Genetic Control of X Chromosome Inactivation in Mice: Definition of
... N mammals, X chromosome inactivation serves to equalize X-linked gene expression between the sexes. Early in female development, each somatic cell inactivates one of its two X chromosomes. This choice is then faithfully transmitted to all daughter cells through mitosis, such that the adult female is ...
... N mammals, X chromosome inactivation serves to equalize X-linked gene expression between the sexes. Early in female development, each somatic cell inactivates one of its two X chromosomes. This choice is then faithfully transmitted to all daughter cells through mitosis, such that the adult female is ...
Milestone2
... Many eukaryotic genes contain a DNA sequence, called a TATA box, in their promoter region, i.e., just upstream of their start codon. The TATA box is so named because it often consists of the following hexamer (i.e., 6 nucleotide) motif: “TATAAA”. Write a Python program named TATA.py, which reads in ...
... Many eukaryotic genes contain a DNA sequence, called a TATA box, in their promoter region, i.e., just upstream of their start codon. The TATA box is so named because it often consists of the following hexamer (i.e., 6 nucleotide) motif: “TATAAA”. Write a Python program named TATA.py, which reads in ...
Transgenic Tobacco Plants Expressing the Drosophila
... needlelike phenotypes failed to produce a leaf blade, although midrib-specific cells were unaltered (Figure 6B), and that those with broad-leaf phenotypes showed some characteristic alterations in the blade. In comparison to wild-type tissue (Figures 6A and 6C), the numbers of cells per area was red ...
... needlelike phenotypes failed to produce a leaf blade, although midrib-specific cells were unaltered (Figure 6B), and that those with broad-leaf phenotypes showed some characteristic alterations in the blade. In comparison to wild-type tissue (Figures 6A and 6C), the numbers of cells per area was red ...
Metatranscriptomic analysis of the Gut microbial community
... flora. The fermentation of carbohydrates and other nutrients by the gut microbiota on a high fat/high carbohydrate diet can result in an increase SCFA concentration and can result in increased absorption. The SCFA absorbed can promote fat storage via activation of GPR43 and 41 receptors. The presenc ...
... flora. The fermentation of carbohydrates and other nutrients by the gut microbiota on a high fat/high carbohydrate diet can result in an increase SCFA concentration and can result in increased absorption. The SCFA absorbed can promote fat storage via activation of GPR43 and 41 receptors. The presenc ...
Genetic Evidence that the Operator Locus is Distinct from the z gene
... fact, the derepression of trp by the trpR- allele, results /in a 17 times increase in the rate of /?-galactosidase synthesis (Table 2). We have described elsewhere the isolation of fusion strains similar to X7713, except that in these other strains, the luc operator is intact (Reznikoff et al., manu ...
... fact, the derepression of trp by the trpR- allele, results /in a 17 times increase in the rate of /?-galactosidase synthesis (Table 2). We have described elsewhere the isolation of fusion strains similar to X7713, except that in these other strains, the luc operator is intact (Reznikoff et al., manu ...
Chapter 25.
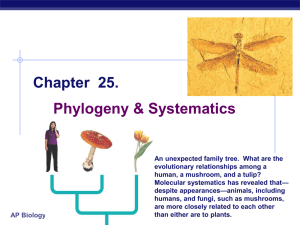
... An unexpected family tree. What are the evolutionary relationships among a human, a mushroom, and a tulip? Molecular systematics has revealed that— despite appearances—animals, including humans, and fungi, such as mushrooms, are more closely related to each other than either are to plants. ...
... An unexpected family tree. What are the evolutionary relationships among a human, a mushroom, and a tulip? Molecular systematics has revealed that— despite appearances—animals, including humans, and fungi, such as mushrooms, are more closely related to each other than either are to plants. ...
Comparative Analysis Using DNA Microarrays: Sensitivity
... Analysis of DNA Microarray Data: Sensitivity, Specificity, and Other Real-World Issues ...
... Analysis of DNA Microarray Data: Sensitivity, Specificity, and Other Real-World Issues ...
Molecular Biology of the Cell
... (A) The tethering of a region of chromatin to nuclear pore complex. (B) The tight binding of barrier proteins to a group of nucleosomes. (C) By recruiting a histone modifying enzymes, barriers can erase the histone marks that are required for heterochromatin to spread. For example, HS4 barrier DNA s ...
