11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population
... • Mutation is a random change in the DNA of a gene. – can form new allele – can be passed on to offspring if in reproductive cells ...
... • Mutation is a random change in the DNA of a gene. – can form new allele – can be passed on to offspring if in reproductive cells ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population
... • Mutation is a random change in the DNA of a gene. – can form new allele – can be passed on to offspring if in reproductive cells ...
... • Mutation is a random change in the DNA of a gene. – can form new allele – can be passed on to offspring if in reproductive cells ...
Evolution Quiz Week 3
... 1) Which is not one of the 4 steps in evolution by natural selection? a. Variation among individuals b. Different survival/reproduction between individuals c. Change in genetic composition of population d. Adapting organisms to a future environment e. Evolution 2) What is relative fitness? a. The nu ...
... 1) Which is not one of the 4 steps in evolution by natural selection? a. Variation among individuals b. Different survival/reproduction between individuals c. Change in genetic composition of population d. Adapting organisms to a future environment e. Evolution 2) What is relative fitness? a. The nu ...
Chapter One Outline
... CHAPTER 22-24 OUTLINE part 1 EVOLUTION by Natural Selection depends on FIVE factors: More offspring are produced than can survive to reproduce The characteristics of living things differ among individuals of same species. Many differences are the result of heritable genetic differences Some ...
... CHAPTER 22-24 OUTLINE part 1 EVOLUTION by Natural Selection depends on FIVE factors: More offspring are produced than can survive to reproduce The characteristics of living things differ among individuals of same species. Many differences are the result of heritable genetic differences Some ...
Ertertewt ertwetr
... Some mutations will cause a change in an animal’s phenotype. This change might alter its ability to survive in 2 ways. 1. Beneficial mutation 2. Harmful mutation ...
... Some mutations will cause a change in an animal’s phenotype. This change might alter its ability to survive in 2 ways. 1. Beneficial mutation 2. Harmful mutation ...
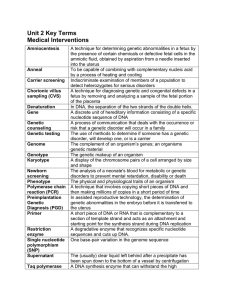
Unit 2 Terms
... The physical and physiological traits of an organism A technique that involves copying short pieces of DNA and then making millions of copies in a short period of time In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred to the uterus ...
... The physical and physiological traits of an organism A technique that involves copying short pieces of DNA and then making millions of copies in a short period of time In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred to the uterus ...
Ertertewt ertwetr - Campbell County Schools
... Some mutations will cause a change in an animal’s phenotype. This change might alter its ability to survive in 2 ways. 1. Beneficial mutation 2. Harmful mutation ...
... Some mutations will cause a change in an animal’s phenotype. This change might alter its ability to survive in 2 ways. 1. Beneficial mutation 2. Harmful mutation ...
BIO 1102 - Makerere University Courses
... 6 Epistasis and gene interactions; types of epistasis, multiple alleles, linkage and lethal genes. 7 Chromosome and gene mutations; causes, classification, types, advantages and disadvantages 8 Sex linked and limited traits. 9 Cloning (gene and organism cloning). 10 Polygenic inheritance (punnett sq ...
... 6 Epistasis and gene interactions; types of epistasis, multiple alleles, linkage and lethal genes. 7 Chromosome and gene mutations; causes, classification, types, advantages and disadvantages 8 Sex linked and limited traits. 9 Cloning (gene and organism cloning). 10 Polygenic inheritance (punnett sq ...
Midterm exam questions pool is here.
... postzygotic reproductive incompatibilities, DM incompatibilities, Haldane’s rule. Describe two different mechanisms that can maintain genetic polymorphism in a population. Describe two population-genetics processes, which can lead to the accumulation of genetic differences in allopatry. If you have ...
... postzygotic reproductive incompatibilities, DM incompatibilities, Haldane’s rule. Describe two different mechanisms that can maintain genetic polymorphism in a population. Describe two population-genetics processes, which can lead to the accumulation of genetic differences in allopatry. If you have ...
word - marric
... 54. Using the Punnett square above, box 4 should contain which genotype? 55. How many of the offspring in the Punnett square above would be hemophiliacs? 56. In fruit flies, the gene for red eyes (R) is dominant and the gene for sepia eyes (r) is recessive. What are the possible combinations of gene ...
