Fossil Galaxies
... Astronomers and cosmologists have a problem on their hands. Their trusted computer simulations of the evolving universe predict that thousands of dwarf galaxies should currently exist in orbit around our Milky Way galaxy. However, only a few dozen dwarf galaxies have been observed. Called the “missi ...
... Astronomers and cosmologists have a problem on their hands. Their trusted computer simulations of the evolving universe predict that thousands of dwarf galaxies should currently exist in orbit around our Milky Way galaxy. However, only a few dozen dwarf galaxies have been observed. Called the “missi ...
26.5 The Expanding Universe
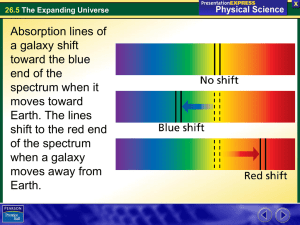
... This relationship, called Hubble’s Law, says that the speed at which a galaxy is moving away is proportional to its distance from us. The most distant observed galaxies are moving away at more than 90 percent of the speed of light! ...
... This relationship, called Hubble’s Law, says that the speed at which a galaxy is moving away is proportional to its distance from us. The most distant observed galaxies are moving away at more than 90 percent of the speed of light! ...
Infrared Astronomy More than Our Eyes Can See
... same area in the constellation Orion. These images dramatically illustrate holV features that cannot be seen in visible light show up very brightly in the infrared. The infrared image shows several regions of hot, dense cores within clouds of gas and dusl. These are the stellar nurseries where new s ...
... same area in the constellation Orion. These images dramatically illustrate holV features that cannot be seen in visible light show up very brightly in the infrared. The infrared image shows several regions of hot, dense cores within clouds of gas and dusl. These are the stellar nurseries where new s ...
Question 1
... the source of energy is very small. energy is coming from matter and antimatter. the energy source is rotating rapidly. a chain reaction of supernovas occurs. there are many separate sources of energy in the core. ...
... the source of energy is very small. energy is coming from matter and antimatter. the energy source is rotating rapidly. a chain reaction of supernovas occurs. there are many separate sources of energy in the core. ...
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the stars of the disk
... a) group of galaxies which forms a ring in inter-galactic space b) something Al gave to his mother c) the theory that say the universe is a continuous ring of space time d) distortion of an image due to gravitational effects 23. Why is the energy source of active galaxies thought to be extremely com ...
... a) group of galaxies which forms a ring in inter-galactic space b) something Al gave to his mother c) the theory that say the universe is a continuous ring of space time d) distortion of an image due to gravitational effects 23. Why is the energy source of active galaxies thought to be extremely com ...
Chapter 27
... • This picture was taken by pointing the Hubble telescope at a tiny region of space, empty of nearby stars or galaxies. • It required combining many hours of observations to make this picture. • More than 10,000 galaxies are found in this picture! March 21, 2006 ...
... • This picture was taken by pointing the Hubble telescope at a tiny region of space, empty of nearby stars or galaxies. • It required combining many hours of observations to make this picture. • More than 10,000 galaxies are found in this picture! March 21, 2006 ...
1 Introduction - Wiley-VCH
... stellar population, as traced by the near-infrared image at 3.6 μm obtained by the Spitzer space mission, is relatively smooth. Old stars are the dominant stellar population in the companion NGC 5195, an early-type galaxy interacting with NGC 5194. The distribution of the young stellar component, as ...
... stellar population, as traced by the near-infrared image at 3.6 μm obtained by the Spitzer space mission, is relatively smooth. Old stars are the dominant stellar population in the companion NGC 5195, an early-type galaxy interacting with NGC 5194. The distribution of the young stellar component, as ...
Lecture 12: Galaxy Evolution
... E.g., if galaxies are evolving such that β=0.5 and γ=-0.3 what kind of evolution is this and what is the relative luminosity density at z=1 ? • L(z=1)=1.41L(z=0), I.e., galaxies brighter in past • φ(z=1)=0.81φ(z=1), I.e., fewer galaxies in past • 20% of galaxies have formed below z=1, the galaxi ...
... E.g., if galaxies are evolving such that β=0.5 and γ=-0.3 what kind of evolution is this and what is the relative luminosity density at z=1 ? • L(z=1)=1.41L(z=0), I.e., galaxies brighter in past • φ(z=1)=0.81φ(z=1), I.e., fewer galaxies in past • 20% of galaxies have formed below z=1, the galaxi ...