... (A) The tethering of a region of chromatin to nuclear pore complex. (B) The tight binding of barrier proteins to a group of nucleosomes. (C) By recruiting a histone modifying enzymes, barriers can erase the histone marks that are required for heterochromatin to spread. For example, HS4 barrier DNA s ...
Package `tmod`
... Just like a heatmap corresponds to a single numeric matrix, the pvalue / effect plot corresponds to two matrices: one with the effect size, and another one with the p-values. Each cell in the matrix corresponds to the results of a single statistical test. For example, a number of genes or transcript ...
... Just like a heatmap corresponds to a single numeric matrix, the pvalue / effect plot corresponds to two matrices: one with the effect size, and another one with the p-values. Each cell in the matrix corresponds to the results of a single statistical test. For example, a number of genes or transcript ...
Educator Guide - Cheryl Bardoe
... To see how this works, have students color the Punnett Square worksheet on page 7 of this guide. Using the genes inside the peas, students can predict the color on the outside of the peas. (Answer key provided on page 9 of this guide.) ...
... To see how this works, have students color the Punnett Square worksheet on page 7 of this guide. Using the genes inside the peas, students can predict the color on the outside of the peas. (Answer key provided on page 9 of this guide.) ...
Notes
... • Genetic counselors and researchers often use pedigree charts to track the inheritance of a genetic disorder in a family. • Analysis of a pedigree chart can reveal whether a trait is the result of a dominant allele, a recessive allele, or other pattern of inheritance. • Different genetic disorders ...
... • Genetic counselors and researchers often use pedigree charts to track the inheritance of a genetic disorder in a family. • Analysis of a pedigree chart can reveal whether a trait is the result of a dominant allele, a recessive allele, or other pattern of inheritance. • Different genetic disorders ...
Cloning, Sequencing, and Characterization of the Pradimicin
... cyclase genes, prmD, prmL, and prmK, whose products are thought to be responsible for subsequent intramolecular aldol reactions, and for producing the stepwise ring closures that lead to the angular pentacyclic molecular structure (Fig. 1). PrmD shows high sequence similarity to the N-terminal regio ...
... cyclase genes, prmD, prmL, and prmK, whose products are thought to be responsible for subsequent intramolecular aldol reactions, and for producing the stepwise ring closures that lead to the angular pentacyclic molecular structure (Fig. 1). PrmD shows high sequence similarity to the N-terminal regio ...
Genetics and Melanoma
... of melanocytes and surrounding tissue form benign (non-cancerous) growths they are called moles. Moles are also referred to as naevus; the plural is naevi. They are very common and most people have between 10 and 40. When moles are surgically removed, they normally do not return. However, often, but ...
... of melanocytes and surrounding tissue form benign (non-cancerous) growths they are called moles. Moles are also referred to as naevus; the plural is naevi. They are very common and most people have between 10 and 40. When moles are surgically removed, they normally do not return. However, often, but ...
Trachemys scripta elegans Red-Eared Turtle ( Fc)
... which the secretory tail is not encoded by a separate exon but rather by the sequence immediately downstream of the CH2 exon (21). Because Igs play important roles in the adaptive immune system of all jawed vertebrates (1, 2), they have been extensively studied in various groups of animals, includin ...
... which the secretory tail is not encoded by a separate exon but rather by the sequence immediately downstream of the CH2 exon (21). Because Igs play important roles in the adaptive immune system of all jawed vertebrates (1, 2), they have been extensively studied in various groups of animals, includin ...
Metazoan Remaining Genes for Essential Amino Acid Biosynthesis
... amino acid supplements [1]. This means that pathways for de novo amino acid biosynthesis are missing in their genomes, characterizing the Essential Amino Acid (EAA) phenotype. There is no consensus over the exact number of essential amino acids, but it is normally accepted that His, Ile, Leu, Lys, M ...
... amino acid supplements [1]. This means that pathways for de novo amino acid biosynthesis are missing in their genomes, characterizing the Essential Amino Acid (EAA) phenotype. There is no consensus over the exact number of essential amino acids, but it is normally accepted that His, Ile, Leu, Lys, M ...
Human Genome Project The Human Genome Project
... around 2000 base pairs which were critical elements enabling the development of the first genome assembly programs for reconstruction of large regions of genomes (aka 'contigs'). Three years later, in 1998, the announcement by the newly-formed Celera Genomics that it would scale up the shotgun seque ...
... around 2000 base pairs which were critical elements enabling the development of the first genome assembly programs for reconstruction of large regions of genomes (aka 'contigs'). Three years later, in 1998, the announcement by the newly-formed Celera Genomics that it would scale up the shotgun seque ...
