Ch5LIPIDS
... • Short chain = • Medium chain = • Long chain = • The shorter the carbon chain, the more liquid the fatty acid is ...
... • Short chain = • Medium chain = • Long chain = • The shorter the carbon chain, the more liquid the fatty acid is ...
Molecular Modeling Activity Lipids (Saturated and Unsaturated Fats
... Triglycerides are the most common type of lipid found in the body and in foods. Triglycerides include the edible fats and oils in our dietssubstances such as olive oil, corn oil, peanut oil, butter, and lard. They are solid or semi-solid at room temperature are classified as fats, and occur predom ...
... Triglycerides are the most common type of lipid found in the body and in foods. Triglycerides include the edible fats and oils in our dietssubstances such as olive oil, corn oil, peanut oil, butter, and lard. They are solid or semi-solid at room temperature are classified as fats, and occur predom ...
5.6. membrane lipids
... • They can be branched and saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated (contain ...
... • They can be branched and saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated (contain ...
3. LIPIDS
... Trans Fatty acids, unlike Cis isomers, increase plasma cholesterol levels ( total and LDL ) and decrease HDL-cholesterol Current concerns about trans fatty acid intake and attempt to ↓ their dietary intake ...
... Trans Fatty acids, unlike Cis isomers, increase plasma cholesterol levels ( total and LDL ) and decrease HDL-cholesterol Current concerns about trans fatty acid intake and attempt to ↓ their dietary intake ...
Review for Midterm Exam
... intestine breaks things down to disaccharides, and sucrase, lactase, and maltase break these into monosaccharides that get absorbed. Soluble fiber is fermented by the bacteria in the large intestine and insoluble fiber passes into the stool without ...
... intestine breaks things down to disaccharides, and sucrase, lactase, and maltase break these into monosaccharides that get absorbed. Soluble fiber is fermented by the bacteria in the large intestine and insoluble fiber passes into the stool without ...
Classes of Biomolecules Lipids Biological Functions of Lipids
... • Commonality is they are are polymers of monmeric units • Final class of biomolecules are the lipids ...
... • Commonality is they are are polymers of monmeric units • Final class of biomolecules are the lipids ...
Overview of Lipid Metabolism
... – Saturated Fatty Acids: have no double bonds e.g. Palmitic acid and Stearic acid – Unsaturated Fatty Acids: have one or more double bonds • Essential Fatty Acids – Fatty Acids that can not be synthesized de novo and have to supplied in the diet – Linoleic acid ...
... – Saturated Fatty Acids: have no double bonds e.g. Palmitic acid and Stearic acid – Unsaturated Fatty Acids: have one or more double bonds • Essential Fatty Acids – Fatty Acids that can not be synthesized de novo and have to supplied in the diet – Linoleic acid ...
Fatty acids and their derivatives
... Fatty acids – monocarboxylic acids that contain hydrocarbon chains of variable length (12-20 C), R-COOH 2 types saturated ...
... Fatty acids – monocarboxylic acids that contain hydrocarbon chains of variable length (12-20 C), R-COOH 2 types saturated ...
Lipids and Their Structures - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Lipids and Their Structures Definition: Organic molecule of biological origin that is insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. Solubility Explained: Lipids do have both nonpolar and polar regions; however, the majority of the molecule is nonpolar (due to large nonpolar tails). Since ...
... Lipids and Their Structures Definition: Organic molecule of biological origin that is insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. Solubility Explained: Lipids do have both nonpolar and polar regions; however, the majority of the molecule is nonpolar (due to large nonpolar tails). Since ...
Group A_lipid - UniMAP Portal
... Composed of 4 fused rings Distinguished from each other by placement of carbon-carbon double bonds and various constituents (OH, Carbonyl & alkyl groups) Eg cholesterol, progesterone, testosterone, estradiol ...
... Composed of 4 fused rings Distinguished from each other by placement of carbon-carbon double bonds and various constituents (OH, Carbonyl & alkyl groups) Eg cholesterol, progesterone, testosterone, estradiol ...
week 7_lipid - UniMAP Portal
... Naturally occurring FA are in cis-configuration The presence of cis double bond causes ‘kink’ in FA chain Thus, unsaturated FA do not pack closely together as saturated FA. Less energy is required to disrupt the intermolecular forces between unsaturated FA- lower melting points and liquid in R.T ...
... Naturally occurring FA are in cis-configuration The presence of cis double bond causes ‘kink’ in FA chain Thus, unsaturated FA do not pack closely together as saturated FA. Less energy is required to disrupt the intermolecular forces between unsaturated FA- lower melting points and liquid in R.T ...
Qualitative tests of lipids 2
... The "acrolein test" is used to detect glycrol or fats Most lipid are found in the form of triglycerides, an ester formed from glycerol and fatty acids. Principle: When a fat is heated strongly in the presence of a dehydrating agent such as KHSO4, the glycerol portion of the molecule is dehydrated t ...
... The "acrolein test" is used to detect glycrol or fats Most lipid are found in the form of triglycerides, an ester formed from glycerol and fatty acids. Principle: When a fat is heated strongly in the presence of a dehydrating agent such as KHSO4, the glycerol portion of the molecule is dehydrated t ...
