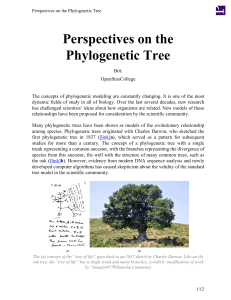
Control (n=217)
... • Investigation of the epigenetic status of duplicated genes to check if the duplication is affecting the gene expression. • The effect of gene dosage on increasing the severity of infertile phenotype and the underlying mechanism is yet to be explored at the functional level. • To understand that co ...
... • Investigation of the epigenetic status of duplicated genes to check if the duplication is affecting the gene expression. • The effect of gene dosage on increasing the severity of infertile phenotype and the underlying mechanism is yet to be explored at the functional level. • To understand that co ...
High Frequency of Recombination (Hfr)
... colonies. Place at 37oC overnight. Remove the next day and store at 4oC. ...
... colonies. Place at 37oC overnight. Remove the next day and store at 4oC. ...
These practice questions are from prior LS4 finals and are courtesy
... 2. A male is affected with the X-linked recessive condition hemophilia. He marries a carrier woman. What percentage of their male children will be affected? 50%. The father’s status is unimportant because he does not pass his X-chromosome on to his male offspring. 3. A woman is the offspring of a fa ...
... 2. A male is affected with the X-linked recessive condition hemophilia. He marries a carrier woman. What percentage of their male children will be affected? 50%. The father’s status is unimportant because he does not pass his X-chromosome on to his male offspring. 3. A woman is the offspring of a fa ...
Consultation process for this DIR application
... The parent organisms are wheat (cultivars ‘Bobwhite’, ‘Drysdale’ and ‘Frame’) and barley (cultivars ‘Golden Promise’ and ‘W14330’), which are exotic to Australia. Commercial wheat and barley cultivation occurs in the wheat belt from south eastern Queensland through New South Wales, Victoria, souther ...
... The parent organisms are wheat (cultivars ‘Bobwhite’, ‘Drysdale’ and ‘Frame’) and barley (cultivars ‘Golden Promise’ and ‘W14330’), which are exotic to Australia. Commercial wheat and barley cultivation occurs in the wheat belt from south eastern Queensland through New South Wales, Victoria, souther ...
Tài liệu PDF
... 3. Conjugation: the use a hollow tube called a pilus to transfer genes between organisms More recently, a fourth mechanism of gene transfer between prokaryotes has been discovered. Small, virus-like particles called gene transfer agents (GTAs) transfer random genomic segments from one species of pro ...
... 3. Conjugation: the use a hollow tube called a pilus to transfer genes between organisms More recently, a fourth mechanism of gene transfer between prokaryotes has been discovered. Small, virus-like particles called gene transfer agents (GTAs) transfer random genomic segments from one species of pro ...
n - 1
... conservation biology. Environmental change is a continuous process & genetic diversity is required for populations to evolve to adapt to such change. Loss of genetic diversity is often associated with inbreeding and reduction in reproductive ...
... conservation biology. Environmental change is a continuous process & genetic diversity is required for populations to evolve to adapt to such change. Loss of genetic diversity is often associated with inbreeding and reduction in reproductive ...
AND Я
... Sickle Cell Anemia is a hereditary disease which is cause by a disorder in the blood, a mutation in the Hemoglobin Beta Gene which can be found in the chromosome 11. This disease causes the body to make abnormally shapes red blood cells. A normal red blood cell is shaped as a round donut while the ...
... Sickle Cell Anemia is a hereditary disease which is cause by a disorder in the blood, a mutation in the Hemoglobin Beta Gene which can be found in the chromosome 11. This disease causes the body to make abnormally shapes red blood cells. A normal red blood cell is shaped as a round donut while the ...
2014-2015 Internship descriptions
... The genetic variation in germplasm of food crops is limited and will soon become insufficient to meet the demands of an increasing world population. Related wild species comprise crucial sources of genetic variation, including resistance to pathogens or tolerance to changed climate conditions. The t ...
... The genetic variation in germplasm of food crops is limited and will soon become insufficient to meet the demands of an increasing world population. Related wild species comprise crucial sources of genetic variation, including resistance to pathogens or tolerance to changed climate conditions. The t ...
Genetic disorders
... called acoustic neurofibromatosis. Although there is some overlap in clinical features, these two entities are genetically distinct. ...
... called acoustic neurofibromatosis. Although there is some overlap in clinical features, these two entities are genetically distinct. ...
Name____________________ Genetics Study Guide/Reality Check
... 29. What phenotype (dominant or recessive) do all heterozygous individuals show? Why? _Dominant because all heterozygous organisms have a copy of each allele; dominant and recessive. Since the organism has a copy of the dominant allele, the individual will show the dominant trait. 30. How is probabi ...
... 29. What phenotype (dominant or recessive) do all heterozygous individuals show? Why? _Dominant because all heterozygous organisms have a copy of each allele; dominant and recessive. Since the organism has a copy of the dominant allele, the individual will show the dominant trait. 30. How is probabi ...
Pedigree Chart
... Pedigree charts show a record of the family of an individual. It can be used to study the transmission of a hereditary condition. It is particularly useful when there are large families and a good family record over several generations. You cannot make humans of different types breed together so ped ...
