chapter 20: dna technology and genomics
... This is simply the tool that will carry the gene of interest. b) It is usually DNA that will carry the new or foreign gene into whatever cell we want the gene to be expressed. ...
... This is simply the tool that will carry the gene of interest. b) It is usually DNA that will carry the new or foreign gene into whatever cell we want the gene to be expressed. ...
Cystic Fibrosis - Bellarmine University
... Now they apply Pilocarpene to the skin – wait 30 minutes - and measure chloride levels. ...
... Now they apply Pilocarpene to the skin – wait 30 minutes - and measure chloride levels. ...
Short Exam Questions
... 56. Name the scientists who are associated with the Theory of Natural Selection and refer to any one observation that prompted its development. 57. What is meant by evolution? 58. Outline the evidence for evolution from any one named source. 59. What is meant by genetic engineering? 60. State two ap ...
... 56. Name the scientists who are associated with the Theory of Natural Selection and refer to any one observation that prompted its development. 57. What is meant by evolution? 58. Outline the evidence for evolution from any one named source. 59. What is meant by genetic engineering? 60. State two ap ...
Classification of Microorganisms
... • Can distinguish between closely related strains • While rRNA gene sequence analysis is capable of identifying organisms to the genus level, MLST is useful for identifying organisms to the species level and below. MLST is not useful above the species level because is it too sensitive • This techniq ...
... • Can distinguish between closely related strains • While rRNA gene sequence analysis is capable of identifying organisms to the genus level, MLST is useful for identifying organisms to the species level and below. MLST is not useful above the species level because is it too sensitive • This techniq ...
unit 5 study guide 15
... What are the two major differences between sexual and asexual reproduction? Two organisms genetic material is combined and creates a new and genetically different offspring. What type of reproduction allows this genetic diversity? ...
... What are the two major differences between sexual and asexual reproduction? Two organisms genetic material is combined and creates a new and genetically different offspring. What type of reproduction allows this genetic diversity? ...
Chapter 9: Patterns of Inheritance
... Genetics is the study of how genes are inherited AND how they influence the physical characteristics of each individual. Genetics relates to 2 basic processes: 1) the distribution of genes into haploid gametes • i.e., by meiosis ...
... Genetics is the study of how genes are inherited AND how they influence the physical characteristics of each individual. Genetics relates to 2 basic processes: 1) the distribution of genes into haploid gametes • i.e., by meiosis ...
Allopatric Speciation
... lighter individuals in the population on the right. Notice that a mutation for spotting has arisen in the population on the right. After an additional 20 generations, the color difference has continued to evolve, and the mutation for spotting is spreading among the lizards in the population on the r ...
... lighter individuals in the population on the right. Notice that a mutation for spotting has arisen in the population on the right. After an additional 20 generations, the color difference has continued to evolve, and the mutation for spotting is spreading among the lizards in the population on the r ...
Introduction to Genetics
... The reassortment of chromosomes and the genetic information that they carry by segregation and crossing over. For example: In humans, n = 23, so the number of different gametes that can be produced is 223 (more than 8 million). When fertilization occurs, 223 x 223, or 70 trillion different z ...
... The reassortment of chromosomes and the genetic information that they carry by segregation and crossing over. For example: In humans, n = 23, so the number of different gametes that can be produced is 223 (more than 8 million). When fertilization occurs, 223 x 223, or 70 trillion different z ...
PDF Ch. 18: Regulation of Gene Expression AP Reading Guide
... 28. In prokaryotes, functionally related genes are usually clustered in a single operon. What has been found to be the case in eukaryotes? 29. Operons have not been found in eukaryotic cells, and the genes coding for the enzymes of a particular metabolic pathway are often scattered over different ch ...
... 28. In prokaryotes, functionally related genes are usually clustered in a single operon. What has been found to be the case in eukaryotes? 29. Operons have not been found in eukaryotic cells, and the genes coding for the enzymes of a particular metabolic pathway are often scattered over different ch ...
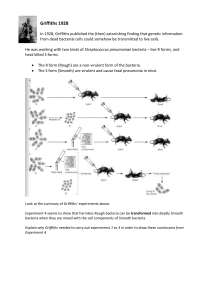
DNA experiments exercise
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Powerpoint show for lecture
... of genotype and environment. Genotype: the constitution of alleles at any gene in an individual. Gene: continuous stretch of DNA sufficient to encode a messenger RNA or a functional RNA. Locus: A region of a chromosome, usually for a single gene. Messenger RNA: the RNA message for a single protein. ...
... of genotype and environment. Genotype: the constitution of alleles at any gene in an individual. Gene: continuous stretch of DNA sufficient to encode a messenger RNA or a functional RNA. Locus: A region of a chromosome, usually for a single gene. Messenger RNA: the RNA message for a single protein. ...
src
... It was found that cDNAsarc binds to DNA from all vertebrate classes, including mammals, but not to the DNA from sea urchins, fruit flies, or bacteria. Conclusion: The src gene is not only present in the RNA of the ASV genome and the genome of the chicken cells it can infect, but a homologous gene is ...
... It was found that cDNAsarc binds to DNA from all vertebrate classes, including mammals, but not to the DNA from sea urchins, fruit flies, or bacteria. Conclusion: The src gene is not only present in the RNA of the ASV genome and the genome of the chicken cells it can infect, but a homologous gene is ...
Chapter 11 Notes: Mendelian Genetics
... a. There are two types of chromosomes. i. ___________________________: Of the 46 chromosomes, 44 of them (22 pairs of chromosomes) are called autosomes (______________________ chromosomes). ii. Sex chromosomes: The last two chromosomes are called the sex chromosomes because they determine the ...