PPT
... Protective wax coatings found on some plants Energy-rich compounds with low densities Storage form of energy for plants and animals Structural components, especially in cellular membrane formation ...
... Protective wax coatings found on some plants Energy-rich compounds with low densities Storage form of energy for plants and animals Structural components, especially in cellular membrane formation ...
Lipids
... • Important cell component – animal cell membranes – precursor of all other steroids • including vertebrate sex hormones ...
... • Important cell component – animal cell membranes – precursor of all other steroids • including vertebrate sex hormones ...
Extraction and Characterization of Fish Oil from Monopterus albus
... Abstract. Fish oils have been recognized as good sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) which are widely used for pharmaceutical purposes and as food supplements. It has been reported that tropical fishes are rich in arachidonic acid (AA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids have ...
... Abstract. Fish oils have been recognized as good sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) which are widely used for pharmaceutical purposes and as food supplements. It has been reported that tropical fishes are rich in arachidonic acid (AA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids have ...
Hein and Arena - University of Wisconsin–Eau Claire
... -Prevent ovulation. -Cause changes on the uterus wall. ...
... -Prevent ovulation. -Cause changes on the uterus wall. ...
Examination III Key
... 28. [7 points] Serine, generally available within cells in an unlimted amount, can be metabolized to a key metabolic intermediate that can be used to spare some methionine from being degraded. a. [3 points] What is the name of this key metabolic intermediate? Methylene-tetrahydrofolate (methylene-TH ...
... 28. [7 points] Serine, generally available within cells in an unlimted amount, can be metabolized to a key metabolic intermediate that can be used to spare some methionine from being degraded. a. [3 points] What is the name of this key metabolic intermediate? Methylene-tetrahydrofolate (methylene-TH ...
Saturated fatty acid
... • Saturated fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid containing only carbon–carbon single bonds. • Unsaturated fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid containing one or more carbon–carbon double bonds. • If double bonds are present in naturally occurring fats and oils, the double bonds are usually ...
... • Saturated fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid containing only carbon–carbon single bonds. • Unsaturated fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid containing one or more carbon–carbon double bonds. • If double bonds are present in naturally occurring fats and oils, the double bonds are usually ...
proper omega-3 Olive oil Canola oil Coconut oil Palm oil
... Excess polyunsaturated fatty acids, PUFA, with two or more double bonds may be a severe threat to public health in several ways. This is due to the destructive biochemical reactions termed lipid peroxidation. Reactive structure: Dietary PUFA have a very reactive CH2 group between two double bonds. T ...
... Excess polyunsaturated fatty acids, PUFA, with two or more double bonds may be a severe threat to public health in several ways. This is due to the destructive biochemical reactions termed lipid peroxidation. Reactive structure: Dietary PUFA have a very reactive CH2 group between two double bonds. T ...
Lipids
... have been identified as essential fatty acids They have important roles in immune function and vision, help form cell membranes, and produce hormone-like compounds called eicosanoids The body has no means to produce double bonds between any carbon atoms from the first to the ninth carbon Alpha ...
... have been identified as essential fatty acids They have important roles in immune function and vision, help form cell membranes, and produce hormone-like compounds called eicosanoids The body has no means to produce double bonds between any carbon atoms from the first to the ninth carbon Alpha ...
4. Essential fatty acid
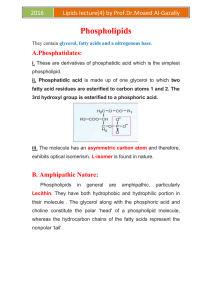
... (A) Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid and choline (B) Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid and ethanolamine (C) Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid and inositol (D) Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid and serine ...
... (A) Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid and choline (B) Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid and ethanolamine (C) Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid and inositol (D) Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphoric acid and serine ...
Chapter 4
... • Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) – Plasma – Forms a fatty acidcholesterol ester – This is transferred to chylomicron or VLDL – Helps maintain stability of those molecules as triglycerides are removed ...
... • Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) – Plasma – Forms a fatty acidcholesterol ester – This is transferred to chylomicron or VLDL – Helps maintain stability of those molecules as triglycerides are removed ...
Resolvin

Resolvins are compounds that are made by the human body from the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). They are produced by the COX-2 pathway especially in the presence of aspirin. Experimental evidence indicates that resolvins reduce cellular inflammation by inhibiting the production and transportation of inflammatory cells and chemicals to the sites of inflammation. Other biological actions have been reported, with therapeutical potential such as a reduction in inflammatory pain. The EPA-derived resolvins are nonclassic eicosanoids.A translational study from 2015 questions the notion that resolvins and other members of this family (called specialized pro-resolving mediators) are indeed formed in the human body from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. This study failed to detect a consistent signal of resolvin formation in urine or plasma of healthy volunteers who had taken fish oil. This study also found no alteration in the formation of resolvins during the resolution of inflammation which was induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. By contrast, formation of a series of established enzymatic and nonenzymatic oxidation products formed from omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids could readily be demonstrated in vivo. On this basis, the study authors conclude that their study fails to provide evidence consistent with the hypothesis that resolvins mediate an anti-inflammatory action of fish oil. Further information can be found in a commentary accompanying this translational work.