Genetics Practice II
... Baldness in humans is a dominant, sex-influenced trait. This gene is on the autosomes, not the sex chromosomes. A man who is BB or Bb will be bald and will be normal only if he is bb. A woman will only be bald if she is BB and normal if she is Bb or bb (it’s almost like B is dominant in males and b ...
... Baldness in humans is a dominant, sex-influenced trait. This gene is on the autosomes, not the sex chromosomes. A man who is BB or Bb will be bald and will be normal only if he is bb. A woman will only be bald if she is BB and normal if she is Bb or bb (it’s almost like B is dominant in males and b ...
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES
... Oncogene amplification can be accompanied by gene rearrangement but most amplified oncogenes are apparently normal on the basis of restriction endonuclease mapping. Gene amplification arises from a segment of DNA replicating more than once during a single cell cycle. There is evidence that there are ...
... Oncogene amplification can be accompanied by gene rearrangement but most amplified oncogenes are apparently normal on the basis of restriction endonuclease mapping. Gene amplification arises from a segment of DNA replicating more than once during a single cell cycle. There is evidence that there are ...
Name ____________________________ Genetics for Honors Chem Sophs
... Use the information to answer the next four questions Sickle cell Disease Sickle cell disease is a group of inherited disorders in which deoxygenated red blood cells become distorted and take on a shape like a sickle. There are two common alleles for this gene. One causes normally shaped red blood c ...
... Use the information to answer the next four questions Sickle cell Disease Sickle cell disease is a group of inherited disorders in which deoxygenated red blood cells become distorted and take on a shape like a sickle. There are two common alleles for this gene. One causes normally shaped red blood c ...
Microarrays
... corrected p-value of / N (0.5/10,000) Assign gene with second smallest p-value a corrected p-value of / N-1 ...
... corrected p-value of / N (0.5/10,000) Assign gene with second smallest p-value a corrected p-value of / N-1 ...
Intro (15min): finish Kahoots Activity #1 (30min): Short Answer
... 4. Imagine that you have two zygotes. The gametes that formed the first zygote contain chromosomes that experienced a lot of crossing over while the chromosomes in the second zygote didn’t undergo any c ...
... 4. Imagine that you have two zygotes. The gametes that formed the first zygote contain chromosomes that experienced a lot of crossing over while the chromosomes in the second zygote didn’t undergo any c ...
Genome_annotation
... •pilot phase focused on 30 Mb (~ 1%) of the genome •international consortium of computational and laboratory-based scientists working to develop and apply high-throughput approaches for detecting all sequence elements that confer biological function •now in its second phase, extending study to entir ...
... •pilot phase focused on 30 Mb (~ 1%) of the genome •international consortium of computational and laboratory-based scientists working to develop and apply high-throughput approaches for detecting all sequence elements that confer biological function •now in its second phase, extending study to entir ...
Document
... • Autosomal disorders, in general, affect males and females equally. • Males have only a single X and are therefore hemizygous with respect to X-linked genes • Females can be heterozygous or homozygous at X-linked loci. ...
... • Autosomal disorders, in general, affect males and females equally. • Males have only a single X and are therefore hemizygous with respect to X-linked genes • Females can be heterozygous or homozygous at X-linked loci. ...
Document
... 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome – ensures that females, like males, have one functional copy of the X chromosome in each b ...
... 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome – ensures that females, like males, have one functional copy of the X chromosome in each b ...
Genomics of Autoimmune Diseases
... databases, meaning that these studies would likely have not been possible before genome sequencing became so inexpensive and restrictions on sequencing freed up with the new paradigm of genetic thinking. This is most likely because autoimmune diseases are generally not life threatening but still hav ...
... databases, meaning that these studies would likely have not been possible before genome sequencing became so inexpensive and restrictions on sequencing freed up with the new paradigm of genetic thinking. This is most likely because autoimmune diseases are generally not life threatening but still hav ...
Genetics 200A 2009 Prokaryotes Lecture 1 (Cox)
... Results: Alan Campbell isolated 130 mutants: they grow in bacterial strain C600 (suII+) but not in wild-type bacterial strain such as 594 (su°). Do the mutations affect different functions/genes? This can be determined by doing pairwise co-infections with individual mutants. It is important that mo ...
... Results: Alan Campbell isolated 130 mutants: they grow in bacterial strain C600 (suII+) but not in wild-type bacterial strain such as 594 (su°). Do the mutations affect different functions/genes? This can be determined by doing pairwise co-infections with individual mutants. It is important that mo ...
Important questions from the unit genetics and
... In bacteria, as soon as the polymerase enzyme encounters the terminator region, the nascent RNA so formed falls off. The polymerase enzyme associates transiently with termination factor (ρ) to terminate the transcription. Actually, the association with termination factor alters the specificity of RN ...
... In bacteria, as soon as the polymerase enzyme encounters the terminator region, the nascent RNA so formed falls off. The polymerase enzyme associates transiently with termination factor (ρ) to terminate the transcription. Actually, the association with termination factor alters the specificity of RN ...
the Highest Connected Isoforms
... zebrafish, which implies that they evolved at least 460 million years ago. • As a comparison mouse and human conserve fewer than 20% of AS exons. ...