... 54. Using the Punnett square above, box 4 should contain which genotype? 55. How many of the offspring in the Punnett square above would be hemophiliacs? 56. In fruit flies, the gene for red eyes (R) is dominant and the gene for sepia eyes (r) is recessive. What are the possible combinations of gene ...
File
... a population remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. ...
... a population remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. ...
File
... Genes in general are about 1000 bases long. Therefore, you will see variation in the sequences from individual to individual. The general rule is that individuals that are the same species will have DNA sequences that are very ...
... Genes in general are about 1000 bases long. Therefore, you will see variation in the sequences from individual to individual. The general rule is that individuals that are the same species will have DNA sequences that are very ...
27. The micro-evolution of FMDV
... can be ruled out. High levels of epistasis will increase the role for quasi-species dynamics in the ‘within-individual’ evolution of FMDV but we know next to nothing about either the intensity or genomic scale of epistasis. Evidence is accumulating that recombination rates may be sufficiently high t ...
... can be ruled out. High levels of epistasis will increase the role for quasi-species dynamics in the ‘within-individual’ evolution of FMDV but we know next to nothing about either the intensity or genomic scale of epistasis. Evidence is accumulating that recombination rates may be sufficiently high t ...
Natural Selection and Evidence to Support Evolution
... was the mechanisms proposed by Charles Darwin to explain how evolution (change over time in organisms) takes place • Key ideas of natural selection: – There is a limited amount of resources – Differential Survival Rate – Those better fit for environment produce more offspring – Over time frequency o ...
... was the mechanisms proposed by Charles Darwin to explain how evolution (change over time in organisms) takes place • Key ideas of natural selection: – There is a limited amount of resources – Differential Survival Rate – Those better fit for environment produce more offspring – Over time frequency o ...
Name________________ Where does variation come from
... _____________, there is _______________ or differences within the populations genes. ________________________: process by which organisms with traits best suited to the environment are most likely to survive, reproduce and pass on their genes to next generation. There is a certain amount of genetic ...
... _____________, there is _______________ or differences within the populations genes. ________________________: process by which organisms with traits best suited to the environment are most likely to survive, reproduce and pass on their genes to next generation. There is a certain amount of genetic ...
Gene Linkage
... • Make a pedigree for the following family: • 3 generations, some members have the recessive trait of color blindness • Genotypes are written as XBXB – for female with normal vision, XBXb for a female who is normal but is a carrier for colorblind, and XbXb for a female who is colorblind; XBY for a ...
... • Make a pedigree for the following family: • 3 generations, some members have the recessive trait of color blindness • Genotypes are written as XBXB – for female with normal vision, XBXb for a female who is normal but is a carrier for colorblind, and XbXb for a female who is colorblind; XBY for a ...
LE 3
... DNA REPLICATION pg. 47 fig 3 -4 Involves the production of identical copies of DNA to pass genetic information to offspring. ...
... DNA REPLICATION pg. 47 fig 3 -4 Involves the production of identical copies of DNA to pass genetic information to offspring. ...
Population genetics is the study of evolution from a genetic
... 3- 5. Variations in genotype arise in three main ways. (1) __________________ results from flawed copies of individual genes. (2) __________________ is the reassociation of genes in a diploid individual. Recombination occurs during meiosis by the independent assortment of genes on nonhomologous, or ...
... 3- 5. Variations in genotype arise in three main ways. (1) __________________ results from flawed copies of individual genes. (2) __________________ is the reassociation of genes in a diploid individual. Recombination occurs during meiosis by the independent assortment of genes on nonhomologous, or ...
File
... serve no obvious function. Simple single-celled eukaryotes have relatively small amounts of such DNA, whereas the genomes of complex multicellular organisms, including humans, contain an absolute majority of DNA without an identified function. Protein-coding DNA only makes up 2% of the total human g ...
... serve no obvious function. Simple single-celled eukaryotes have relatively small amounts of such DNA, whereas the genomes of complex multicellular organisms, including humans, contain an absolute majority of DNA without an identified function. Protein-coding DNA only makes up 2% of the total human g ...
Natural selection at work File
... Two examples are peppered moth and mosquitoes. Peppered moth: in a heavily industrialized regions, moth colour changed from white to brown. A selective agent such as a bird can easily spot them against the white lichen covering the trees. But when peppered moth cover a tree trunk that has been black ...
... Two examples are peppered moth and mosquitoes. Peppered moth: in a heavily industrialized regions, moth colour changed from white to brown. A selective agent such as a bird can easily spot them against the white lichen covering the trees. But when peppered moth cover a tree trunk that has been black ...