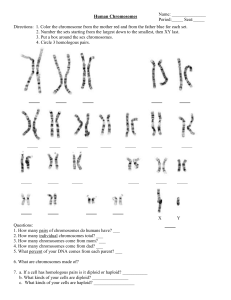
Human Chromosomes
... 7. a. If a cell has homologous pairs is it diploid or haploid? ___________ b. What kinds of your cells are diploid? ________________ c. What kinds of your cells are haploid? __________________ ...
... 7. a. If a cell has homologous pairs is it diploid or haploid? ___________ b. What kinds of your cells are diploid? ________________ c. What kinds of your cells are haploid? __________________ ...
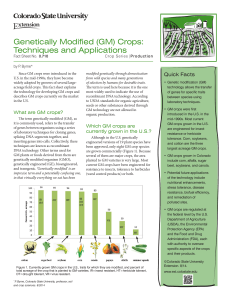
Genetically Modified (GM) Crops - