use of genomic tools to discover the cause of
... given to all outside sources. I understand that I am solely responsible for obtaining any needed copyright permissions. I have obtained needed written permission statement(s) from the owner(s) of each thirdparty copyrighted matter to be included in my work, allowing electronic distribution (if such ...
... given to all outside sources. I understand that I am solely responsible for obtaining any needed copyright permissions. I have obtained needed written permission statement(s) from the owner(s) of each thirdparty copyrighted matter to be included in my work, allowing electronic distribution (if such ...
Mendelian Genetics
... Cross Results F2 plants showed dominant-torecessive ratio that averaged 3:1 ...
... Cross Results F2 plants showed dominant-torecessive ratio that averaged 3:1 ...
Fruit Fly Dihybrid Cross (EXERCISE)
... linked). Mendel saw these laws at work in his pea plants, as he observed patterns in the number of each phenotype (appearance) in different offspring. These laws are utilized today to explain heredity (what traits are passed from one generation to the next) and variation (the differences between par ...
... linked). Mendel saw these laws at work in his pea plants, as he observed patterns in the number of each phenotype (appearance) in different offspring. These laws are utilized today to explain heredity (what traits are passed from one generation to the next) and variation (the differences between par ...
A genome-wide association study identifies an osteoarthritis
... authors and do not necessarily represent the official position or policies of the Tufts Clinical and Translational Science Institute. Supported by the Research Institute for Diseases in the Elderly (RIDE2) (014-93-015), The Netherlands Genomics Initiative (NGI)/Netherlands Organization for Scientifi ...
... authors and do not necessarily represent the official position or policies of the Tufts Clinical and Translational Science Institute. Supported by the Research Institute for Diseases in the Elderly (RIDE2) (014-93-015), The Netherlands Genomics Initiative (NGI)/Netherlands Organization for Scientifi ...
Human longevity is influenced by many genetic variants: evidence
... phenotype (at least one parent very long-lived) two variants (rs528161076 and rs75824829, on chromosome 7 and 9 respectively; see Supplementary Figures 8-9 for Locus Zoom plots) were found to be significant (p<5x10-8). rs75824829 may be anomalous as it is not in a “peak” of associations expected of ...
... phenotype (at least one parent very long-lived) two variants (rs528161076 and rs75824829, on chromosome 7 and 9 respectively; see Supplementary Figures 8-9 for Locus Zoom plots) were found to be significant (p<5x10-8). rs75824829 may be anomalous as it is not in a “peak” of associations expected of ...
Lab 2 - Variation Lab Website Introduction To Variation Goals
... variation in biological investigations • To be able to distinguish different types of variation, and understand the distribution of variation across different scales * – What types are evolutionarily significant? ...
... variation in biological investigations • To be able to distinguish different types of variation, and understand the distribution of variation across different scales * – What types are evolutionarily significant? ...
1 - F
... Identity in state (homozygosity) does not necessarily imply recent identity by descent. (Conversely ...) F for fixation index: homozygosity, or “fixation”, results from inbreeding. ...
... Identity in state (homozygosity) does not necessarily imply recent identity by descent. (Conversely ...) F for fixation index: homozygosity, or “fixation”, results from inbreeding. ...
View PDF - Genetics
... into adult flies is increased when the sperms used in fertilizing the females have been previously treated with ionizing radiation. It is generally believed that these induced failures of development are due to “dominant-lethal” changes in the genetic material of the treated sperms. These changes ha ...
... into adult flies is increased when the sperms used in fertilizing the females have been previously treated with ionizing radiation. It is generally believed that these induced failures of development are due to “dominant-lethal” changes in the genetic material of the treated sperms. These changes ha ...
Chromosomal Basis of Heredity
... genes act as if found on separate chromosomes and are inherited independently. • In fact, several genes studies by Mendel are located on the same chromosome. • For example, seed color and flower color are far enough apart that linkage is not observed. • Plant height and pod shape should show linkage ...
... genes act as if found on separate chromosomes and are inherited independently. • In fact, several genes studies by Mendel are located on the same chromosome. • For example, seed color and flower color are far enough apart that linkage is not observed. • Plant height and pod shape should show linkage ...
IGA 8/e Chapter 4
... 10. Eight phenotypic classes are expected for three autosomal genes, whether or not they are linked, when all three genes have simple dominant-recessive relationships among their alleles. The general formula for the number of expected phenotypes is 2n , where n is the number of genes being studied. ...
... 10. Eight phenotypic classes are expected for three autosomal genes, whether or not they are linked, when all three genes have simple dominant-recessive relationships among their alleles. The general formula for the number of expected phenotypes is 2n , where n is the number of genes being studied. ...
Pairing of homologous regions in the mouse genome is associated
... larger regions of the chromosomes would come into close proximity, we used whole chromosome painting together with probes marking the KvDMR region and a region near the centromeric end of chromosome 7. Most nuclei showed two separate chromosome 7 domains which tended to be positioned away from each ...
... larger regions of the chromosomes would come into close proximity, we used whole chromosome painting together with probes marking the KvDMR region and a region near the centromeric end of chromosome 7. Most nuclei showed two separate chromosome 7 domains which tended to be positioned away from each ...
Distinct genetic regulation of progression of diabetes and renal
... Longitudinal linkage changes were also evident on chromosome 5, although the pattern was more complex. A peak with a LOD of 4.7 at D5Mgh11 was identified at 3 mo of age. While this peak disappeared at 6 mo, a biphasic peak mapping to a similar region emerged at 9 mo of age (LOD of 4.6 at D5Mit4 and ...
