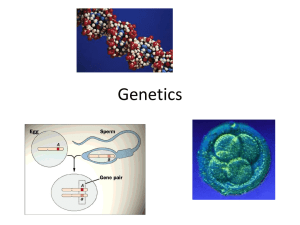
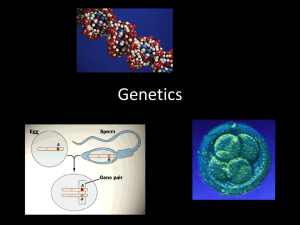
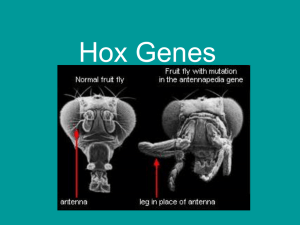
Mutations
... mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms chance for survival and reproduction • A mutation is helpful if it improves an organism’s chance for survival and reproduc ...
... mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms chance for survival and reproduction • A mutation is helpful if it improves an organism’s chance for survival and reproduc ...
Topic 4: Wearing Your Genes Continuous vs. Discrete Variation
... genes for the trait; when mixed with genes for a dominant trait, a recessive trait does not show up in the offspring. Mutations: Mutations are changes in the DNA, the genetic material. These are caused by mutagens. Most often mutations do not have any effect on the organism (usually that cell dies ...
... genes for the trait; when mixed with genes for a dominant trait, a recessive trait does not show up in the offspring. Mutations: Mutations are changes in the DNA, the genetic material. These are caused by mutagens. Most often mutations do not have any effect on the organism (usually that cell dies ...
Presentations:Questions
... Of the four techniques in inserting a gene, what is the most common way and what is one example of what scientists use to transfer the GOI? Recombinant DNA and they usually use either a plasmid from bacteria or a virus ...
... Of the four techniques in inserting a gene, what is the most common way and what is one example of what scientists use to transfer the GOI? Recombinant DNA and they usually use either a plasmid from bacteria or a virus ...
What is the difference between Autotrophs and heterotrophs?
... a. separation of alleles during gamete formation b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g ...
... a. separation of alleles during gamete formation b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g ...
Biology 105
... • Principle of segregation • Before sexual reproduction occurs, the two alleles carried by an individual parent must separate. Each sex cell carries only one allele for each trait. ...
... • Principle of segregation • Before sexual reproduction occurs, the two alleles carried by an individual parent must separate. Each sex cell carries only one allele for each trait. ...
File
... in another plant, but didn’t work because the plant reproduced asexually! • Work was largely ignored for 34 years, until 1900, when 3 independent botanists rediscovered Mendel’s work. ...
... in another plant, but didn’t work because the plant reproduced asexually! • Work was largely ignored for 34 years, until 1900, when 3 independent botanists rediscovered Mendel’s work. ...
Genetics - Dave Brodbeck
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
RAFT: Genetics - Catawba County Schools
... Investigate and understand that organisms reproduce and transmit genetic information to new generations Utilize appropriate information systems to build an understanding of heredity and genetics Objectives: The students will KNOW Vocabulary: gene, DNA, RNA, recessive trait, dominant trait, bac ...
... Investigate and understand that organisms reproduce and transmit genetic information to new generations Utilize appropriate information systems to build an understanding of heredity and genetics Objectives: The students will KNOW Vocabulary: gene, DNA, RNA, recessive trait, dominant trait, bac ...
Genetics Basics 3 - The Science Spot
... 1. What term refers to the actual genetic make-up of a trait? Example: Yy or RR 2. What term refers to the gene that is NOT expressed when two different genes for a trait are present in a gene pair? 3. If you are the parental generation, what term would refer to your grandchildren? 4. What type of p ...
... 1. What term refers to the actual genetic make-up of a trait? Example: Yy or RR 2. What term refers to the gene that is NOT expressed when two different genes for a trait are present in a gene pair? 3. If you are the parental generation, what term would refer to your grandchildren? 4. What type of p ...
Heredity
... uses genes to treat or prevent disease by inserting working copies of a gene directly into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder • Researchers are testing several approaches to gene therapy, including: – Replacing a mutated gene that causes disease with a healthy copy of the gene. – Inactiva ...
... uses genes to treat or prevent disease by inserting working copies of a gene directly into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder • Researchers are testing several approaches to gene therapy, including: – Replacing a mutated gene that causes disease with a healthy copy of the gene. – Inactiva ...
therapeutic approaches and perspective
... repairing or chimeraplast, using a synthetic blend of DNA and the related RNA, which tricks the patient's own cells to repair the mutation. The chimeraplasts match the patients' own DNA except for where the mutation occurs, attach to the DNA, and then activate DNA repair mechanisms. ...
... repairing or chimeraplast, using a synthetic blend of DNA and the related RNA, which tricks the patient's own cells to repair the mutation. The chimeraplasts match the patients' own DNA except for where the mutation occurs, attach to the DNA, and then activate DNA repair mechanisms. ...
Gene Therapy
... How are the fragments separated? (by what trait) What is the end result? What are some uses of electrophoresis? ...
... How are the fragments separated? (by what trait) What is the end result? What are some uses of electrophoresis? ...
Introduction to DNA webquest: Name http://learn.genetics.utah.
... B. Go back and Click onto “what is a gene” ...
... B. Go back and Click onto “what is a gene” ...
explaining GM powerpoint
... The microinjection needle is delivering genetically modified DNA to the nucleus. If successful, this GM DNA will be incorporated into the nucleus DNA and will appear in every cell that divides afterwards, eventually resulting in a GM sheep. ...
... The microinjection needle is delivering genetically modified DNA to the nucleus. If successful, this GM DNA will be incorporated into the nucleus DNA and will appear in every cell that divides afterwards, eventually resulting in a GM sheep. ...
Our new understanding of genetic mechanisms is leading to
... • Medicine – One or more molecules – Bond to specific molecules – Change cellular chemistry ...
... • Medicine – One or more molecules – Bond to specific molecules – Change cellular chemistry ...
Glossary - Bioethics Advisory Committee
... person’s lifetime. If a mutation occurs in an egg or sperm cell during a person’s life, there is a chance that the person’s children will inherit the mutation. Most mutations do not cause genetic disorders. For example, some mutations alter a gene's DNA base sequence but don’t change the function of ...
... person’s lifetime. If a mutation occurs in an egg or sperm cell during a person’s life, there is a chance that the person’s children will inherit the mutation. Most mutations do not cause genetic disorders. For example, some mutations alter a gene's DNA base sequence but don’t change the function of ...
Document
... Codominance: When both traits show up (both are fully expressed). If an animal has a gene for black fur and gene for white fur, he has both black and white hair (not gray). B=Black W = White BW= Black and White 25% Black; 25% White; 50% Black and White ...
... Codominance: When both traits show up (both are fully expressed). If an animal has a gene for black fur and gene for white fur, he has both black and white hair (not gray). B=Black W = White BW= Black and White 25% Black; 25% White; 50% Black and White ...