Human Genetics
... the alleles that we inherit are shown or expressed. Some alleles, the dominant ones, cover the expression of the recessive alleles. The recessive alleles don’t disappear. They may show up in future generations when not paired with a dominant allele. When the same allele for a single gene is on both ...
... the alleles that we inherit are shown or expressed. Some alleles, the dominant ones, cover the expression of the recessive alleles. The recessive alleles don’t disappear. They may show up in future generations when not paired with a dominant allele. When the same allele for a single gene is on both ...
Gene Interaction that produces novel Phenotype
... 4.4 GENE INTERACTION TAKES PLACE WHEN GENES AT MULTIPLE LOCI DETERMINE A SINGLE PHENOTYPE • Gene interaction: Effects of genes at one locus depend on the presence of genes at other loci. • Gene interaction that produces novel phenotypes. • Fig. 4.17 ...
... 4.4 GENE INTERACTION TAKES PLACE WHEN GENES AT MULTIPLE LOCI DETERMINE A SINGLE PHENOTYPE • Gene interaction: Effects of genes at one locus depend on the presence of genes at other loci. • Gene interaction that produces novel phenotypes. • Fig. 4.17 ...
Active GE relation
... 3.1 The Biology of Heredity • The first 22 pairs of chromosomes are autosomes and the 23rd pair is sex chromosomes • Genotype is one’s complete set of genes and phenotype is one’s physical, behavioral, and psychological features ...
... 3.1 The Biology of Heredity • The first 22 pairs of chromosomes are autosomes and the 23rd pair is sex chromosomes • Genotype is one’s complete set of genes and phenotype is one’s physical, behavioral, and psychological features ...
Introduction - GEOCITIES.ws
... An organism with two identical alleles for a character is homozygous for that character. Organisms with two different alleles for a character is heterozygous for that character. A description of an organism’s traits is its phenotype. A description of its genetic makeup is its genotype. Two ...
... An organism with two identical alleles for a character is homozygous for that character. Organisms with two different alleles for a character is heterozygous for that character. A description of an organism’s traits is its phenotype. A description of its genetic makeup is its genotype. Two ...
Life Science vocabulary
... clone An offspring produced by asexual reproduction that is genetically identifcal, either naturally or through artificial processes. egg cell A cell produced by a female that contains half of the number of chromosomes present in other body cells. A female reproductive cell. fertilization The union ...
... clone An offspring produced by asexual reproduction that is genetically identifcal, either naturally or through artificial processes. egg cell A cell produced by a female that contains half of the number of chromosomes present in other body cells. A female reproductive cell. fertilization The union ...
Unit 6 Heredity Chp 14 Mendelian Genetics Notes
... Mendel repeated the dihybrid cross experiment for other pairs of characters and always observed a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ration in the F2 generation. ...
... Mendel repeated the dihybrid cross experiment for other pairs of characters and always observed a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ration in the F2 generation. ...
Flip Folder 5 KEY - Madison County Schools
... “sexual” characteristics we normally see in individuals. The “sexual” traits are missing because there is no second sex chromosome to help create those traits. These individuals are usually ...
... “sexual” characteristics we normally see in individuals. The “sexual” traits are missing because there is no second sex chromosome to help create those traits. These individuals are usually ...
Population Genetics
... The Hardy-Weinberg Law • This law states an equilibrium of allele frequencies in a gene pool – p2 + 2pq+q2 = 1 – Remains in effect in each succeeding generation of a sexually reproducing population if five conditions are met. 1) No mutation: no allelic changes occur. 2) No gene flow: migration of a ...
... The Hardy-Weinberg Law • This law states an equilibrium of allele frequencies in a gene pool – p2 + 2pq+q2 = 1 – Remains in effect in each succeeding generation of a sexually reproducing population if five conditions are met. 1) No mutation: no allelic changes occur. 2) No gene flow: migration of a ...
Chapter 2
... o the base change does not change the sequence or amount of protein, or o because the change in protein sequence has no effect. Leaky mutations do affect the function of the gene product, but are not revealed in the phenotype because sufficient activity remains. ...
... o the base change does not change the sequence or amount of protein, or o because the change in protein sequence has no effect. Leaky mutations do affect the function of the gene product, but are not revealed in the phenotype because sufficient activity remains. ...
Mendelian inheritance
... sequences) of the same gene or genetic locus. Often called A,B or A,a. • Polymorphic: Polymorphic loci have several different alleles. At non-‐polymorphic loci, there is no variation from person to person. ...
... sequences) of the same gene or genetic locus. Often called A,B or A,a. • Polymorphic: Polymorphic loci have several different alleles. At non-‐polymorphic loci, there is no variation from person to person. ...
230-Evolution III
... DEFINITION* -- ALL of the genes AND alleles in a population taking into account their frequency It is the total supply of genetic units available to form the next generation Not possible to study the whole gene pool Will look at a “mini” gene pool (for the gene “A”) Only two alleles: A and a 3 ...
... DEFINITION* -- ALL of the genes AND alleles in a population taking into account their frequency It is the total supply of genetic units available to form the next generation Not possible to study the whole gene pool Will look at a “mini” gene pool (for the gene “A”) Only two alleles: A and a 3 ...
Use a Venn diagram to compare and contrast sexual and asexual
... found: genes DNA chromosomes nucleus ...
... found: genes DNA chromosomes nucleus ...
