Elementary Genetics Powerpoint
... Sex Cells Duplicate through MEIOSIS Have half as many chromosomes as other cells Are called “eggs” in females Are called “sperm” in males Must join to begin life ...
... Sex Cells Duplicate through MEIOSIS Have half as many chromosomes as other cells Are called “eggs” in females Are called “sperm” in males Must join to begin life ...
Lec 18 - Crossing Over
... Procedure for the chromosome mapping In fact genes are plotted on the chromosome on the basis of crossing over results between different pairs of linked genes. The actual distance between two genes is said to be equivalent to the percentage of crossing over between these genes. When the % of crossin ...
... Procedure for the chromosome mapping In fact genes are plotted on the chromosome on the basis of crossing over results between different pairs of linked genes. The actual distance between two genes is said to be equivalent to the percentage of crossing over between these genes. When the % of crossin ...
Lecture - Computational Bioscience Program
... “cDNA microarrays and a clustering algorithm were used to identify patterns of gene expression in human mammary epithelial cells growing in culture and in primary human breast tumors. Clusters of coexpressed genes identified through manipulations of mammary epithelial cells in vitro also showed cons ...
... “cDNA microarrays and a clustering algorithm were used to identify patterns of gene expression in human mammary epithelial cells growing in culture and in primary human breast tumors. Clusters of coexpressed genes identified through manipulations of mammary epithelial cells in vitro also showed cons ...
Allele- and parent-of-origin-specific effects on expression of the
... Allele-specific expression (ASE) occurs throughout the mammalian genome (Tycko, 2010), may be a consequence of genetic and epigenetic mechanisms, and may have effects on phenotypic variation (Muráni et al., 2009; Tuch et al., 2010). The major genetic causes of ASE are polymorphisms in cis-regulatory ...
... Allele-specific expression (ASE) occurs throughout the mammalian genome (Tycko, 2010), may be a consequence of genetic and epigenetic mechanisms, and may have effects on phenotypic variation (Muráni et al., 2009; Tuch et al., 2010). The major genetic causes of ASE are polymorphisms in cis-regulatory ...
Chapter 11 Genetics
... 2. Phenotype - observable traits of an individual or how these traits are expressed (What you see) C. inheritance of traits 1. P parental generation 2. F1 first-generation of offspring 3. F2 second-generation of offspring II. THEORY OF SEGREGATION A. Theory of segregation 1. 2n organisms inherit 2 a ...
... 2. Phenotype - observable traits of an individual or how these traits are expressed (What you see) C. inheritance of traits 1. P parental generation 2. F1 first-generation of offspring 3. F2 second-generation of offspring II. THEORY OF SEGREGATION A. Theory of segregation 1. 2n organisms inherit 2 a ...
Incomplete Dominance/Codominance
... Proteins on their surfaces are called antigens, controlled by genes Antigens make antibodies to foreign substances, which includes RBCs with different antigens on their surface ...
... Proteins on their surfaces are called antigens, controlled by genes Antigens make antibodies to foreign substances, which includes RBCs with different antigens on their surface ...
Editorials Hereditary retinopathies: insights into a complex genetic
... isolation and characterisation of such genes. With a genome consisting of some three billion base pairs of DNA and probably between 50000 and 100 000 genes, the task of locating a single disease-causing gene, particularly when the biochemical defect is unknown, would seem, to say the least, daunting ...
... isolation and characterisation of such genes. With a genome consisting of some three billion base pairs of DNA and probably between 50000 and 100 000 genes, the task of locating a single disease-causing gene, particularly when the biochemical defect is unknown, would seem, to say the least, daunting ...
Activity #3a - Center for Occupational Research and Development
... In Activities #1 and #2, you learned the scientific basis for how DNA microarray technology works and how it can be used to illustrate variations in gene expression by examining the gene expression data from two mythological creatures. Different gene expression results in different characteristics. ...
