Briefing - Emerging Technology
... Not surprisingly, given their background, the scientists concluded that “when used to introduce small changes only, such techniques do not present a significantly greater food safety concern than other forms ...
... Not surprisingly, given their background, the scientists concluded that “when used to introduce small changes only, such techniques do not present a significantly greater food safety concern than other forms ...
215 KB - Epilepsy Genetics
... Genetics is believed to play a role in most forms of epilepsy. However, perhaps surprisingly, most people with epilepsy do not have any affected relatives. Current scientific evidence suggests that the role of genetics in epilepsy is complex – many genes with a small or modest effect on risk are lik ...
... Genetics is believed to play a role in most forms of epilepsy. However, perhaps surprisingly, most people with epilepsy do not have any affected relatives. Current scientific evidence suggests that the role of genetics in epilepsy is complex – many genes with a small or modest effect on risk are lik ...
LBSC 708L Session 1
... Transcription of the nirIX gene cluster itself was controlled by NNR, a member of the family of FNR-like transcriptional activators. An NNR binding sequence is located in the middle of the intergenic region between the nirI and nirS genes with its centre located at position -41.5 relative to the tra ...
... Transcription of the nirIX gene cluster itself was controlled by NNR, a member of the family of FNR-like transcriptional activators. An NNR binding sequence is located in the middle of the intergenic region between the nirI and nirS genes with its centre located at position -41.5 relative to the tra ...
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
... so what might be sensible! if n (the number of samples) is large-ish and we use a t-test to compare two groups! and if H0: no difference between the group means is true, for all genes! then the elements of x are approximately t with n-1 df (for large n this is approximately N(0,1))! so that the elem ...
... so what might be sensible! if n (the number of samples) is large-ish and we use a t-test to compare two groups! and if H0: no difference between the group means is true, for all genes! then the elements of x are approximately t with n-1 df (for large n this is approximately N(0,1))! so that the elem ...
Designer Babies
... debate whether modifying genes for disorders is immoral or not (fig. 2). Another ethical issue is whether or not everyone will be able to design their baby or will it only be provided to the rich and upper class? Will designer babies be like designer clothes, where only the wealthy can afford them? ...
... debate whether modifying genes for disorders is immoral or not (fig. 2). Another ethical issue is whether or not everyone will be able to design their baby or will it only be provided to the rich and upper class? Will designer babies be like designer clothes, where only the wealthy can afford them? ...
The UCSC Human Genome Browser
... fact about 75% of the sequence is Venter’s, and he subsequently paid about $100m to finish his. Humans are such a young species that we differ from each other, and indeed the two genomes in each of us differ, at roughly 1/1000bp or 0.1%. Therefore using multiple DNA sources is not a major problem, i ...
... fact about 75% of the sequence is Venter’s, and he subsequently paid about $100m to finish his. Humans are such a young species that we differ from each other, and indeed the two genomes in each of us differ, at roughly 1/1000bp or 0.1%. Therefore using multiple DNA sources is not a major problem, i ...
4. Chromosomes and Inheritance
... c. Based on the actual results of this cross, do you think these 2 gene loci are linked or unlinked? Explain your answer. d. Assuming that your answer to part C is correct, why don’t the actual results of the cross agree more closely with your predicted results? Describe as many possible reasons as ...
... c. Based on the actual results of this cross, do you think these 2 gene loci are linked or unlinked? Explain your answer. d. Assuming that your answer to part C is correct, why don’t the actual results of the cross agree more closely with your predicted results? Describe as many possible reasons as ...
Genetics Since Mendel
... polygenic inheritance, and give examples of each. Describe two human genetic disorders and how they are inherited. Explain how sex-linked traits are passed to offspring. ...
... polygenic inheritance, and give examples of each. Describe two human genetic disorders and how they are inherited. Explain how sex-linked traits are passed to offspring. ...
Evolution notes 2
... Evolution – change in gene frequency in a population over time (through natural selection) Natural selection Variation among offspring ...
... Evolution – change in gene frequency in a population over time (through natural selection) Natural selection Variation among offspring ...
DNA Power Point - Chapter 4 Biology
... •The structure of DNA allows it to hold information. •The order of the bases on one side of DNA is a code that carries information. •GENE: String of nucleotides that give cell the information about how to make a specific trait. •There is an ENORMOUS AMOUNT OF DNA so there is a large variety of trait ...
... •The structure of DNA allows it to hold information. •The order of the bases on one side of DNA is a code that carries information. •GENE: String of nucleotides that give cell the information about how to make a specific trait. •There is an ENORMOUS AMOUNT OF DNA so there is a large variety of trait ...
GENE INTERACTIONS
... • The C and P genes independently assort, the presence of a recessive genotype at one locus (i.e., cc or pp) masks the effects of the alleles at the other locus. • There are 9 combinations of alleles in the F1 generation that feature at least 1 dominant C and 1 dominant P allele, which would yield a ...
... • The C and P genes independently assort, the presence of a recessive genotype at one locus (i.e., cc or pp) masks the effects of the alleles at the other locus. • There are 9 combinations of alleles in the F1 generation that feature at least 1 dominant C and 1 dominant P allele, which would yield a ...
Chapter 4 Heredity and Evolution
... altered in small populations that are taken from, or are remnants of, larger populations. A new population will be established, and as long as mates are chosen only within this population, all the members will be descended from the founders. An allele that was rare in the founders’ parent population ...