... zebrafish, which implies that they evolved at least 460 million years ago. • As a comparison mouse and human conserve fewer than 20% of AS exons. ...
press release - Université de Genève
... The transition from water to land is one of the most fascinating enigmas of evolution. In particular, the evolution of limbs from ancestral fish fins remains a mystery. Both fish and land animals possess clusters of Hoxa and Hoxd genes, which are necessary for both fin and limb formation during embr ...
... The transition from water to land is one of the most fascinating enigmas of evolution. In particular, the evolution of limbs from ancestral fish fins remains a mystery. Both fish and land animals possess clusters of Hoxa and Hoxd genes, which are necessary for both fin and limb formation during embr ...
Document
... 2. High-throughput genome-wide studies like linkage analysis and gene expression profiling, tend to be most useful for classification and characterization but do not provide sufficient information to identify or prioritize specific disease causal genes. ...
... 2. High-throughput genome-wide studies like linkage analysis and gene expression profiling, tend to be most useful for classification and characterization but do not provide sufficient information to identify or prioritize specific disease causal genes. ...
Introduction to Molecular Biology and Genomics
... For a completely distinguishing gene where, all of its values for class P are ‘h’, and all of its values for class N are ‘l’, Lg , P H g , N 0 and, rg , takes its maximum positive value. In this case the gene is considered to be descriptive of (associated with) class P. The gene remains complete ...
... For a completely distinguishing gene where, all of its values for class P are ‘h’, and all of its values for class N are ‘l’, Lg , P H g , N 0 and, rg , takes its maximum positive value. In this case the gene is considered to be descriptive of (associated with) class P. The gene remains complete ...
Name Quiz 13
... 3. Contrast or differentiate: Describe phenotype and genotype. Answer: a. phenotype is the from traits b. as genotype is its genetic composition 4. Describe: Segregation in sex cells. Answer: Segregation in sex cells is when the separate from each this ussaully happens when sex cells are formed. 5. ...
... 3. Contrast or differentiate: Describe phenotype and genotype. Answer: a. phenotype is the from traits b. as genotype is its genetic composition 4. Describe: Segregation in sex cells. Answer: Segregation in sex cells is when the separate from each this ussaully happens when sex cells are formed. 5. ...
Chapt 11
... 11.12 Plant cloning shows that differentiated cells may retain all of their genetic potential Most differentiated cells retain a full set of genes, even though only a subset may be expressed. Evidence is available from – plant cloning, in which a root cell can divide to form an adult plant and ...
... 11.12 Plant cloning shows that differentiated cells may retain all of their genetic potential Most differentiated cells retain a full set of genes, even though only a subset may be expressed. Evidence is available from – plant cloning, in which a root cell can divide to form an adult plant and ...
No Slide Title
... No protein coat Smaller than viruses (few hundreds of bases) Smallest known virus is 3.2 kbp in size RNA does not code for any known protein Some even lack the AUG initiation codon Replication mechanism is unknown Viroids cannot recognize and infect host cell Relies on cells being weak or i ...
... No protein coat Smaller than viruses (few hundreds of bases) Smallest known virus is 3.2 kbp in size RNA does not code for any known protein Some even lack the AUG initiation codon Replication mechanism is unknown Viroids cannot recognize and infect host cell Relies on cells being weak or i ...
Gregor Mendel, and Austrian monk, was the first person to succeed
... Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, was the first person to succeed in predicting how traits are inherited from generation to generation. He worked with pea plants and studied how genes are passed down from the parent generation (P1) to their offspring (F1). While many human traits are not as simple as ...
... Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, was the first person to succeed in predicting how traits are inherited from generation to generation. He worked with pea plants and studied how genes are passed down from the parent generation (P1) to their offspring (F1). While many human traits are not as simple as ...
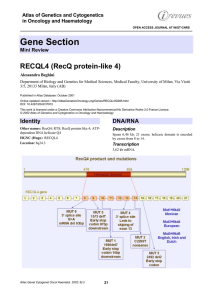
Gene Section RECQL4 (RecQ protein-like 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
PDF - Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics
... duration, and other mechanics of transcription, translation, and posttranslational modification, which may correlate with other yet to be uncovered attributes of the raw primary sequence.11 The increased frequency of synonymous variation in cardiomyopathy genes is difficult to explain, but may refle ...
... duration, and other mechanics of transcription, translation, and posttranslational modification, which may correlate with other yet to be uncovered attributes of the raw primary sequence.11 The increased frequency of synonymous variation in cardiomyopathy genes is difficult to explain, but may refle ...
Lecture file (PowerPoint) - Department of Molecular & Cell Biology
... adults, to being relatively well even until old age. Increasing numbers of genetic loci have now been identified that can modulate sickle cell disease phenotype, from nucleotide motifs within the beta-globin gene cluster, to genes located on different chromosomes. With recent success of the human ge ...
... adults, to being relatively well even until old age. Increasing numbers of genetic loci have now been identified that can modulate sickle cell disease phenotype, from nucleotide motifs within the beta-globin gene cluster, to genes located on different chromosomes. With recent success of the human ge ...
Looking Beyond Our DNA - Federation of American Societies for
... when and how they are turned on (gene activation). It is these differences in the activation of genes that result in a broad array of cell types with various functions (i.e., muscle, skin, nerve, bone, etc.), a process known as differentiation. The most widely recognized and studied epigenetic modif ...
... when and how they are turned on (gene activation). It is these differences in the activation of genes that result in a broad array of cell types with various functions (i.e., muscle, skin, nerve, bone, etc.), a process known as differentiation. The most widely recognized and studied epigenetic modif ...