... a. There are two types of chromosomes. i. ___________________________: Of the 46 chromosomes, 44 of them (22 pairs of chromosomes) are called autosomes (______________________ chromosomes). ii. Sex chromosomes: The last two chromosomes are called the sex chromosomes because they determine the ...
Name - Hightower Trail
... Which traits are multi-allelic (controlled by more than one allele)? Is trait expression purely genetic or can environment be involved? Heterozygous, homozygous, dominant and recessive mean:___ Genes, alleles, and traits are________ What happened when Mendel crossed purebred tall and short plants? W ...
... Which traits are multi-allelic (controlled by more than one allele)? Is trait expression purely genetic or can environment be involved? Heterozygous, homozygous, dominant and recessive mean:___ Genes, alleles, and traits are________ What happened when Mendel crossed purebred tall and short plants? W ...
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Chapter7
... available including P1-derived artificial chromosomes (PACs) that carry up to 300 kpb fragments, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) that carry fragments of 300 kpb and greater, and yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs, described in Chapter 1) that are able to accommodate 600-1400 kpb fragments. T ...
... available including P1-derived artificial chromosomes (PACs) that carry up to 300 kpb fragments, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) that carry fragments of 300 kpb and greater, and yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs, described in Chapter 1) that are able to accommodate 600-1400 kpb fragments. T ...
Document
... definition: MAPKKK cascade involved in transduction of transduction of mating pheromone signal, as described in mating pheromone signal, as described in Saccharomyces Saccharomyces. definition_reference: PMID:9561267 ...
... definition: MAPKKK cascade involved in transduction of transduction of mating pheromone signal, as described in mating pheromone signal, as described in Saccharomyces Saccharomyces. definition_reference: PMID:9561267 ...
HYRS_presentation
... Want to do science? High school students and early undergraduates can do great research that matters. iGEM is just one of many opportunities. ...
... Want to do science? High school students and early undergraduates can do great research that matters. iGEM is just one of many opportunities. ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet - Answers
... - Do all mutations result in a faulty protein? Why or why not? No, because if you make mRNA that codes for same amino acids, you will end up with the same protein. This happens because some codons code for the same aa. - What is trisomy 21? What is another name for this disease? Trisomy 21 occurs wh ...
... - Do all mutations result in a faulty protein? Why or why not? No, because if you make mRNA that codes for same amino acids, you will end up with the same protein. This happens because some codons code for the same aa. - What is trisomy 21? What is another name for this disease? Trisomy 21 occurs wh ...
ch14_sec1 NOTES
... original chromosome, but in a reverse direction. • A translocation occurs when a chromosome piece ends up in a completely different, nonhomologous chromosome. • A chromosomal mutation can move an entire gene to a ...
... original chromosome, but in a reverse direction. • A translocation occurs when a chromosome piece ends up in a completely different, nonhomologous chromosome. • A chromosomal mutation can move an entire gene to a ...
Comparative Gene Expression Analysis: Data Analysis Issues
... partitions (Strehl and Ghosh, 2002) – Measures of distance between partitions – Evaluate which clusters contribute most to the distance – Catch: Works only for the same data set (Correlation matrices for the two organisms in this case) ...
... partitions (Strehl and Ghosh, 2002) – Measures of distance between partitions – Evaluate which clusters contribute most to the distance – Catch: Works only for the same data set (Correlation matrices for the two organisms in this case) ...
userfiles/153/my files/23_lecture_presentation?id=3697
... (PKU) is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium given that: 1. The PKU gene mutation rate is low 2. Mate selection is random with respect to whether or not an individual is a carrier for the PKU allele 3. Natural selection can only act on rare homozygous individuals who do not follow dietary restrictions 4. ...
... (PKU) is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium given that: 1. The PKU gene mutation rate is low 2. Mate selection is random with respect to whether or not an individual is a carrier for the PKU allele 3. Natural selection can only act on rare homozygous individuals who do not follow dietary restrictions 4. ...
I. Down Syndrome - Plain Local Schools
... C. Inversion involves reversing a fragment of the original chromosome D. Translocation occurs when a fragment of one chromosome attaches to a non-homologous chromosome IV. Jumping Genes A. Single genes may move from one location to another in a chromosome or to a different chromosome B. This was dis ...
... C. Inversion involves reversing a fragment of the original chromosome D. Translocation occurs when a fragment of one chromosome attaches to a non-homologous chromosome IV. Jumping Genes A. Single genes may move from one location to another in a chromosome or to a different chromosome B. This was dis ...
Module 03_lecture
... Fraternal Twins • Twins who developed from separate eggs; the are genetically no more similar than other siblings, but they share a fetal environment • Called dizygotic twins ...
... Fraternal Twins • Twins who developed from separate eggs; the are genetically no more similar than other siblings, but they share a fetal environment • Called dizygotic twins ...
Birth of the domains Bacteria, Archaea and Eucarya and of major
... A hypothesis to explain how the birth of the Bacteria, Archaea and Eucarya domains and of major taxa within them took place is presented. It is proposed that the birth of each domain was an independent event consisting in the genetic isolation of a particular cell from a very diverse pool of "primit ...
... A hypothesis to explain how the birth of the Bacteria, Archaea and Eucarya domains and of major taxa within them took place is presented. It is proposed that the birth of each domain was an independent event consisting in the genetic isolation of a particular cell from a very diverse pool of "primit ...