... altered in small populations that are taken from, or are remnants of, larger populations. A new population will be established, and as long as mates are chosen only within this population, all the members will be descended from the founders. An allele that was rare in the founders’ parent population ...
Sex-linked traits
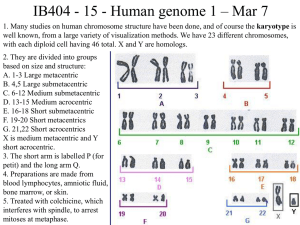
... Most human cells have 46 chromosomes: a karyotype lets us see these chromosomes visually. • Humans have 46 chromosomes= 23 pairs • Each chromosome of a pair is a homologous chromosome – (one strand of dsDNA X 2) • We have 22 autologous chromosomes • We have one sex-chromosome – It is either two X-c ...
... Most human cells have 46 chromosomes: a karyotype lets us see these chromosomes visually. • Humans have 46 chromosomes= 23 pairs • Each chromosome of a pair is a homologous chromosome – (one strand of dsDNA X 2) • We have 22 autologous chromosomes • We have one sex-chromosome – It is either two X-c ...
Microarray Analysis 2
... 1. We could reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true, i.e., our results were obtained by chance. (Type I error). 2. We could fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false, i.e. our experiment failed to detect the true difference that exists. (Type II error) ...
... 1. We could reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true, i.e., our results were obtained by chance. (Type I error). 2. We could fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false, i.e. our experiment failed to detect the true difference that exists. (Type II error) ...
TASSEL
... forms or traits) that they produce. Limitations of using natural populations: It requires the growth of three generations before linkage analysis is possible. Very large segregating populations are needed to achieve a high resolution map. The molecular markers may be specific (polymorphic) to ...
... forms or traits) that they produce. Limitations of using natural populations: It requires the growth of three generations before linkage analysis is possible. Very large segregating populations are needed to achieve a high resolution map. The molecular markers may be specific (polymorphic) to ...
Baby Boom Alien Crosses
... BI2. c. Students know how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. BI2. g. Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. BI3. a. Students know how to predict the prob ...
... BI2. c. Students know how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. BI2. g. Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. BI3. a. Students know how to predict the prob ...
Lecture 2
... Ex: Hans with PKU, won’t be a preferable mate, not likely to have many, if any offspring Euthanasia of Hans isn’t going to much to decrease rates of PKU Carriers of PKU would need to be killed, may as well just kill everyone… Principle of genetic load ...
... Ex: Hans with PKU, won’t be a preferable mate, not likely to have many, if any offspring Euthanasia of Hans isn’t going to much to decrease rates of PKU Carriers of PKU would need to be killed, may as well just kill everyone… Principle of genetic load ...
Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles
... Traits controlled by 2 or more genes. Ex. Eye color in fruit flies (3 genes). Ex. Human skin color. Wide range of skin colors because 4 genes control color. ...
... Traits controlled by 2 or more genes. Ex. Eye color in fruit flies (3 genes). Ex. Human skin color. Wide range of skin colors because 4 genes control color. ...
Mendelian Genetics Study Guide In Preparation for California
... 10. In fruit flies, the red eye gene (R) is dominant and the gene for sepia eyes (r) is recessive. What are the possible combinations of genes in the offspring of two red-eyed heterozygous flies (Rr)? RR, Rr, and rr 11. In certain breeds of dogs, deafness is due to a recessive allele (d) of a partic ...
... 10. In fruit flies, the red eye gene (R) is dominant and the gene for sepia eyes (r) is recessive. What are the possible combinations of genes in the offspring of two red-eyed heterozygous flies (Rr)? RR, Rr, and rr 11. In certain breeds of dogs, deafness is due to a recessive allele (d) of a partic ...
Mendelian Genetics
... the F1 generation. The second generation offspring are called the F2 generation. Dominant traits are observed in the organism’s characteristics if present. Recessive traits are traits that are hidden if the dominate trait is present. Recessive traits can only be seen in the organisms if both alleles ...
... the F1 generation. The second generation offspring are called the F2 generation. Dominant traits are observed in the organism’s characteristics if present. Recessive traits are traits that are hidden if the dominate trait is present. Recessive traits can only be seen in the organisms if both alleles ...
E. coli
... 2. Mendel’s law: gene pairs on different chromosomes assort independently in gamete formation ...
... 2. Mendel’s law: gene pairs on different chromosomes assort independently in gamete formation ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... 1. from one cell into the culture medium, where it is taken up by another cell. 2. with the help of a viral go-between. 3. in a bidirectional fashion between two cells. 4. from one bacterium to another. ...
... 1. from one cell into the culture medium, where it is taken up by another cell. 2. with the help of a viral go-between. 3. in a bidirectional fashion between two cells. 4. from one bacterium to another. ...
Genetic-Explanantion..
... Tamminga and Schulz (1991)Research has failed to isolate a single recessive or dominant gene that that seems to cause the illness. However Kelly and Murray (2000) suggest that each of the genes identified by molecular genetics is not innocent in itself, however people who inherit a number of them ar ...
... Tamminga and Schulz (1991)Research has failed to isolate a single recessive or dominant gene that that seems to cause the illness. However Kelly and Murray (2000) suggest that each of the genes identified by molecular genetics is not innocent in itself, however people who inherit a number of them ar ...