DNA
... C. Describe the process of DNA replication D. Describe the steps of translation and transcription in changing DNA into traits E. Describe the effect of DNA mutations and list genetic diseases that would result F. Debate the use of genetic technologies in ...
... C. Describe the process of DNA replication D. Describe the steps of translation and transcription in changing DNA into traits E. Describe the effect of DNA mutations and list genetic diseases that would result F. Debate the use of genetic technologies in ...
FAQs about Breed Predispositions for Acquired Cardiac Disease
... and abnormal proteins may be unable to perform their job correctly. This can ultimately lead to acquired cardiac (heart) disease. What is a breed predisposition? Since breeds are created by allowing closely-related individuals to procreate, a genetic predisposition for heart disease may develop. Whi ...
... and abnormal proteins may be unable to perform their job correctly. This can ultimately lead to acquired cardiac (heart) disease. What is a breed predisposition? Since breeds are created by allowing closely-related individuals to procreate, a genetic predisposition for heart disease may develop. Whi ...
Next lectures: Differential Gene expression
... • Enhancers are the major determinant of differential transcription in time and space • Enhancers can work far from the promoter so multiple signals can be integrated to determine if a gene will be transcribed. Genes can have several enhancers and each enhancer can bind multiple proteins ...
... • Enhancers are the major determinant of differential transcription in time and space • Enhancers can work far from the promoter so multiple signals can be integrated to determine if a gene will be transcribed. Genes can have several enhancers and each enhancer can bind multiple proteins ...
Genetic background of systemic sclerosis: autoimmune genes take
... genetic and environmental factors contribute to disease susceptibility and clinical expression or progression [13]. Complex genetic diseases are influenced by the interplay of multiple genes and/or the environment; susceptibility genes act in concert to increase an individual’s risk of disease. Thus ...
... genetic and environmental factors contribute to disease susceptibility and clinical expression or progression [13]. Complex genetic diseases are influenced by the interplay of multiple genes and/or the environment; susceptibility genes act in concert to increase an individual’s risk of disease. Thus ...
Supplementary Material PDF
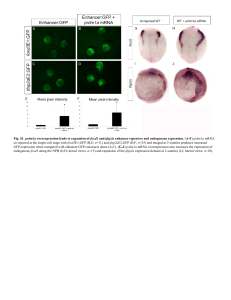
... (E,G) at 2-somites. Dorsal views show the absence of foxd3 and prdm1a expression at the NPB in tfap2a/tfap2c morphants (arrows, E,G). (H) qRTPCR for prdm1a and foxd3 was also performed on WT and tfap2a/c morphants and showed decreased expression of both genes in the morphants. NPB, neural plate bord ...
... (E,G) at 2-somites. Dorsal views show the absence of foxd3 and prdm1a expression at the NPB in tfap2a/tfap2c morphants (arrows, E,G). (H) qRTPCR for prdm1a and foxd3 was also performed on WT and tfap2a/c morphants and showed decreased expression of both genes in the morphants. NPB, neural plate bord ...
Lecture
... Each person has a unique set of fingerprints. As with a person’s fingerprint no two individuals share the same genetic makeup. This genetic makeup, which is the hereditary blueprint imparted to us by our parents, is stored in the chemical deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the basic molecule of life. Exam ...
... Each person has a unique set of fingerprints. As with a person’s fingerprint no two individuals share the same genetic makeup. This genetic makeup, which is the hereditary blueprint imparted to us by our parents, is stored in the chemical deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the basic molecule of life. Exam ...
Introduction to Genetics - Bruce Walsh's Home Page
... with a pure-breeding green line. Let P1 denote the pure-breeding yellow (parental line 1) P2 the pure-breed green (parental line 2) The F1, or first filial, generation is the cross of P1 x P2 (yellow x green). All resulting F1 were yellow The F2, or second filial, generation is a cross of two F1’s I ...
... with a pure-breeding green line. Let P1 denote the pure-breeding yellow (parental line 1) P2 the pure-breed green (parental line 2) The F1, or first filial, generation is the cross of P1 x P2 (yellow x green). All resulting F1 were yellow The F2, or second filial, generation is a cross of two F1’s I ...
GENETICS Review
... enlargement, reduced facial and body hair, and infertility KLINEFELTER SYNDROME This extra chromosome is the result of which mistake during meiosis? NON-DISJUNCTION ...
... enlargement, reduced facial and body hair, and infertility KLINEFELTER SYNDROME This extra chromosome is the result of which mistake during meiosis? NON-DISJUNCTION ...
"Genetic Redundancy".
... The Organizational Levels of Genetic Redundancy Biologists frequently describe genetic redundancy, also referred to as functional redundancy, in relation to the knockout of one or more genetic transcripts. Subsequent to the elimination of a transcript, the absence of a scoreable change in phenotype, ...
... The Organizational Levels of Genetic Redundancy Biologists frequently describe genetic redundancy, also referred to as functional redundancy, in relation to the knockout of one or more genetic transcripts. Subsequent to the elimination of a transcript, the absence of a scoreable change in phenotype, ...
THE THEORETICAL GENETICS OF THE SEX RATIO`** EX ratios
... effect on fitness will be considered in detail. The kind of selection each gene is subject to and consequently the effect which the presence of such a gene would have on the sex ratio of a population will be determined. Some facts are already known about the population behavior of sex ratio genes an ...
... effect on fitness will be considered in detail. The kind of selection each gene is subject to and consequently the effect which the presence of such a gene would have on the sex ratio of a population will be determined. Some facts are already known about the population behavior of sex ratio genes an ...
