Lecture 17
... Omega is the last letter of the Greek alphabet. These are called omega three because you are suppose to count from the other end of the molecule, contrary to the IUPAC convention. Remenber these acids are present as triglycerides in fish oil and other sources ...
... Omega is the last letter of the Greek alphabet. These are called omega three because you are suppose to count from the other end of the molecule, contrary to the IUPAC convention. Remenber these acids are present as triglycerides in fish oil and other sources ...
Lipids
... C=C double bonds in the fatty acids plant & fish fats vegetable oils liquid at room temperature ...
... C=C double bonds in the fatty acids plant & fish fats vegetable oils liquid at room temperature ...
Classes of Biomolecules Lipids Biological Functions of Lipids
... constructing the honeycomb, • any of numerous substances of plant or animal origin that differ from fats in being less greasy, harder, and more brittle and in containing principally compounds of high molecular weight (as fatty acids, alcohols, and saturated hydrocarbons) • Long chain fatty acid wi ...
... constructing the honeycomb, • any of numerous substances of plant or animal origin that differ from fats in being less greasy, harder, and more brittle and in containing principally compounds of high molecular weight (as fatty acids, alcohols, and saturated hydrocarbons) • Long chain fatty acid wi ...
lipids
... • Simple triacylglycerols are composed of three identical fatty acid side chains • mixed triacylglycerols have two or three different fatty acids. What are the characteristics of these fatty acids? • All fatty acid chains are unbranched, but they may be saturated or unsaturated. • Naturally occur ...
... • Simple triacylglycerols are composed of three identical fatty acid side chains • mixed triacylglycerols have two or three different fatty acids. What are the characteristics of these fatty acids? • All fatty acid chains are unbranched, but they may be saturated or unsaturated. • Naturally occur ...
Lipid Metabolism
... • Induced by hormone epinephrine , norepinephrine, glucagon and adreno corticotropic hormone • the lipolytic products are then released into the blood • The free fatty acids bind to serum albumin and transport to tissues that require energy. The energy is generated by catabolic β-oxidation pathway ( ...
... • Induced by hormone epinephrine , norepinephrine, glucagon and adreno corticotropic hormone • the lipolytic products are then released into the blood • The free fatty acids bind to serum albumin and transport to tissues that require energy. The energy is generated by catabolic β-oxidation pathway ( ...
没有幻灯片标题
... leads to activation of the membrane bound phospholipase C. 5.2.2 Phospholipase C catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol 4,5bisphophate (PIP2) to form inositol 1,4,5triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). ...
... leads to activation of the membrane bound phospholipase C. 5.2.2 Phospholipase C catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol 4,5bisphophate (PIP2) to form inositol 1,4,5triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). ...
Chemistry of Lipids
... Essential fatty acids or PUFA: PUFA: N t synthesized th i d iin th d and d should h ld b li d Not the b body be supplied through diet. Contain more than one double bond bond. Eg: Linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid. acid These are not synthesised in human body due to lack of ...
... Essential fatty acids or PUFA: PUFA: N t synthesized th i d iin th d and d should h ld b li d Not the b body be supplied through diet. Contain more than one double bond bond. Eg: Linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid. acid These are not synthesised in human body due to lack of ...
5.6. membrane lipids
... - Low-density lipoproteins (LDL): they transport cholesterol and its esters to the tissues. - High-density lipoproteins (HDL): Rich in cholesterol but poor in triacyglycerol (they promote the excretion of the excess of cholesterol). ...
... - Low-density lipoproteins (LDL): they transport cholesterol and its esters to the tissues. - High-density lipoproteins (HDL): Rich in cholesterol but poor in triacyglycerol (they promote the excretion of the excess of cholesterol). ...
Review for Midterm Exam
... A: Salivary amylase starts breaking up starch in the mouth, but quits when it hits stomach acid. Pancreatic amylase in the small intestine breaks things down to disaccharides, and sucrase, lactase, and maltase break these into monosaccharides that get absorbed. Soluble fiber is fermented by the bact ...
... A: Salivary amylase starts breaking up starch in the mouth, but quits when it hits stomach acid. Pancreatic amylase in the small intestine breaks things down to disaccharides, and sucrase, lactase, and maltase break these into monosaccharides that get absorbed. Soluble fiber is fermented by the bact ...
week 7_lipid - UniMAP Portal
... obtained by the ingestion of LDL by foam cells- directly correlated with high risk for coronary heart disease. High plasma HDL- low risk for coronary artery disease. Liver cells are the only cells that possess HDL receptors. ...
... obtained by the ingestion of LDL by foam cells- directly correlated with high risk for coronary heart disease. High plasma HDL- low risk for coronary artery disease. Liver cells are the only cells that possess HDL receptors. ...
Lipids and Their Structures - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Definition: Organic molecule of biological origin that is insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. Solubility Explained: Lipids do have both nonpolar and polar regions; however, the majority of the molecule is nonpolar (due to large nonpolar tails). Since "like dissolves like", lipid ...
... Definition: Organic molecule of biological origin that is insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. Solubility Explained: Lipids do have both nonpolar and polar regions; however, the majority of the molecule is nonpolar (due to large nonpolar tails). Since "like dissolves like", lipid ...
Fats - Nutritious And Delicious
... phospholipids & triglycerides (the most abundant, which make up 90–95% of fats found in our foods). The main biological functions of lipids include storing energy, signalling and acting as structural components of cell membranes – such as saturated fats. Play an important role in regulat ...