... Longitudinal linkage changes were also evident on chromosome 5, although the pattern was more complex. A peak with a LOD of 4.7 at D5Mgh11 was identified at 3 mo of age. While this peak disappeared at 6 mo, a biphasic peak mapping to a similar region emerged at 9 mo of age (LOD of 4.6 at D5Mit4 and ...
slides
... • Mitochondria are only passed along from the mother, because they are present in the egg at fer/liza/on, while the sperm contributes only its nucleus to the egg (no cytoplasm, and thus no organelles ...
... • Mitochondria are only passed along from the mother, because they are present in the egg at fer/liza/on, while the sperm contributes only its nucleus to the egg (no cytoplasm, and thus no organelles ...
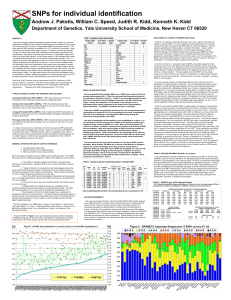
SNPs for individual identification
... 31 populations are given in Figure 1. These 31 are the larger populations more likely to be relevant in forensic settings, especially in the USA and Europe. Figure 1 shows the comparison of Fst values in the reduced set of 31 populations (blue circles) compared to the original set of 40 populations ...
... 31 populations are given in Figure 1. These 31 are the larger populations more likely to be relevant in forensic settings, especially in the USA and Europe. Figure 1 shows the comparison of Fst values in the reduced set of 31 populations (blue circles) compared to the original set of 40 populations ...
Problem Sets - MIT Biology
... Part e) is a proper complementation test that clearly shows that wild-type alleles of A and B will rescue the mutant phenotype if the mutations are on different genes but not if they are on the same gene. Other crosses are not complementation tests because, either, mutations giving dominant phenotyp ...
... Part e) is a proper complementation test that clearly shows that wild-type alleles of A and B will rescue the mutant phenotype if the mutations are on different genes but not if they are on the same gene. Other crosses are not complementation tests because, either, mutations giving dominant phenotyp ...
The Advantages of Segregation and the Evolution of Sex
... allele k. As indicated by the first part of Equation 1, F measures the difference between the observed frequency of a genotype and its expected frequency at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. As indicated by the second part of Equation 1, F also measures whether homozygotes are more frequent (F ⬎ 0) or les ...
... allele k. As indicated by the first part of Equation 1, F measures the difference between the observed frequency of a genotype and its expected frequency at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. As indicated by the second part of Equation 1, F also measures whether homozygotes are more frequent (F ⬎ 0) or les ...
Chapter 6 GENETIC LINKAGE AND MAPPING IN EUKARYOTES
... In Chapter 2, we were introduced to Mendel’s laws of inheritance. According to these principles, we expect that two different genes will segregate and independently assort themselves during the process that creates gametes. After Mendel’s work was rediscovered at the turn of the twentieth century, c ...
... In Chapter 2, we were introduced to Mendel’s laws of inheritance. According to these principles, we expect that two different genes will segregate and independently assort themselves during the process that creates gametes. After Mendel’s work was rediscovered at the turn of the twentieth century, c ...
Bio II Ch 15 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... assortments of alleles not found in the parents. • If the seed color and seed coat genes were linked, we would expect the F1 offspring to produce only two types of gametes, YR and yr when the tetrads separate. • One homologous chromosome from a P generation parent carries the Y and R alleles on the ...
... assortments of alleles not found in the parents. • If the seed color and seed coat genes were linked, we would expect the F1 offspring to produce only two types of gametes, YR and yr when the tetrads separate. • One homologous chromosome from a P generation parent carries the Y and R alleles on the ...
of Gray Alpacas - North Sound Alpaca Association
... can include classic grays bred to non-gray animals with white markings. Such breedings will yield BEWs 25% of the time. It also means that some BEWs can actually make gray cria if they are bred to solid, non-white mates. Indeed, these BEWs out of classic grays should make classic grays 50% of the ti ...
... can include classic grays bred to non-gray animals with white markings. Such breedings will yield BEWs 25% of the time. It also means that some BEWs can actually make gray cria if they are bred to solid, non-white mates. Indeed, these BEWs out of classic grays should make classic grays 50% of the ti ...
Pedigrees
... Interpreting a Pedigree Chart 2. Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive. – If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. – If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. ...
... Interpreting a Pedigree Chart 2. Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive. – If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. – If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. ...
chapter 14 notes
... parental generation has identical alleles, PP or pp. Gametes (circles) each contain only one allele for the flower-color gene. In this case, every gamete produced by one parent has the same allele. ...
... parental generation has identical alleles, PP or pp. Gametes (circles) each contain only one allele for the flower-color gene. In this case, every gamete produced by one parent has the same allele. ...
video slide - Fayetteville State University
... parental generation has identical alleles, PP or pp. Gametes (circles) each contain only one allele for the flower-color gene. In this case, every gamete produced by one parent has the same allele. ...
... parental generation has identical alleles, PP or pp. Gametes (circles) each contain only one allele for the flower-color gene. In this case, every gamete produced by one parent has the same allele. ...
Mendel & the Gene Idea
... parental generation has identical alleles, PP or pp. Gametes (circles) each contain only one allele for the flower-color gene. In this case, every gamete produced by one parent has the same allele. ...
... parental generation has identical alleles, PP or pp. Gametes (circles) each contain only one allele for the flower-color gene. In this case, every gamete produced by one parent has the same allele. ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.