... Pedigree charts show a record of the family of an individual. It can be used to study the transmission of a hereditary condition. It is particularly useful when there are large families and a good family record over several generations. You cannot make humans of different types breed together so ped ...
CHERCHER PREPARATORY SCHOOL Department of Natural
... Worksheet on Genetic crosses for Grade 12 Natural Science Students, 2005/2012 1. If a plant cell having 16 chromosomes undergoes meiotic cell division, how many chromosomes would the resulting daughter cells have? 2. What percentage of tall plants results from a cross between hybrid tall and pure sh ...
... Worksheet on Genetic crosses for Grade 12 Natural Science Students, 2005/2012 1. If a plant cell having 16 chromosomes undergoes meiotic cell division, how many chromosomes would the resulting daughter cells have? 2. What percentage of tall plants results from a cross between hybrid tall and pure sh ...
Lab Final supplement to notes
... Be able to distinguish between tracheophytes from non tracheophytes. What is a gymnosperm? What is an angiosperm? Archegonia vs. anther Microspores vs. megaspores Identify structures of a flower Identify male vs female plant structures Describe evolution of water to land (i.e. vascularization and me ...
... Be able to distinguish between tracheophytes from non tracheophytes. What is a gymnosperm? What is an angiosperm? Archegonia vs. anther Microspores vs. megaspores Identify structures of a flower Identify male vs female plant structures Describe evolution of water to land (i.e. vascularization and me ...
TRANSCRIPTION-TRANSLATION PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... 4.Sentences begin with a capital to indicate a start. In codon language starts are indicated by AUG which is the code that translates to the amino acid methionine 5. Sentences indicate a completion of information with a period. RNA indicates the end of the code with a stop signal, which are specific ...
... 4.Sentences begin with a capital to indicate a start. In codon language starts are indicated by AUG which is the code that translates to the amino acid methionine 5. Sentences indicate a completion of information with a period. RNA indicates the end of the code with a stop signal, which are specific ...
File
... Which mutations represent different genes and which genes are linked? How did you arrive at your conclusions? Answer: Genes 1 and 2 are linked, since they yield less than 25% wild-type. Twenty-five percent wild-type is expected for independent assortment, the other recombinant—the double mutant—bein ...
... Which mutations represent different genes and which genes are linked? How did you arrive at your conclusions? Answer: Genes 1 and 2 are linked, since they yield less than 25% wild-type. Twenty-five percent wild-type is expected for independent assortment, the other recombinant—the double mutant—bein ...
7.014 Problem Set 6
... i. Based on the results observed in (h), are tail length and attitude linked traits? Explain your answer. ...
... i. Based on the results observed in (h), are tail length and attitude linked traits? Explain your answer. ...
this PDF file - Association for the Advancement of Artificial
... level. All continuously varying quantitative traits (such as height) must be polygenic (involving several genes), which can make inheritance appear to be a blending rather than an all or nothing phenomenon. Most medically important traits (such as proclivity to cancer or heart disease) are polygenic ...
... level. All continuously varying quantitative traits (such as height) must be polygenic (involving several genes), which can make inheritance appear to be a blending rather than an all or nothing phenomenon. Most medically important traits (such as proclivity to cancer or heart disease) are polygenic ...
Chapter 14 Powerpoint
... marries a woman with normal vision whose father was color-blind. What is the probability that they will have a color-blind daughter? What is the probability that their first son will be color-blind? (NOTE: the two questions are worded differently) ...
... marries a woman with normal vision whose father was color-blind. What is the probability that they will have a color-blind daughter? What is the probability that their first son will be color-blind? (NOTE: the two questions are worded differently) ...
Genetic evaluation with major genes and polygenic inheritance
... use pedigree, genotype and phenotype information when some individuals are not genotyped. We propose to consider gene content at the major gene as a second trait correlated to the quantitative trait, in a gene content multipletrait best linear unbiased prediction (GCMTBLUP) method. Results: The gen ...
... use pedigree, genotype and phenotype information when some individuals are not genotyped. We propose to consider gene content at the major gene as a second trait correlated to the quantitative trait, in a gene content multipletrait best linear unbiased prediction (GCMTBLUP) method. Results: The gen ...
Genetic evaluation with major genes and polygenic
... use pedigree, genotype and phenotype information when some individuals are not genotyped. We propose to consider gene content at the major gene as a second trait correlated to the quantitative trait, in a gene content multipletrait best linear unbiased prediction (GCMTBLUP) method. Results: The gen ...
... use pedigree, genotype and phenotype information when some individuals are not genotyped. We propose to consider gene content at the major gene as a second trait correlated to the quantitative trait, in a gene content multipletrait best linear unbiased prediction (GCMTBLUP) method. Results: The gen ...
Substitution Rates in a New Silene latifolia Sex
... X chromosome. When differences in silent substitution rate are taken into account, the Y-linked gene still demonstrates significantly faster accumulation of nonsynonymous substitutions, which is consistent with the theoretical prediction of relaxed purifying selection in Y-linked genes, leading to t ...
... X chromosome. When differences in silent substitution rate are taken into account, the Y-linked gene still demonstrates significantly faster accumulation of nonsynonymous substitutions, which is consistent with the theoretical prediction of relaxed purifying selection in Y-linked genes, leading to t ...