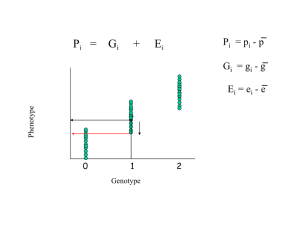Chromosomal theory of inheritance
... – If penetrance or expressivity is < 100% other genes/modifiers may be involved. ...
... – If penetrance or expressivity is < 100% other genes/modifiers may be involved. ...
What is Genetics?
... Incomplete Dominance Self-Check 1. If a trait, like flower color, exhibits incomplete dominance, how many phenotypes are there? 2. Cross 2 pink flowers, what are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios? 3. Are pink flowers heterozygous or homozygous? ...
... Incomplete Dominance Self-Check 1. If a trait, like flower color, exhibits incomplete dominance, how many phenotypes are there? 2. Cross 2 pink flowers, what are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios? 3. Are pink flowers heterozygous or homozygous? ...
Chapter 10: DIPLOIDY
... GA maintained extra diversity at loci where alternative alleles were emphasized in the recent past [Smith et al. 1992]. In effect, diploidy embodied a form of temporal memory that is distributed across the population. Analysis also revealed that abeyant recessives are sensitive to past environmental ...
... GA maintained extra diversity at loci where alternative alleles were emphasized in the recent past [Smith et al. 1992]. In effect, diploidy embodied a form of temporal memory that is distributed across the population. Analysis also revealed that abeyant recessives are sensitive to past environmental ...
Gene and Genotype frequencies
... The genetics of a population is concerned with genetic constitution of individuals and also with the transmission of genes from one generation to the next In this transmission, genotypes of parents are broken down and it is genes that are transmitted in the gametes New set of genotypes are theref ...
... The genetics of a population is concerned with genetic constitution of individuals and also with the transmission of genes from one generation to the next In this transmission, genotypes of parents are broken down and it is genes that are transmitted in the gametes New set of genotypes are theref ...
Here`s - MathBench
... chromosome stayed on the same chromosome. If that was true, then each parent could only have 2 rather than 4 variations on their gametes, and the punnett squares would be easy to figure out. However, just because two alleles start out on the same chromosome does not mean they stay there! Chromosomes ...
... chromosome stayed on the same chromosome. If that was true, then each parent could only have 2 rather than 4 variations on their gametes, and the punnett squares would be easy to figure out. However, just because two alleles start out on the same chromosome does not mean they stay there! Chromosomes ...
chapter 5 powerpoint
... Autosomal dominant Flo Hyman was a 6’5” star on the U.S. women’s volleyball team that won a silver medal in the 1984 Olympics. Two years later, at the age of 31, she died in a volley ball game from a ruptured aorta caused by Marfan Syndrome. The gene responsible for Marfan Syndrome is located on chr ...
... Autosomal dominant Flo Hyman was a 6’5” star on the U.S. women’s volleyball team that won a silver medal in the 1984 Olympics. Two years later, at the age of 31, she died in a volley ball game from a ruptured aorta caused by Marfan Syndrome. The gene responsible for Marfan Syndrome is located on chr ...
DNA Tests for Genetic Improvement of Beef Cattle
... ing value is equal to twice an EPD. A breeding value is the genetic potential of an animal where an EPD is the genetic potential of an animal as a parent given that only half of an animal’s alleles will be passed to the next generation. Just like an EPD, these results are reported in units of the tr ...
... ing value is equal to twice an EPD. A breeding value is the genetic potential of an animal where an EPD is the genetic potential of an animal as a parent given that only half of an animal’s alleles will be passed to the next generation. Just like an EPD, these results are reported in units of the tr ...
Why Is He Difierent from Both Parents? The Genetics of ABO Blood
... The next day, Kevein and Peter met Ms. B. and explained Kevin’s puzzle about his family’s blood types. “Ah, good question,” replied Ms. B. “Let me explain how blood types work so that it will help you to understand why your parents couldn’t donate blood to you and how you can all have different bloo ...
... The next day, Kevein and Peter met Ms. B. and explained Kevin’s puzzle about his family’s blood types. “Ah, good question,” replied Ms. B. “Let me explain how blood types work so that it will help you to understand why your parents couldn’t donate blood to you and how you can all have different bloo ...
Genetic Variation of the Major Histocompatibility Complex DRB3.2
... while Hariana is a prominent dual-purpose breed reared both as a dairy animal and for bullock production. A total of 30 different BoLADRB3.2 alleles were observed to be present in the 3 Bos indicus breeds. Certain alleles were common amongst the three breeds while there were others that were unique ...
... while Hariana is a prominent dual-purpose breed reared both as a dairy animal and for bullock production. A total of 30 different BoLADRB3.2 alleles were observed to be present in the 3 Bos indicus breeds. Certain alleles were common amongst the three breeds while there were others that were unique ...
Linkage Mapping in Drosophila written by JD Hendrix
... pioneered the use of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, as a model organism in genetic studies. Drosophila has a diploid chromosome number of eight, or four pairs of homologous chromosomes numbered 1 - 4. Chromosome 1 is the X chromosome (sex chromosome) and is responsible for sex determination ...
... pioneered the use of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, as a model organism in genetic studies. Drosophila has a diploid chromosome number of eight, or four pairs of homologous chromosomes numbered 1 - 4. Chromosome 1 is the X chromosome (sex chromosome) and is responsible for sex determination ...