Chapter 8
... All species of living organisms are able to reproduce. This is how the species is perpetuated. Reproduction may be asexual reproduction, in which a single organism, or part of it, divides by mitosis to produce a new organism that is genetically identical to the parent. Animals, however, and also pla ...
... All species of living organisms are able to reproduce. This is how the species is perpetuated. Reproduction may be asexual reproduction, in which a single organism, or part of it, divides by mitosis to produce a new organism that is genetically identical to the parent. Animals, however, and also pla ...
Axial homeosis and appendicular skeleton defects in mice with a
... the chromosomal position of the Hox genes reflects the order of the anterior boundaries of expression for each gene along the anteroposterior (A-P) axis. The 3′ genes extend more anteriorly while those on the 5′ end of the complex are limited to more posterior regions (Duboule and Dollé, 1989; Graha ...
... the chromosomal position of the Hox genes reflects the order of the anterior boundaries of expression for each gene along the anteroposterior (A-P) axis. The 3′ genes extend more anteriorly while those on the 5′ end of the complex are limited to more posterior regions (Duboule and Dollé, 1989; Graha ...
Ch. 2
... person inherits heterozygous alleles in which one allele is stronger than the other yet does not completely dominate. – For example: sickle cell anemia Kuther, Lifespan Development. © 2017, SAGE Publications. ...
... person inherits heterozygous alleles in which one allele is stronger than the other yet does not completely dominate. – For example: sickle cell anemia Kuther, Lifespan Development. © 2017, SAGE Publications. ...
Use of wheat gene resources with different grain colour in breeding
... Vavilov, coming from the Abyssinian region in Ethiopia. It is characterized by the presence of anthocyanins in the surface layer (pericarp) of the grain. According to ABDEL-AAL and HUCL (2003) and KNIEVEL et al. (2009) cyanidin 3-glucoside, cyanidin 3-rutinoside, and succinyl glucoside are most repr ...
... Vavilov, coming from the Abyssinian region in Ethiopia. It is characterized by the presence of anthocyanins in the surface layer (pericarp) of the grain. According to ABDEL-AAL and HUCL (2003) and KNIEVEL et al. (2009) cyanidin 3-glucoside, cyanidin 3-rutinoside, and succinyl glucoside are most repr ...
Chapter 10 Meiosis
... –passed from parent to offspring – Genes for each trait come in slightly different forms called alleles, originally produced by mutations – Meiosis shuffles the alleles during gamete formation, and fertilization produces offspring with unique combinations of alleles ...
... –passed from parent to offspring – Genes for each trait come in slightly different forms called alleles, originally produced by mutations – Meiosis shuffles the alleles during gamete formation, and fertilization produces offspring with unique combinations of alleles ...
Evidence for autosomal recessive inheritance in SPG3A
... Previous studies have shown that heterozygous ATL1 mutations are associated with a spectrum of phenotypes ranging from ‘pure’ to ‘complicated’ forms of SPG3A,9,10,19 variable age of onset14,20 and gender-related penetrance in some families.15 The identification of ATL1 mutation in autosomal dominant ...
... Previous studies have shown that heterozygous ATL1 mutations are associated with a spectrum of phenotypes ranging from ‘pure’ to ‘complicated’ forms of SPG3A,9,10,19 variable age of onset14,20 and gender-related penetrance in some families.15 The identification of ATL1 mutation in autosomal dominant ...
extensions
... • Most random mutations produce alleles that are inherited in a recessive fashion ...
... • Most random mutations produce alleles that are inherited in a recessive fashion ...
Slide 1
... • There is not much deviation in the fitness values of the generated chromosomes for frames of length up to one third the length of the chromosome. • There is a sharp decrease in fitness afterwards. • Permutation encoding mutation when performed by swapping two individual genes (ie. single gene muta ...
... • There is not much deviation in the fitness values of the generated chromosomes for frames of length up to one third the length of the chromosome. • There is a sharp decrease in fitness afterwards. • Permutation encoding mutation when performed by swapping two individual genes (ie. single gene muta ...
Sequencing a genome and Basic Sequence Alignment
... The figure shows to sequences of nucleic acids. Some have the same base (nucleic acid ) and so there is a match at this position between the strands. This is represented by a vertical line and a blue highlight. Others do not match and have no vertical line and blue highlight: these are unmatched pai ...
... The figure shows to sequences of nucleic acids. Some have the same base (nucleic acid ) and so there is a match at this position between the strands. This is represented by a vertical line and a blue highlight. Others do not match and have no vertical line and blue highlight: these are unmatched pai ...
10 new
... a. State which symbol (a, b, or c) represents each of the lac genes I, O, and Z. b. In the table, a superscript minus sign on a gene symbol merely indicates a mutant, but you know that some mutant behaviors in this system are given special mutant designations. Use the conventional gene symbols for t ...
... a. State which symbol (a, b, or c) represents each of the lac genes I, O, and Z. b. In the table, a superscript minus sign on a gene symbol merely indicates a mutant, but you know that some mutant behaviors in this system are given special mutant designations. Use the conventional gene symbols for t ...
Practice with Punnett Squares
... 10. What would the offspring phenotype and genotype probabilities be when a pea plant with constricted seed pods crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for inflated seed pods? You will need the pea plant chart on the next page to complete this problem. ...
... 10. What would the offspring phenotype and genotype probabilities be when a pea plant with constricted seed pods crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for inflated seed pods? You will need the pea plant chart on the next page to complete this problem. ...