... phospholipids & triglycerides (the most abundant, which make up 90–95% of fats found in our foods). The main biological functions of lipids include storing energy, signalling and acting as structural components of cell membranes – such as saturated fats. Play an important role in regulat ...
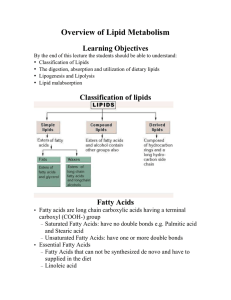
Overview of Lipid Metabolism
... – Saturated Fatty Acids: have no double bonds e.g. Palmitic acid and Stearic acid – Unsaturated Fatty Acids: have one or more double bonds • Essential Fatty Acids – Fatty Acids that can not be synthesized de novo and have to supplied in the diet – Linoleic acid ...
... – Saturated Fatty Acids: have no double bonds e.g. Palmitic acid and Stearic acid – Unsaturated Fatty Acids: have one or more double bonds • Essential Fatty Acids – Fatty Acids that can not be synthesized de novo and have to supplied in the diet – Linoleic acid ...
Versatile roles of lipids and carotenoids in membranes
... cerebroside – a ceramide with a monosaccharide (galactose or glucose) head group globoside – a ceramide with a di-, tri- or tetrasaccharide head group (containing glucose, galactose or N-acetyl-D-galactosamine sugars) ganglioside – a ceramide with a polar head group that is a complex oligosaccharide ...
... cerebroside – a ceramide with a monosaccharide (galactose or glucose) head group globoside – a ceramide with a di-, tri- or tetrasaccharide head group (containing glucose, galactose or N-acetyl-D-galactosamine sugars) ganglioside – a ceramide with a polar head group that is a complex oligosaccharide ...
Saturated fatty acid
... 36 carbons, whereas the alcohols have an even number from 24 to 36 carbons. ► A component in beeswax is the ester formed from a 30-C alcohol (triacontanol) and a 16-C acid (palmitic acid). ...
... 36 carbons, whereas the alcohols have an even number from 24 to 36 carbons. ► A component in beeswax is the ester formed from a 30-C alcohol (triacontanol) and a 16-C acid (palmitic acid). ...
Fatty acids and their derivatives
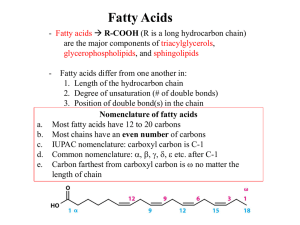
... Fatty acids – monocarboxylic acids that contain hydrocarbon chains of variable length (12-20 C), R-COOH 2 types saturated ...
... Fatty acids – monocarboxylic acids that contain hydrocarbon chains of variable length (12-20 C), R-COOH 2 types saturated ...
Principles of Biochemistry 4/e
... - Cholesterol is converted to cholesteryl esters for cell storage or transport in blood. - Fatty acid is esterified to C-3 OH of Cholesterol - Cholesterol esters are very hydrophobic and must be complexed with phospholipids or amphipathic proteins found in lipoproteins (e.g. HDL and LDL) for transpo ...
... - Cholesterol is converted to cholesteryl esters for cell storage or transport in blood. - Fatty acid is esterified to C-3 OH of Cholesterol - Cholesterol esters are very hydrophobic and must be complexed with phospholipids or amphipathic proteins found in lipoproteins (e.g. HDL and LDL) for transpo ...
NUTRITION - Purdue University
... Metaplasia (change of cell type) Infections Dozens of other symptoms, as Vit A is involved all over the body ...
... Metaplasia (change of cell type) Infections Dozens of other symptoms, as Vit A is involved all over the body ...
FATS - Catherine Huff`s Site
... fatty acids have the first double bond between the third and fourth carbon atoms. Omega 6 have the first double bond between the sixth and seventh carbon atoms. Fats from each of these families are important. The body can convert one omega 3 to another omega 3 but cannot create an omega 3 from scrat ...
... fatty acids have the first double bond between the third and fourth carbon atoms. Omega 6 have the first double bond between the sixth and seventh carbon atoms. Fats from each of these families are important. The body can convert one omega 3 to another omega 3 but cannot create an omega 3 from scrat ...
Phospholipids and Membrane
... *PGI2: vasodilator, inhibit platelet aggregration *PGI3: help effect of PGI2 *TXA2: increase platelets aggregation, vasoconstriction *TXA3: less potent than TXA2 N3 fatty acids compete with N6 for elongase, desaturase, cyclooxyenase and lipoxigenase ...
... *PGI2: vasodilator, inhibit platelet aggregration *PGI3: help effect of PGI2 *TXA2: increase platelets aggregation, vasoconstriction *TXA3: less potent than TXA2 N3 fatty acids compete with N6 for elongase, desaturase, cyclooxyenase and lipoxigenase ...
Lipoxin
Lipoxins are members of the family of bioactive products generated from Arachidonic Acid (AA). They have a number of immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory actions. Lipoxins are short lived endogenously produced nonclassic eicosanoids whose appearance in inflammation signals the resolution of inflammation. They are abbreviated as LX, an acronym for lipoxygenase (LO) interaction products. At present two lipoxins have been identified; lipoxin A4 (LXA4) and lipoxin B4 (LXB4).