Answers - Dr Terry Dwyer National Curriculum mathematics and
... a) CTG is coded to leucine and GTG is coded to valine b) If CTG, part of the gene sequence for haemoglobin, changes to GTG then haemoglobin may not be properly sequenced and may not perform its function properly. 6 Chromosomes are tightly coiled long strands of DNA. Chromosomes are found in the ...
... a) CTG is coded to leucine and GTG is coded to valine b) If CTG, part of the gene sequence for haemoglobin, changes to GTG then haemoglobin may not be properly sequenced and may not perform its function properly. 6 Chromosomes are tightly coiled long strands of DNA. Chromosomes are found in the ...
Genetic simulation
... Single Allele Traits 1. Determine which partner will toss for the male and which will toss for the female. Each of you will get a penny. 2. Have the parter who is representing the male flip the coin, if the coin lands heads up, the offspring is female, if tails, then the offspring is male. What sex ...
... Single Allele Traits 1. Determine which partner will toss for the male and which will toss for the female. Each of you will get a penny. 2. Have the parter who is representing the male flip the coin, if the coin lands heads up, the offspring is female, if tails, then the offspring is male. What sex ...
relates Mendel`s discoveries to actual behavior of chromosomes
... species of fruit flies (to take advantage of its ability to produce hundreds of offspring from one mating, and its having only four pairs of chromosomes) A. Wild Type- the normal phenotype for a character (such as red eyes in a fruit fly) B. Mutant Phenotype- a trait that is alternative tot he wild ...
... species of fruit flies (to take advantage of its ability to produce hundreds of offspring from one mating, and its having only four pairs of chromosomes) A. Wild Type- the normal phenotype for a character (such as red eyes in a fruit fly) B. Mutant Phenotype- a trait that is alternative tot he wild ...
Mathematical Modeling of the Hardy
... The RAND function returns random numbers between 0 and 1 in decimal format. This is a powerful feature of spreadsheets. It allows us to enter a sense of randomness to our calculations if it is appropriate — and here it is when we are “randomly” choosing gametes from a gene pool. Go ahead and delete ...
... The RAND function returns random numbers between 0 and 1 in decimal format. This is a powerful feature of spreadsheets. It allows us to enter a sense of randomness to our calculations if it is appropriate — and here it is when we are “randomly” choosing gametes from a gene pool. Go ahead and delete ...
December 2013 Newsletter - Wynnum Redlands Budgerigar Society
... parent is paired with another identical chromosome from the other parent. Because they are identical, they share the same gene arrangement and have the same loci for various characteristics. With recessive characteristics, each gene from the expression needs to be matched by another identical gene o ...
... parent is paired with another identical chromosome from the other parent. Because they are identical, they share the same gene arrangement and have the same loci for various characteristics. With recessive characteristics, each gene from the expression needs to be matched by another identical gene o ...
Week 4 - Familiarization with Drosophila Fruit Flies v v+ Cy Cy+
... them in the laboratory, 2) they have short generation times (2 weeks), 3) they have a few, large chromosomes. Today we will familiarize ourselves with these flies and we will study the mode of inheritance of several mutant forms of them. Some rules for naming alleles and genotypes in flies In Drosop ...
... them in the laboratory, 2) they have short generation times (2 weeks), 3) they have a few, large chromosomes. Today we will familiarize ourselves with these flies and we will study the mode of inheritance of several mutant forms of them. Some rules for naming alleles and genotypes in flies In Drosop ...
KEY
... c. purple flowers must be considered the "wild type" phenotype d. a plant with purple flowers exhibits heterozygote advantage e. more than one of the above is true (Codominance means that two different products, both functional, are being produced. Incomplete dominance would mean that only half the ...
... c. purple flowers must be considered the "wild type" phenotype d. a plant with purple flowers exhibits heterozygote advantage e. more than one of the above is true (Codominance means that two different products, both functional, are being produced. Incomplete dominance would mean that only half the ...
Face Lab
... Why do people, even closely related people, look slightly different from each other? The reason for these differences in physical characteristics (called phenotypes) is the different combination of genes possessed by each individual. To illustrate the tremendous variety possible when you begin to co ...
