5.1 Human Inheritance File
... POINT > Describe sex determination During meiosis, the sex chromosomes split apart (like the other 22 pairs) In women, all egg cells have an X chromosome In men, half of the sperm cells get an X and the other half get a Y ...
... POINT > Describe sex determination During meiosis, the sex chromosomes split apart (like the other 22 pairs) In women, all egg cells have an X chromosome In men, half of the sperm cells get an X and the other half get a Y ...
Lctures Clinical genetics – 4
... length of the CGG repeat, 55 (unaffected by the syndrome), above 55 unstable a premutation (at risk of fragile X associated disorders), or full mutation 200 or > (usually affected by the syndrome). As gc repeats are difficult to amplify or detect by pcr so Southern blottB, x –inactivation of repeat ...
... length of the CGG repeat, 55 (unaffected by the syndrome), above 55 unstable a premutation (at risk of fragile X associated disorders), or full mutation 200 or > (usually affected by the syndrome). As gc repeats are difficult to amplify or detect by pcr so Southern blottB, x –inactivation of repeat ...
Complete Nucleotide Sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... A description of the function of the genes. A description of the protein most similar to the other genes is also listed. Genes with no listing in this column have no homologs (BLASTX score usually less than 70). Column 5: The BLASTX (18) score for the alignment of the encoded protein to its closest ...
... A description of the function of the genes. A description of the protein most similar to the other genes is also listed. Genes with no listing in this column have no homologs (BLASTX score usually less than 70). Column 5: The BLASTX (18) score for the alignment of the encoded protein to its closest ...
Abstract - Plant Sulfur Network
... efficiently when the main pathway of cysteine synthesis from O-acetylserine is impaired. In consequence, mutations in the cysA and cysB genes lead to elevated synthesis of homocysteine by homocysteine synthase so they suppress mutations in the metB, metG and metA genes. In fact, mutations in cys gen ...
... efficiently when the main pathway of cysteine synthesis from O-acetylserine is impaired. In consequence, mutations in the cysA and cysB genes lead to elevated synthesis of homocysteine by homocysteine synthase so they suppress mutations in the metB, metG and metA genes. In fact, mutations in cys gen ...
GENE WIKI CONCEPTUAL OVERVIEW
... Document Objective: The Gene Wiki concept, as described in this document, has been discussed with a few scientists and has generally received positive reviews. This document is high-level with illustrations so that readers may quickly read it to get a general understanding of our functional concept ...
... Document Objective: The Gene Wiki concept, as described in this document, has been discussed with a few scientists and has generally received positive reviews. This document is high-level with illustrations so that readers may quickly read it to get a general understanding of our functional concept ...
Slide 1
... 2. Why is the fate of most duplicate genes to rates, compared to angiosperms? Or, on eventually become silenced? Could the other hand, could the silenced genes mutations accumulate in both copies at the hold the key to the long history of fern same rate causing subfunctionalization, evolution? where ...
... 2. Why is the fate of most duplicate genes to rates, compared to angiosperms? Or, on eventually become silenced? Could the other hand, could the silenced genes mutations accumulate in both copies at the hold the key to the long history of fern same rate causing subfunctionalization, evolution? where ...
A Penetrating Look at stochasticity in Development
... technique allows the authors to observe noisiness in end-1 expression that appears to be the only variable input into elt-2 in this mutant condition. This variation is resolved at the level of elt-2 expression, which displays a bimodal ON/OFF distribution of mRNA levels (Figure 1B). The bimodal resp ...
... technique allows the authors to observe noisiness in end-1 expression that appears to be the only variable input into elt-2 in this mutant condition. This variation is resolved at the level of elt-2 expression, which displays a bimodal ON/OFF distribution of mRNA levels (Figure 1B). The bimodal resp ...
Sodium Bisulfite Methods
... • Why are they good? – Quick and efficient genome-wide assessment of DNA methylation ...
... • Why are they good? – Quick and efficient genome-wide assessment of DNA methylation ...
Predicting Inherited Characteristics
... recessive allele for this trait Dd – is how this is shown ** the dominant trait will always show in ...
... recessive allele for this trait Dd – is how this is shown ** the dominant trait will always show in ...
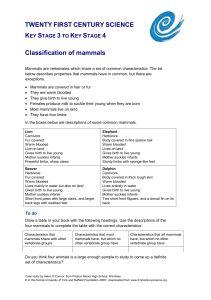
worksheet: classifying mammals
... characteristics which are determined by genes. We human beings have about 30,000 genes, but simpler organisms have a lot fewer genes. The more genes that humans have in common, the more similar they are. It follows that the more genes two different animals have in common, the more similar they are. ...
... characteristics which are determined by genes. We human beings have about 30,000 genes, but simpler organisms have a lot fewer genes. The more genes that humans have in common, the more similar they are. It follows that the more genes two different animals have in common, the more similar they are. ...
Chapter 01 A Brief History
... From https://passtest.eu/Test-Bank-for-Molecular-Biology-5-E-by-Weave ...
... From https://passtest.eu/Test-Bank-for-Molecular-Biology-5-E-by-Weave ...
Study Guide
... Somatic cells are any cells in the body that are not gametes. Somatic cells are diploid (2n) meaning they have 2 sets of chromosomes (46). Gametes (sperm and egg) are haploid (n); they contain half the number of chromosomes of somatic cells (23). One homologous chromosome from each pair is inh ...
