Light and an exogenous transcription factor
... target gene were amplified and, for each transcript, the average Ct (threshold cycle) was determined. Ct is defined as the point at which fluorescence rises appreciably above the background. Standard curves for target and housekeeping genes were obtained by the amplification of a serially diluted mi ...
... target gene were amplified and, for each transcript, the average Ct (threshold cycle) was determined. Ct is defined as the point at which fluorescence rises appreciably above the background. Standard curves for target and housekeeping genes were obtained by the amplification of a serially diluted mi ...
Practice with Punnett Squares
... Complete each of the following problems in your journal! Be sure to follow all six steps and show your work. Step 1: Assign codes to alleles (unless already provided for you). Step 2: Determine the genotype of the parents. Step 3: Determine the gamete possibilities. Step 4: Set-up and comple ...
... Complete each of the following problems in your journal! Be sure to follow all six steps and show your work. Step 1: Assign codes to alleles (unless already provided for you). Step 2: Determine the genotype of the parents. Step 3: Determine the gamete possibilities. Step 4: Set-up and comple ...
Genome-wide RNAi Robert Barstead
... C. elegans chromosome III genes with early cell division phenotypes, all showed RNAi phenotypes that matched the genuine genetic mutant phenotype. This result validates the reliability of RNAi for this class of genes in C. elegans. Secondly, only 11 of the 133 genes identified by this work were asso ...
... C. elegans chromosome III genes with early cell division phenotypes, all showed RNAi phenotypes that matched the genuine genetic mutant phenotype. This result validates the reliability of RNAi for this class of genes in C. elegans. Secondly, only 11 of the 133 genes identified by this work were asso ...
1 Characterization of the p.Q189X nonsense mutation in dpy
... and dpy-18. The parental cross was created by crossing three WT males with three Dpy hermaphrodites that have the dpy gene of interest in order to create heterozygous males. Three F1 crosses were generated by crossing three F1 heterozygous males with three L4 Dpy hermaphrodites from each of the thre ...
... and dpy-18. The parental cross was created by crossing three WT males with three Dpy hermaphrodites that have the dpy gene of interest in order to create heterozygous males. Three F1 crosses were generated by crossing three F1 heterozygous males with three L4 Dpy hermaphrodites from each of the thre ...
Outline for today`s lecture (Ch. 14, Part I) Ploidy vs. DNA content The
... – Many variable characters (e.g., flower color, seed shape, seed color, etc.) ...
... – Many variable characters (e.g., flower color, seed shape, seed color, etc.) ...
Jobling, M.A. - University of Leicester
... The Y chromosome plays the key role in determining male sex in mammals, including humans. The decision is made early in the life of the embryo, when the undifferentiated sex organs (gonads) have the potential to become either ovaries or testes. In the absence of a Y chromosome they follow their ‘def ...
... The Y chromosome plays the key role in determining male sex in mammals, including humans. The decision is made early in the life of the embryo, when the undifferentiated sex organs (gonads) have the potential to become either ovaries or testes. In the absence of a Y chromosome they follow their ‘def ...
AzotoOxidativePhosphorylation
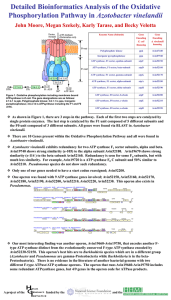
... Azotobacter vinelandii exhibits redundancy for two ATP synthase F1 sector subunits, alpha and beta. Avin19740 shows strong similarity (e-105) to the alpha subunit Avin52180. Avin19670 shows strong similarity (e-114 ) to the beta subunit Avin52160. Redundancy is seen for some F0 subunits, but with ...
... Azotobacter vinelandii exhibits redundancy for two ATP synthase F1 sector subunits, alpha and beta. Avin19740 shows strong similarity (e-105) to the alpha subunit Avin52180. Avin19670 shows strong similarity (e-114 ) to the beta subunit Avin52160. Redundancy is seen for some F0 subunits, but with ...
RrYy
... • Ploidy vs. DNA content • The basis of heredity ca. 1850s • Mendel’s Experiments and Theory – Law of Segregation – Law of Independent Assortment ...
... • Ploidy vs. DNA content • The basis of heredity ca. 1850s • Mendel’s Experiments and Theory – Law of Segregation – Law of Independent Assortment ...
Quantitative and Single-Gene Perspectives on the Study of Behavior
... for QTL analysis of any phenotype. Single-gene mutant analysis as a means of defining mechanisms traces its origins to microbial genetics, which concentrated on cellular mechanisms to the virtual exclusion of all evolutionary or environmental questions. It consisted of the induction of mutants to id ...
... for QTL analysis of any phenotype. Single-gene mutant analysis as a means of defining mechanisms traces its origins to microbial genetics, which concentrated on cellular mechanisms to the virtual exclusion of all evolutionary or environmental questions. It consisted of the induction of mutants to id ...
2001_butterfield_THE SUGARCANE GENOME
... number of 2n=103, suggesting the loss of nine parental chromosomes. They also demonstrated that the frequency of chromosomes pairing as trivalents increased linearly with generations from the initial I1 hybrids. In R570, Glaszmann et al. (2001) found that more than two chromosomes may be left unpair ...