Chapter 28 - Evolution Textbook
... per se, the set of genes that it is associated with changes from generation to generation. Whether reproduction is sexual or asexual, a population can be modeled by keeping track of the proportion of each type of offspring. This is much harder for a sexual population, because so many different types ...
... per se, the set of genes that it is associated with changes from generation to generation. Whether reproduction is sexual or asexual, a population can be modeled by keeping track of the proportion of each type of offspring. This is much harder for a sexual population, because so many different types ...
061_paper_4465_manuscript_66_0
... genotype of the jth QTL of the ith individual that xij = 1 when the genotype is AA otherwise is zero, yij = 1 when the genotype is Aa or aA otherwise is zero and zij = 1 when the genotype is aa otherwise is zero. Moreover, pjr and qjr are the allelic frequencies (A or a) for the jth QTL in breed r, ...
... genotype of the jth QTL of the ith individual that xij = 1 when the genotype is AA otherwise is zero, yij = 1 when the genotype is Aa or aA otherwise is zero and zij = 1 when the genotype is aa otherwise is zero. Moreover, pjr and qjr are the allelic frequencies (A or a) for the jth QTL in breed r, ...
Linkage and Recombination
... We will study linkage, recombination, and gene mapping as follows: 1. Linkage (as it was first seen and understood in Drosophila) 2. Definition and mechanisms of recombination 3. Using recombination frequencies to map genes ...
... We will study linkage, recombination, and gene mapping as follows: 1. Linkage (as it was first seen and understood in Drosophila) 2. Definition and mechanisms of recombination 3. Using recombination frequencies to map genes ...
Rare coding SNP in DZIP1 gene associated with late
... RCs must be rank ordered and statistical resolution decreases with increasing rank, thus overly liberal RC creation is pointless (1; 22). A total of 23 RCs were constructed (Table 1). The first 15 RCs, containing individual SNPs, were based on the following factors: Genomic region - we grouped SNPs ...
... RCs must be rank ordered and statistical resolution decreases with increasing rank, thus overly liberal RC creation is pointless (1; 22). A total of 23 RCs were constructed (Table 1). The first 15 RCs, containing individual SNPs, were based on the following factors: Genomic region - we grouped SNPs ...
X-linked
... Compare “observed” vs. “expected” data is variance from expected due to “random chance”? or is there another factor influencing data? ...
... Compare “observed” vs. “expected” data is variance from expected due to “random chance”? or is there another factor influencing data? ...
human-development-5th-edition-kail-test-bank
... C. her biological parents were not the same as the parents who reared her. D. the woman who carried her as a baby was not the woman who reared her. 69. Which event occurs following in vitro fertilization? A. A fertilized egg is placed directly into the uterus. B. A sperm is injected directly into th ...
... C. her biological parents were not the same as the parents who reared her. D. the woman who carried her as a baby was not the woman who reared her. 69. Which event occurs following in vitro fertilization? A. A fertilized egg is placed directly into the uterus. B. A sperm is injected directly into th ...
introduction to mendelian genetics
... generation for the possible methods and comparing them to your data using the Chi square test. Read Comparing Count Data: Dealing with Variability in your lab manual in Appendix C beginning at the bottom of the second column on page 449 and ending on page 452. This will explain the null and alternat ...
... generation for the possible methods and comparing them to your data using the Chi square test. Read Comparing Count Data: Dealing with Variability in your lab manual in Appendix C beginning at the bottom of the second column on page 449 and ending on page 452. This will explain the null and alternat ...
MQ (54) LIV 2 contents
... population with lower trait values” (Turchin et al, 2012). Another prediction of the polygenic selection model (explicitly advanced and tested here for the first time) is that alleles with similar function are statistically associated at the population level, so that populations which have undergone ...
... population with lower trait values” (Turchin et al, 2012). Another prediction of the polygenic selection model (explicitly advanced and tested here for the first time) is that alleles with similar function are statistically associated at the population level, so that populations which have undergone ...
Patterns of Inheritance - American Society of Human Genetics
... • Increased consanguinity (over general ...
... • Increased consanguinity (over general ...
Sex- Linked Traits
... _____ 13. A normal male’s genotype would be XNY. _____ 14. A normal male’s genotype would be XnY. _____ 15. A colorblind male’s genotype would be XNY. _____ 16. A colorblind male’s genotype would be XnY. _____ 17. A normal female’s genotype would be XNXN or XNXn. _____ 18. A normal female’s genotype ...
... _____ 13. A normal male’s genotype would be XNY. _____ 14. A normal male’s genotype would be XnY. _____ 15. A colorblind male’s genotype would be XNY. _____ 16. A colorblind male’s genotype would be XnY. _____ 17. A normal female’s genotype would be XNXN or XNXn. _____ 18. A normal female’s genotype ...
Document
... CovO,P = 1/2 VA + 1/2 Cov (A,D) + 1/2 Cov (A,EP ) + Cov (A,EO ) + Cov (D,EO ) + Cov (EP,EO ) ...
... CovO,P = 1/2 VA + 1/2 Cov (A,D) + 1/2 Cov (A,EP ) + Cov (A,EO ) + Cov (D,EO ) + Cov (EP,EO ) ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.