... Somatic cells are any cells in the body that are not gametes. Somatic cells are diploid (2n) meaning they have 2 sets of chromosomes (46). Gametes (sperm and egg) are haploid (n); they contain half the number of chromosomes of somatic cells (23). One homologous chromosome from each pair is inh ...
On the internal dynamics of mendelian genetics
... show that there are at least as many types of germ cells as there are combinations of traits that become constant in the progeny derived from a hybrid. A self-fertilizing plant is a hybrid if it has a trait that does not breed true, but allows the extraction of constant forms of the trait in its pro ...
... show that there are at least as many types of germ cells as there are combinations of traits that become constant in the progeny derived from a hybrid. A self-fertilizing plant is a hybrid if it has a trait that does not breed true, but allows the extraction of constant forms of the trait in its pro ...
Welcome to the Broad Institute
... Gene Set Enrichment Analysis • Sometimes no individual genes are significantly differentially expressed • We improve statistical power by comparing gene sets • Example: human diabetes – No single gene significant – GSEA was used to assess enrichment of 149 gene sets including 113 pathways from inte ...
... Gene Set Enrichment Analysis • Sometimes no individual genes are significantly differentially expressed • We improve statistical power by comparing gene sets • Example: human diabetes – No single gene significant – GSEA was used to assess enrichment of 149 gene sets including 113 pathways from inte ...
Leukaemia Section t(2;11)(q31;p15) NUP98/HOXD13 t(2;11)(q31;p15) NUP98/HOXD11 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... The t(2;15)(q32;p15) is rare; around 8 cases in literature; reported in male and female with 1:1 ratio; Infants under the age of a year; children (10-15 years) as well as adults (59-62 years); over-representation in Asian race in particular Japanese. It has been shown that NUP98/11p15 is a frequent ...
... The t(2;15)(q32;p15) is rare; around 8 cases in literature; reported in male and female with 1:1 ratio; Infants under the age of a year; children (10-15 years) as well as adults (59-62 years); over-representation in Asian race in particular Japanese. It has been shown that NUP98/11p15 is a frequent ...
Roberta Rivi, MD - Harlem Children Society
... • Goal: determination of the function of every gene (functional genomics) • Gene-driven – also called reverse genetics • Phenotype-driven – also called forward genetics (classical approach) ...
... • Goal: determination of the function of every gene (functional genomics) • Gene-driven – also called reverse genetics • Phenotype-driven – also called forward genetics (classical approach) ...
- SlideBoom
... • When a genetic cross involves the consideration of two factors (such as shape and colour in pea seeds), the cross is called a "dihybrid". • Cross a completely heterozygous round/yellow seeded plant with a completely homozygous round/green seeded ...
... • When a genetic cross involves the consideration of two factors (such as shape and colour in pea seeds), the cross is called a "dihybrid". • Cross a completely heterozygous round/yellow seeded plant with a completely homozygous round/green seeded ...
Human Inheritance
... Inherited human genetic disorders are the result of gene mutations; that is, _a change in the DNA sequence of the gene____. B. Types of Inherited Genetic Disorders 1. Sex-Linked Disorders – Mutated gene is on the _X__ chromosome. 2. Autosomal Genetic Disorders – Gene mutation is on any chromosome ot ...
... Inherited human genetic disorders are the result of gene mutations; that is, _a change in the DNA sequence of the gene____. B. Types of Inherited Genetic Disorders 1. Sex-Linked Disorders – Mutated gene is on the _X__ chromosome. 2. Autosomal Genetic Disorders – Gene mutation is on any chromosome ot ...
Review Sheet
... Gregor Mendel bred a tall pea plant with a short pea plant, in hopes that the offspring would be medium pea plants. Instead, only tall pea plants were among the offspring. He determined that this was because the trait for a plant being tall was dominant and the trait for a plant being short was rece ...
... Gregor Mendel bred a tall pea plant with a short pea plant, in hopes that the offspring would be medium pea plants. Instead, only tall pea plants were among the offspring. He determined that this was because the trait for a plant being tall was dominant and the trait for a plant being short was rece ...
(i) Protonation state of the APV/wild
... removed (i.e., treated as if it were missing) if the probability in (S8) is less than , a user-specified threshold (by default, 0.05 ). The outlier detection and removal scheme described above is consistent with our parametric expression model and can remove up to one outlier per gene. A robus ...
... removed (i.e., treated as if it were missing) if the probability in (S8) is less than , a user-specified threshold (by default, 0.05 ). The outlier detection and removal scheme described above is consistent with our parametric expression model and can remove up to one outlier per gene. A robus ...
Huntington`s disease is an example of a genetic disorder caused by
... 6. Cystic fibrosis can be inherited even if neither parent has the disease. This is because the disease a. requires certain environmental conditions to be expressed b. occurs only in polyploid individuals c. is caused by a recessive allele d. is caused by a dominant allele e. occurs only in individu ...
... 6. Cystic fibrosis can be inherited even if neither parent has the disease. This is because the disease a. requires certain environmental conditions to be expressed b. occurs only in polyploid individuals c. is caused by a recessive allele d. is caused by a dominant allele e. occurs only in individu ...