... In Activities #1 and #2, you learned the scientific basis for how DNA microarray technology works and how it can be used to illustrate variations in gene expression by examining the gene expression data from two mythological creatures. Different gene expression results in different characteristics. ...
2_16S_TREE_RECONSTRUCTION
... To perform cladistic analyses we should first align al sequences in order to recognize all homologous positions. ...
... To perform cladistic analyses we should first align al sequences in order to recognize all homologous positions. ...
Simulating and cleaning gene expression data using
... RUV is a data-driven method that removes systematic noise from gene expression datasets. The particular version of RUV is dependent on the goal of the analysis. We have developed a method, RUVNaiveRidge, for the removal of unwanted variation that focuses on retrieving the true underlying gene-gene c ...
... RUV is a data-driven method that removes systematic noise from gene expression datasets. The particular version of RUV is dependent on the goal of the analysis. We have developed a method, RUVNaiveRidge, for the removal of unwanted variation that focuses on retrieving the true underlying gene-gene c ...
Case of the Hooded Murder
... Lord Robert Lancaster early morning as promised. As Watson explained to Holmes, ”Old Lord Peter (Lord Robert’s father) is shown over the fireplace. As a young man, he had bright red hair. His wife Violet, was a brunette. Half their children, including the late Lord Robert, had red hair the others we ...
... Lord Robert Lancaster early morning as promised. As Watson explained to Holmes, ”Old Lord Peter (Lord Robert’s father) is shown over the fireplace. As a young man, he had bright red hair. His wife Violet, was a brunette. Half their children, including the late Lord Robert, had red hair the others we ...
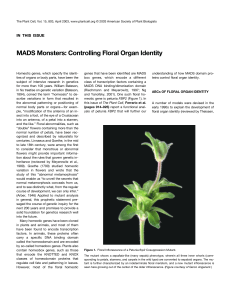
MADS Monsters: Controlling Floral Organ Identity
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
X Linked Inheritance
... Our bodies are made up of millions of cells. Most cells contain a complete set of genes. Genes act like a set of instructions, controlling our growth and how our bodies work. They are also responsible for many of our characteristics, such as our eye colour, blood type and height. We have thousands o ...
... Our bodies are made up of millions of cells. Most cells contain a complete set of genes. Genes act like a set of instructions, controlling our growth and how our bodies work. They are also responsible for many of our characteristics, such as our eye colour, blood type and height. We have thousands o ...
Insect Genetics
... Any question that is not “fill in the blank” you need to write a complete sentence answer on another sheet of paper (on the back of the packet is fine). 1. What is your plan for studying? Which nights, what times, for how long, which lesson, how will you study? 2. What is heredity? 3. Explain the ro ...
... Any question that is not “fill in the blank” you need to write a complete sentence answer on another sheet of paper (on the back of the packet is fine). 1. What is your plan for studying? Which nights, what times, for how long, which lesson, how will you study? 2. What is heredity? 3. Explain the ro ...
Chapter 11 Mendel Study Guide
... 16. In corn, if a purple corn is crossed with a purple (purple is dominant), how would 25% of offspring end up yellow? 17. Tall is dominant to short. If you cross a homozygous tall parent with a homozygous short parent, what % will be medium height? 18. In each P generation you cross a homozygous ta ...
... 16. In corn, if a purple corn is crossed with a purple (purple is dominant), how would 25% of offspring end up yellow? 17. Tall is dominant to short. If you cross a homozygous tall parent with a homozygous short parent, what % will be medium height? 18. In each P generation you cross a homozygous ta ...
Genetics Notes
... properly. Results in an individual with too many or too few chromosomes. Ex. Down's syndrome, Klinefelter's and Turner's syndrome • Polyploidy-More than two complete chromosome sets such as triploidy=3n or tetraploidy=4n. This is common in plant kingdom. • Alterations of chromosome structure-The bre ...