... Why do people, even closely related people, look slightly different from each other? The reason for these differences in physical characteristics (called phenotypes) is the different combination of genes possessed by each individual. To illustrate the tremendous variety possible when you begin to co ...
Signatures of Selection in the Human Olfactory Receptor OR5I1 Gene
... continental regions (fig. 2). Around half of the SNPs analyzed appeared to have derived frequencies equal or greater than 85% across all populations, whereas rs2457239 was found to be fixed. FST values between the 39 populations analyzed were rather low (fig. 1), with an average across SNPs of aroun ...
... continental regions (fig. 2). Around half of the SNPs analyzed appeared to have derived frequencies equal or greater than 85% across all populations, whereas rs2457239 was found to be fixed. FST values between the 39 populations analyzed were rather low (fig. 1), with an average across SNPs of aroun ...
Ch 15: Sex Determination & Sex Linkage
... Sex-linked genes exhibit unique patterns of inheritance ● In humans and other animals, there is a chromosomal basis of sex determination ...
... Sex-linked genes exhibit unique patterns of inheritance ● In humans and other animals, there is a chromosomal basis of sex determination ...
Units&Targets
... from these longer hairpin structures by the RNase III enzyme Dicer. Drosha acts in the nucleus, cleaving the pri-miRNA near the base of the hairpin stem to yield the pre-miRNA sequence. The premiRNA is then exported to the cytoplasm where the stem is cleaved by Dicer to produce a miRNA duplex. One s ...
... from these longer hairpin structures by the RNase III enzyme Dicer. Drosha acts in the nucleus, cleaving the pri-miRNA near the base of the hairpin stem to yield the pre-miRNA sequence. The premiRNA is then exported to the cytoplasm where the stem is cleaved by Dicer to produce a miRNA duplex. One s ...
Transmission-ratio distortion in the Framingham Heart Study | BMC
... This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
... This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
Phenote - National Center for Biomedical Ontology
... Genetic context field Term info navigation Pheno xml writeback ...
... Genetic context field Term info navigation Pheno xml writeback ...
Speciation - eduBuzz.org
... Non-random mating This increases the number of homozygous individuals (but does not change the frequency of the alleles) Inbreeding is a common form of this. In humans this can increase the chances of the offspring inheriting a disease caused by a ...
... Non-random mating This increases the number of homozygous individuals (but does not change the frequency of the alleles) Inbreeding is a common form of this. In humans this can increase the chances of the offspring inheriting a disease caused by a ...
Abbreviated Instructions for using BioQUEST
... VGLII is a computer simulation of genetics. The computer randomly picks one or more characters with one or more traits. It then randomly chooses how each trait is inherited. That way, each time you start the program, you get a different problem (also, every group will get a different problem). Final ...
... VGLII is a computer simulation of genetics. The computer randomly picks one or more characters with one or more traits. It then randomly chooses how each trait is inherited. That way, each time you start the program, you get a different problem (also, every group will get a different problem). Final ...
Chapter 6 - Gregor Mendel and Genetics
... Why does this happen? In a Bb heterozygote, only the B allele is expressed, so the b allele doesn’t influence the phenotype. In general, when only one of two alleles is expressed in the phenotype, the expressed allele is called the dominant allele. The allele that isn’t expressed is called the recess ...
... Why does this happen? In a Bb heterozygote, only the B allele is expressed, so the b allele doesn’t influence the phenotype. In general, when only one of two alleles is expressed in the phenotype, the expressed allele is called the dominant allele. The allele that isn’t expressed is called the recess ...
Chromosome Number
... The sperm may carry either and X or Y If the sperm donates an X in fertilization, the zygote will be female If the sperm donates a Y in fertilization, the zygote will be male Therefore, the sex of all humans is determined by the sperm donated by their father ...
... The sperm may carry either and X or Y If the sperm donates an X in fertilization, the zygote will be female If the sperm donates a Y in fertilization, the zygote will be male Therefore, the sex of all humans is determined by the sperm donated by their father ...