Laboratory #4: Pedigree Exercises Single
... (or variant) will have a different DNA sequence and is considered mutant. Depending on the different alleles being studied, the wild-type (or normal allele) can either be recessive or dominant. An individual human has two copies of each gene, with one copy coming from the mother and the other coming ...
... (or variant) will have a different DNA sequence and is considered mutant. Depending on the different alleles being studied, the wild-type (or normal allele) can either be recessive or dominant. An individual human has two copies of each gene, with one copy coming from the mother and the other coming ...
Gregor Mendel - BHMS
... Only 1 _____________ cell is needed Parent divides by ________________ Daughter cells are __________ __________ copies of parent cell Most cells in ___________________ and most single celled organisms reproduce this way Sexual Reproduction ...
... Only 1 _____________ cell is needed Parent divides by ________________ Daughter cells are __________ __________ copies of parent cell Most cells in ___________________ and most single celled organisms reproduce this way Sexual Reproduction ...
File - Paxson Science
... Using the class as a sample population, the allele frequency of a gene controlling the ability to taste the chemical PTC (phenylthiocarbamide) could be estimated. A bittertaste reaction to PTC is evidence of the presence of a dominant allele in either the homozygous condition (AA) or the heterozygou ...
... Using the class as a sample population, the allele frequency of a gene controlling the ability to taste the chemical PTC (phenylthiocarbamide) could be estimated. A bittertaste reaction to PTC is evidence of the presence of a dominant allele in either the homozygous condition (AA) or the heterozygou ...
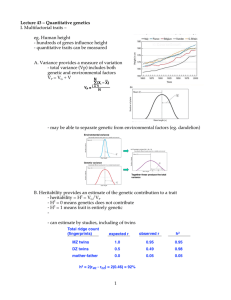
1 Lecture 43 â Quantitative genetics I. Multifactorial traits â eg
... B. Heritability provides an estimate of the genetic contribution to a trait - heritability = H2 = VG/VP - H2 = 0 means genetics does not contribute - H2 = 1 means trait is entirely genetic - can estimate by studies, including of twins ...
... B. Heritability provides an estimate of the genetic contribution to a trait - heritability = H2 = VG/VP - H2 = 0 means genetics does not contribute - H2 = 1 means trait is entirely genetic - can estimate by studies, including of twins ...
Human Genetics Class Survey Data Sheet
... the genetic makeup of the parents. BI3. a. Students know how to predict the probable outcome of phenotypes in a genetic cross from the genotypes of the parents and mode of inheritance (autosomal or X-linked, dominant or recessive). BI3. b. Students know the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws of seg ...
... the genetic makeup of the parents. BI3. a. Students know how to predict the probable outcome of phenotypes in a genetic cross from the genotypes of the parents and mode of inheritance (autosomal or X-linked, dominant or recessive). BI3. b. Students know the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws of seg ...
Factors that Cause Evolutionary Change
... select mates, often on the basis of their phenotypes. E: Increases the proportion of homozygous individuals in a population, but does not affect the frequency of alleles. D: Refers to random change in genetic variation from generation to generation due to chance (“experimental probability”). E: In s ...
... select mates, often on the basis of their phenotypes. E: Increases the proportion of homozygous individuals in a population, but does not affect the frequency of alleles. D: Refers to random change in genetic variation from generation to generation due to chance (“experimental probability”). E: In s ...
Heredity
... trait (eye color from mom & eye color from dad) • Traits are determined by alleles on the chromosomes • Each gene of a gene pair is called an allele • Inherited traits are determined by the alleles on the chromosome ...
... trait (eye color from mom & eye color from dad) • Traits are determined by alleles on the chromosomes • Each gene of a gene pair is called an allele • Inherited traits are determined by the alleles on the chromosome ...
Les 3 Mendelian Genetics
... “Di” means “two” and the parent plants differ from each other by two different traits. In a dihybrid cross, will the two traits stay together in the next generation or will they be inherited independently of each other? ...
... “Di” means “two” and the parent plants differ from each other by two different traits. In a dihybrid cross, will the two traits stay together in the next generation or will they be inherited independently of each other? ...
Ch. 11 Intro to Genetics
... In certain varities of chickens, black and white feather colors are caused by codominant alleles. Thus the heterozygous phenotype, speckled black and white, is a result of the expression of both alleles ...
... In certain varities of chickens, black and white feather colors are caused by codominant alleles. Thus the heterozygous phenotype, speckled black and white, is a result of the expression of both alleles ...
monohybrid cross
... meaning single); that is, a cross between organisms that are heterozygous at a single genetic locus, for example, eye colour in blowflies and flower colour in snapdragons. ...
... meaning single); that is, a cross between organisms that are heterozygous at a single genetic locus, for example, eye colour in blowflies and flower colour in snapdragons. ...
DNA Test For Fluffies - Norwich Terrier Club of America
... “Fluffy is an autosomal recessive trait; therefore dogs that are carriers of the long hair mutation will appear to be normal but will likely pass on the … “fluffy” mutation 50% of the time.” Autosomal recessive means that two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the trait (or d ...
... “Fluffy is an autosomal recessive trait; therefore dogs that are carriers of the long hair mutation will appear to be normal but will likely pass on the … “fluffy” mutation 50% of the time.” Autosomal recessive means that two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the trait (or d ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.