Preview Sample 2
... 4. The cell’s supply of ADP, Pi, and NAD+ is finite (limited). What happens to cellular respiration when all of the cell’s NAD+ has been converted to NADH? If NAD is unavailable, the cell is unable to conduct any processes that involve the conversion of NAD+ to NADH. Because both glycolysis and the ...
... 4. The cell’s supply of ADP, Pi, and NAD+ is finite (limited). What happens to cellular respiration when all of the cell’s NAD+ has been converted to NADH? If NAD is unavailable, the cell is unable to conduct any processes that involve the conversion of NAD+ to NADH. Because both glycolysis and the ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... atypical EPEC. Fourty isolates (80%) of E. coli found do not have any one of the specific virulence genes, these isolates identified as non-EPEC (Figures 1, 2, 3, 4 and Table 3). It was shown that some of E. coli isolates were carriedthe bfpAgene approximately, 200bp which represent the non-specific ...
... atypical EPEC. Fourty isolates (80%) of E. coli found do not have any one of the specific virulence genes, these isolates identified as non-EPEC (Figures 1, 2, 3, 4 and Table 3). It was shown that some of E. coli isolates were carriedthe bfpAgene approximately, 200bp which represent the non-specific ...
shERWOOD-UltramiR shRNA
... FETCH my gene® search tool is designed to help you easily find shRNA-mir clones for your gene of interest and confirm your results using the gene information provided. Use gene accession, gene symbol or gene ID to begin your search. ...
... FETCH my gene® search tool is designed to help you easily find shRNA-mir clones for your gene of interest and confirm your results using the gene information provided. Use gene accession, gene symbol or gene ID to begin your search. ...
Genetics - Garnet Valley School District
... • A woman takes Mr. X to court for child support, but Mr. X swears he is not the father. The woman is blood type A and the baby is blood type A. Which blood type must Mr. X have to prove that he is not the father? ...
... • A woman takes Mr. X to court for child support, but Mr. X swears he is not the father. The woman is blood type A and the baby is blood type A. Which blood type must Mr. X have to prove that he is not the father? ...
Genetic epidemiology: Systemic lupus erythematosus | Arthritis
... strains. These studies have delineated specific genetic pathways that are critical to the development of severe lupus nephritis and have identified allele-specific, suppressive modifiers capable of dramatically influencing disease progression. The ‘synthesis’ of mouse models of systemic autoimmunity ...
... strains. These studies have delineated specific genetic pathways that are critical to the development of severe lupus nephritis and have identified allele-specific, suppressive modifiers capable of dramatically influencing disease progression. The ‘synthesis’ of mouse models of systemic autoimmunity ...
Differentiation of plant cells during symbiotic nitrogen fixation
... export of metabolites to the nodule. Another uninfected cell layer forms an oxygen barrier that helps to protect the oxygen sensitive nitrogenase enzyme [29,40]. Within the infected cells of a mature nodule the bacteroids fix nitrogen in return for nutrients from the plant [52]. There are difference ...
... export of metabolites to the nodule. Another uninfected cell layer forms an oxygen barrier that helps to protect the oxygen sensitive nitrogenase enzyme [29,40]. Within the infected cells of a mature nodule the bacteroids fix nitrogen in return for nutrients from the plant [52]. There are difference ...
LP - Columbia University
... b. Units: 1% RF corresponds to 1 map unit (in the proper range). One map unit is also known as one centiMorgan or 1 cM. c. Procedure -- An example: Suppose you want to order genes A, B and C, and you do the appropriate crosses. For example: AB/ab --(meiosis)--> 14% Ab and aB Bc/bC --(meiosis)--> 4% ...
... b. Units: 1% RF corresponds to 1 map unit (in the proper range). One map unit is also known as one centiMorgan or 1 cM. c. Procedure -- An example: Suppose you want to order genes A, B and C, and you do the appropriate crosses. For example: AB/ab --(meiosis)--> 14% Ab and aB Bc/bC --(meiosis)--> 4% ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... Congenital heart defects are present in approximately 75% of patients with 22q11.2DS and typically constitutes conotruncal malformations such as interrupted aortic arch type B, truncus arteriosus communis, tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect [35]. Although psycho ...
... Congenital heart defects are present in approximately 75% of patients with 22q11.2DS and typically constitutes conotruncal malformations such as interrupted aortic arch type B, truncus arteriosus communis, tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect [35]. Although psycho ...