch Auscultation - listening to sounds emitted from organs Observation - the art of looking ...
... Palpation - examination with the hands, touching feeling, or perceiving by the sense of touch Auscultation - listening to sounds emitted from organs Observation - the art of looking ...
Pelvic Anatomy - Johns Hopkins Medicine
... Placement of deep lateral wall retractors on Psoas at laparotomy? Hyperflexion of the hips in lithotomy position or tight underwear? Leaning on the back of the legs during vaginal surgery or sacrospinous ligament fixation? ...
... Placement of deep lateral wall retractors on Psoas at laparotomy? Hyperflexion of the hips in lithotomy position or tight underwear? Leaning on the back of the legs during vaginal surgery or sacrospinous ligament fixation? ...
as a pdf
... Reconstruction of Large Defects In the majority of cases of vulvar carcinoma, primary closure is possible following resection of the primary tumor because of the laxity of the skin and subcutaneous tissues in the area. The ease of primary closure is dependant on factors such as age, obesity, parity ...
... Reconstruction of Large Defects In the majority of cases of vulvar carcinoma, primary closure is possible following resection of the primary tumor because of the laxity of the skin and subcutaneous tissues in the area. The ease of primary closure is dependant on factors such as age, obesity, parity ...
Anatomy of the male perineum, and reproductive organs
... prostate empty into these two sinuses. • Midway along its length, the urethral crest is enlarged to form a somewhat circular elevation (the seminal colliculus). The seminal colliculus is used to determine the position of the prostate gland during transurethral transection of the prostate. • A small ...
... prostate empty into these two sinuses. • Midway along its length, the urethral crest is enlarged to form a somewhat circular elevation (the seminal colliculus). The seminal colliculus is used to determine the position of the prostate gland during transurethral transection of the prostate. • A small ...
the lower extremity – the pelvic girdle
... Ischium bears the weight of the body when sitting down – it is the anterior inferior section of the girdle The ischium joins with the pubis to surround the obturator foramen through which veins, arteries and nerves pass to lead to the lower extremities ...
... Ischium bears the weight of the body when sitting down – it is the anterior inferior section of the girdle The ischium joins with the pubis to surround the obturator foramen through which veins, arteries and nerves pass to lead to the lower extremities ...
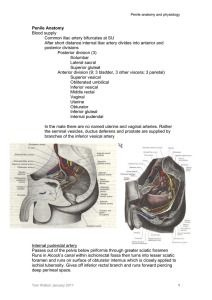
Penile Anatomy Blood supply Common iliac artery bifurcates
... Internal pudendal artery Passes out of the pelvis below piriformis through greater sciatic foramen Runs in Alcock’s canal within ischiorectal fossa then turns into lesser sciatic foramen and runs on surface of obturator internus which is closely applied to ischial tuberosity. Gives off inferior rect ...
... Internal pudendal artery Passes out of the pelvis below piriformis through greater sciatic foramen Runs in Alcock’s canal within ischiorectal fossa then turns into lesser sciatic foramen and runs on surface of obturator internus which is closely applied to ischial tuberosity. Gives off inferior rect ...
10. Development of genital system. Gonads. Genital ducts. External
... o the caudal two thirds of the vagina originates from the sinovaginal bulbs that originate as evaginations of the entodermal urogenital sinus; the vagina forms as a thin persisting mesenchymal tissue plate lined with epithelium of the sinus and vaginal cells; during the perinatal period, the hymen d ...
... o the caudal two thirds of the vagina originates from the sinovaginal bulbs that originate as evaginations of the entodermal urogenital sinus; the vagina forms as a thin persisting mesenchymal tissue plate lined with epithelium of the sinus and vaginal cells; during the perinatal period, the hymen d ...
Pelvis Forum
... smooth muscle; pudendal [S2-4] for contraction of perineal muscles – b. Emission – sympathetic [L1-2] for contraction of smooth muscle in ductus deferens – c. Ejaculation – sympathetic [L1-2] for closure of internal urethral sphincter; parasympathteics [S2-4] for contraction of urethral smooth muscl ...
... smooth muscle; pudendal [S2-4] for contraction of perineal muscles – b. Emission – sympathetic [L1-2] for contraction of smooth muscle in ductus deferens – c. Ejaculation – sympathetic [L1-2] for closure of internal urethral sphincter; parasympathteics [S2-4] for contraction of urethral smooth muscl ...
Anatomy of Pelvis - I Want To Be A Surgeon
... foramen and re-enters pelvis via lesser sciatic foramen • Travels with pudendal vessels along ischiorectal fossa in Alcock’s canal • Supplies sphincters and genitalia via perineal, dorsal root of penis/clitoris and inferior anal nerves • Promotes ejaculation, sexual arousal, anal and bladder sphinct ...
... foramen and re-enters pelvis via lesser sciatic foramen • Travels with pudendal vessels along ischiorectal fossa in Alcock’s canal • Supplies sphincters and genitalia via perineal, dorsal root of penis/clitoris and inferior anal nerves • Promotes ejaculation, sexual arousal, anal and bladder sphinct ...
Vulva

The vulva (from the Latin vulva, plural vulvae, see etymology) consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals.The vulva has many major and minor anatomical structures, including the labia majora, mons pubis, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vulval vestibule, greater and lesser vestibular glands, external urethral orifice and the opening of the vagina (introitus). Its development occurs during several phases, chiefly during the fetal and pubertal periods of time. As the outer portal of the human uterus or womb, it protects its opening by a ""double door"": the labia majora (large lips) and the labia minora (small lips). The vagina is a self-cleaning organ, sustaining healthy microbial flora that flow from the inside out; the vulva needs only simple washing to assure good vulvovaginal health, without recourse to any internal cleansing.The vulva has a sexual function; these external organs are richly innervated and provide pleasure when properly stimulated. In various branches of art, the vulva has been depicted as the organ that has the power both to ""give life"" (often associated with the womb), and to give sexual pleasure to humankind.The vulva also contains the opening of the female urethra, but apart from this has little relevance to the function of urination.