Article A Molecular Evolutionary Reference for the Human Variome
... (30%) of deleterious alleles seen in the collection of private variants. This overall trend may be explained by the action of negative selection, which would prevent deleterious alleles from rising to high frequencies. The effect of negative selection can be directly observed by comparing EPs of min ...
... (30%) of deleterious alleles seen in the collection of private variants. This overall trend may be explained by the action of negative selection, which would prevent deleterious alleles from rising to high frequencies. The effect of negative selection can be directly observed by comparing EPs of min ...
Fun Bugs!
... Background: Genes contain the information that determines traits in living things. Each version of a gene is called an allele. Genes come in pairs on homologous chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis and sort independently of each other. This mixture of genes makes new indi ...
... Background: Genes contain the information that determines traits in living things. Each version of a gene is called an allele. Genes come in pairs on homologous chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis and sort independently of each other. This mixture of genes makes new indi ...
Inheritance PPT
... to be considered when mating animals. •For example, consider that cattle can be horned or polled and white-faced or red-faced. •The horns and red-faced coloring are recessive traits. ...
... to be considered when mating animals. •For example, consider that cattle can be horned or polled and white-faced or red-faced. •The horns and red-faced coloring are recessive traits. ...
Contrasting Effects of ENU Induced Embryonic Lethal Mutations of
... with each lethal allele exhibit a dysmyelinating phenotype similar to qk v homozygotes (Justice and Bode, 1988), with the exception of the qk l-1 allele, which exhibits a transient dysmyelinating phenotype (Shedlovsky et al., 1988). Table 1 summarizes the different alleles of the quaking gene and th ...
... with each lethal allele exhibit a dysmyelinating phenotype similar to qk v homozygotes (Justice and Bode, 1988), with the exception of the qk l-1 allele, which exhibits a transient dysmyelinating phenotype (Shedlovsky et al., 1988). Table 1 summarizes the different alleles of the quaking gene and th ...
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 4 GENETICS 1. Cattle may be red or
... 17.Albinism, is inherited through double recessive genes. If A stands for normal skin colour and a the recessive character, which of these parental crosses would produce 25% albino offspring? A. AA x Aa B. AA x aa C. Aa x Aa D. aa x aa 18. Red flowered peas were crossed with white flowered peas. The ...
... 17.Albinism, is inherited through double recessive genes. If A stands for normal skin colour and a the recessive character, which of these parental crosses would produce 25% albino offspring? A. AA x Aa B. AA x aa C. Aa x Aa D. aa x aa 18. Red flowered peas were crossed with white flowered peas. The ...
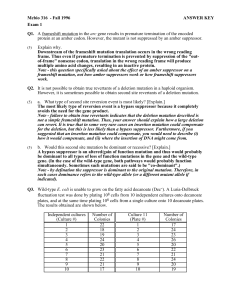
Mcbio 316 - Fall 1996 ANSWER KEY Exam 1 Q1. A frameshift
... avoids the need for the gene product. Note - failure to obtain true revertants indicates that the deletion mutation described is not a simple frameshift mutation. Thus, your answer should explain how a large deletion can revert. It is true that in some very rare cases an insertion mutation could com ...
... avoids the need for the gene product. Note - failure to obtain true revertants indicates that the deletion mutation described is not a simple frameshift mutation. Thus, your answer should explain how a large deletion can revert. It is true that in some very rare cases an insertion mutation could com ...
Basic molecular genetics for epidemiologists
... general increase in the number of epidemiological research articles that apply basic science methods in their studies, resulting in what is known as both molecular and genetic epidemiology, is evident. Actually, genetics has come into the epidemiological scene with plenty of new sophisticated concep ...
... general increase in the number of epidemiological research articles that apply basic science methods in their studies, resulting in what is known as both molecular and genetic epidemiology, is evident. Actually, genetics has come into the epidemiological scene with plenty of new sophisticated concep ...
1 Chromosome Mapping in Eukaryotes
... P of a single exchange between A and B and B and C is directly related to the physical distance between them ...
... P of a single exchange between A and B and B and C is directly related to the physical distance between them ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.