... properly. Results in an individual with too many or too few chromosomes. Ex. Down's syndrome, Klinefelter's and Turner's syndrome • Polyploidy-More than two complete chromosome sets such as triploidy=3n or tetraploidy=4n. This is common in plant kingdom. • Alterations of chromosome structure-The bre ...
X linked
... Female carriers have a 50% chance of passing on a changed gene. If a son inherits a changed gene from his mother, then he will be affected by the condition. If a daughter inherits a changed gene she will be a carrier like her mother. A male who has an X linked recessive condition will always pass on ...
... Female carriers have a 50% chance of passing on a changed gene. If a son inherits a changed gene from his mother, then he will be affected by the condition. If a daughter inherits a changed gene she will be a carrier like her mother. A male who has an X linked recessive condition will always pass on ...
Biology Chapter 1 Study Questions
... Meiosis I is said to be a ___________ division while Meiosis II is said to be a ___________ division. For a species with a diploid number of ten, how many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes are possible for gametes? What are punnett squares used for? If you cross a homozygo ...
... Meiosis I is said to be a ___________ division while Meiosis II is said to be a ___________ division. For a species with a diploid number of ten, how many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes are possible for gametes? What are punnett squares used for? If you cross a homozygo ...
Advanced Mendelian Genetics
... • The Punnett square predicts a 9:3:3:1 ratio in the F 2 generation ...
... • The Punnett square predicts a 9:3:3:1 ratio in the F 2 generation ...
F 6 Biology - Ch 9: Heredity and Genetics Name: ( ) 9.1.1 THE
... Sometimes both alleles express themselves in the phenotype, but one more so than another. This an intermediate stage between complete dominance and codominance. There are many blends of partial dominance which lead to a wide range of intermediate varieties between two extremes, e.g. a cross between ...
... Sometimes both alleles express themselves in the phenotype, but one more so than another. This an intermediate stage between complete dominance and codominance. There are many blends of partial dominance which lead to a wide range of intermediate varieties between two extremes, e.g. a cross between ...
In vitro formation of a catabolic plasmid carrying
... pNDR05) of pSPOl still expressed the two 3hydroxybenzoate catabolic enzymes of the original plasmid but a 2-5 kb EcoRI-Hind111 subclone (Fig. 2, coordinates 6.5-9-0 ; pNDR02) expressed only the monooxygenase activity, suggesting that the EcoRI site was within the maleylpyruvate isomerase gene (mhbl) ...
... pNDR05) of pSPOl still expressed the two 3hydroxybenzoate catabolic enzymes of the original plasmid but a 2-5 kb EcoRI-Hind111 subclone (Fig. 2, coordinates 6.5-9-0 ; pNDR02) expressed only the monooxygenase activity, suggesting that the EcoRI site was within the maleylpyruvate isomerase gene (mhbl) ...
Ch 11 Extra Credit Mendel Study Guide
... 16. In corn, if a purple corn is crossed with a purple (purple is dominant), how would 25% of offspring end up yellow? 17. Tall is dominant to short. If you cross a homozygous tall parent with a homozygous short parent, what % will be medium height? 18. In each P generation you cross a homozygous ta ...
... 16. In corn, if a purple corn is crossed with a purple (purple is dominant), how would 25% of offspring end up yellow? 17. Tall is dominant to short. If you cross a homozygous tall parent with a homozygous short parent, what % will be medium height? 18. In each P generation you cross a homozygous ta ...
Prenatal Care… - Coudersport Area School District / Overview
... 4) Why? Because the male can offer up either the X or Y chromosome… if it’s the Y chromosome then the offspring will be a male. ...
... 4) Why? Because the male can offer up either the X or Y chromosome… if it’s the Y chromosome then the offspring will be a male. ...
1 Pathophysiology Name Introduction to Pathophysiology and
... Incomplete penetrance – an individual who has the genotype for a disease but does not express it. ...
... Incomplete penetrance – an individual who has the genotype for a disease but does not express it. ...