... number of 2n=103, suggesting the loss of nine parental chromosomes. They also demonstrated that the frequency of chromosomes pairing as trivalents increased linearly with generations from the initial I1 hybrids. In R570, Glaszmann et al. (2001) found that more than two chromosomes may be left unpair ...
Gene Expression of Heart and Adipocyte Fatty Acid
... IMF. It is possible that A-FABP induces differential effects on gene expression in the different fat depots due to the ...
... IMF. It is possible that A-FABP induces differential effects on gene expression in the different fat depots due to the ...
Gene Therapy
... • The alteration is made during the embryonic stage, such that the genes altered would be passed down to future generations. • Germline gene therapy can be done by altering the genes of a pre-embryo that carries a serious genetic defect before implantation into the mother or by altering the germ cel ...
... • The alteration is made during the embryonic stage, such that the genes altered would be passed down to future generations. • Germline gene therapy can be done by altering the genes of a pre-embryo that carries a serious genetic defect before implantation into the mother or by altering the germ cel ...
Proportionality between variances in gene expression induced by
... recall again that there are 2 sources in phenotypic variances, genetic and epigenetic. Quantitatively, the former is characterized by the phenotypic variance in a heterogenic population and is due to genetic modifications, as, denoted as Vg, whereas the latter, denoted here as Vip, is the phenotypic ...
... recall again that there are 2 sources in phenotypic variances, genetic and epigenetic. Quantitatively, the former is characterized by the phenotypic variance in a heterogenic population and is due to genetic modifications, as, denoted as Vg, whereas the latter, denoted here as Vip, is the phenotypic ...
Genetics review
... People who are homozygous for the trait usually have many health problems. People who have one copy of the sicklecell allele are usually healthy. Would it ever beneficial to have one copy of the sickle cell allele? A. ...
... People who are homozygous for the trait usually have many health problems. People who have one copy of the sicklecell allele are usually healthy. Would it ever beneficial to have one copy of the sickle cell allele? A. ...
Genome - people.iup.edu
... those in another organism but differ because of speciation Orthologs are genes in different species that evolved from a common ancestral gene by speciation. Normally, orthologs retain the same function in the course of evolution. Identification of orthologs is critical for reliable prediction of gen ...
... those in another organism but differ because of speciation Orthologs are genes in different species that evolved from a common ancestral gene by speciation. Normally, orthologs retain the same function in the course of evolution. Identification of orthologs is critical for reliable prediction of gen ...
benfey_ch10
... © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. / A Pearson Education Company / Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 ...
... © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. / A Pearson Education Company / Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 ...
See a Sample
... © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. / A Pearson Education Company / Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 ...
... © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. / A Pearson Education Company / Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 ...
17 Human Genetics
... 1. What term refers to paired chromosomes arranged by size and shape? karyotype 2. What pair of chromosomes is not homologous in a normal male karyotype? sex chromosomes 3. What syndrome is inherited when an egg carrying two X chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome? Klinefelt ...
... 1. What term refers to paired chromosomes arranged by size and shape? karyotype 2. What pair of chromosomes is not homologous in a normal male karyotype? sex chromosomes 3. What syndrome is inherited when an egg carrying two X chromosomes is fertilized by a sperm carrying one Y chromosome? Klinefelt ...
QTL-mapping of individual resistance against American Apis mellifera
... 2.2. Bulk segregant analysis (BSA) and fine mapping Only the extreme phenotypes were considered for a selective genotyping approach aiming at a clear segregation of alleles (i.e. an accumulation of the responsible alleles in the DNA pools) and thereby a higher detection probability for the controlli ...
... 2.2. Bulk segregant analysis (BSA) and fine mapping Only the extreme phenotypes were considered for a selective genotyping approach aiming at a clear segregation of alleles (i.e. an accumulation of the responsible alleles in the DNA pools) and thereby a higher detection probability for the controlli ...
Section 10.1 Summary – pages 253-262
... The first generation • Mendel selected a six-foot-tall pea plant that came from a population of pea plants, all of which were over six feet tall. • He cross-pollinated this tall pea plant with pollen from a short pea plant. • All of the offspring grew to be as tall as the taller parent. ...
... The first generation • Mendel selected a six-foot-tall pea plant that came from a population of pea plants, all of which were over six feet tall. • He cross-pollinated this tall pea plant with pollen from a short pea plant. • All of the offspring grew to be as tall as the taller parent. ...
Deep Insight Section Common fragile sites and genomic instability
... Specific alterations in the genome that modify the expression of genetic elements involved in the regulation of cell growth and maintenance of genomic integrity are responsible for driving tumorigenesis. These changes are not random, even though each tumor has a particular set of genome alterations. ...
... Specific alterations in the genome that modify the expression of genetic elements involved in the regulation of cell growth and maintenance of genomic integrity are responsible for driving tumorigenesis. These changes are not random, even though each tumor has a particular set of genome alterations. ...
Harry Potter Genetics
... Both Harry’s parents had magical ability so they must both have been mm. They are also ...
... Both Harry’s parents had magical ability so they must both have been mm. They are also ...
The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a
... chick, bovine and rabbit skeletal muscle actins have an identical amino acid sequence (3,5) which differs from the yeast actin sequence at only k9 out of 375 positions (6,7). ...
... chick, bovine and rabbit skeletal muscle actins have an identical amino acid sequence (3,5) which differs from the yeast actin sequence at only k9 out of 375 positions (6,7). ...