Harvesting ALFALFA: Discovering Galaxies in the Pisces
... PPS has been found to be wall of clusters roughly 5h-1 Mpc to 10h-1 Mpc deep extending at least 50h-1 Mpc from the Perseus to Pegasus with a significant overdensity of galaxies at a heliocentric velocity of about 5,000 km/s. (Wegner et al., 1993) between foreground and background voids. All of which ...
... PPS has been found to be wall of clusters roughly 5h-1 Mpc to 10h-1 Mpc deep extending at least 50h-1 Mpc from the Perseus to Pegasus with a significant overdensity of galaxies at a heliocentric velocity of about 5,000 km/s. (Wegner et al., 1993) between foreground and background voids. All of which ...
distance
... Velocities and Distances to Galaxies We know Hubble’s guess wasn’t quite right. Those brightest specs in other galaxies are really clusters of stars, much brighter than single stars. ...
... Velocities and Distances to Galaxies We know Hubble’s guess wasn’t quite right. Those brightest specs in other galaxies are really clusters of stars, much brighter than single stars. ...
Evolution of high-redshift quasars
... tion structure of quasars reached maturity very early on and are probably insensitive to the host galaxy environment. The continuum and emission line scaling relations currently provide the only viable way to estimate black holes mass of quasars at highredshift. This method is very appealing, becaus ...
... tion structure of quasars reached maturity very early on and are probably insensitive to the host galaxy environment. The continuum and emission line scaling relations currently provide the only viable way to estimate black holes mass of quasars at highredshift. This method is very appealing, becaus ...
On the Origin of Early-Type Galaxies and the - N
... present-day EÏs and S0Ïs. We choose to study merger remnants formed at redshift less than 1 to avoid cases in which a major merger is followed by a long period of more quiescent accretion of matter, possibly leading to the formation of a dominant disk. With this cuto† in redshift, we focus our analy ...
... present-day EÏs and S0Ïs. We choose to study merger remnants formed at redshift less than 1 to avoid cases in which a major merger is followed by a long period of more quiescent accretion of matter, possibly leading to the formation of a dominant disk. With this cuto† in redshift, we focus our analy ...
lecture27
... Schmidt realized that the emission lines belonged to Hydrogen, but they were highly redshifted. This object is very (> 1010 light years) far away. ...
... Schmidt realized that the emission lines belonged to Hydrogen, but they were highly redshifted. This object is very (> 1010 light years) far away. ...
Redshift
In physics, redshift happens when light or other electromagnetic radiation from an object is increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum. In general, whether or not the radiation is within the visible spectrum, ""redder"" means an increase in wavelength – equivalent to a lower frequency and a lower photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, the wave and quantum theories of light.Some redshifts are an example of the Doppler effect, familiar in the change of apparent pitches of sirens and frequency of the sound waves emitted by speeding vehicles. A redshift occurs whenever a light source moves away from an observer. Another kind of redshift is cosmological redshift, which is due to the expansion of the universe, and sufficiently distant light sources (generally more than a few million light years away) show redshift corresponding to the rate of increase in their distance from Earth. Finally, gravitational redshift is a relativistic effect observed in electromagnetic radiation moving out of gravitational fields. Conversely, a decrease in wavelength is called blueshift and is generally seen when a light-emitting object moves toward an observer or when electromagnetic radiation moves into a gravitational field. However, redshift is a more common term and sometimes blueshift is referred to as negative redshift.Knowledge of redshifts and blueshifts has been applied to develop several terrestrial technologies such as Doppler radar and radar guns. Redshifts are also seen in the spectroscopic observations of astronomical objects. Its value is represented by the letter z.A special relativistic redshift formula (and its classical approximation) can be used to calculate the redshift of a nearby object when spacetime is flat. However, in many contexts, such as black holes and Big Bang cosmology, redshifts must be calculated using general relativity. Special relativistic, gravitational, and cosmological redshifts can be understood under the umbrella of frame transformation laws. There exist other physical processes that can lead to a shift in the frequency of electromagnetic radiation, including scattering and optical effects; however, the resulting changes are distinguishable from true redshift and are not generally referred to as such (see section on physical optics and radiative transfer).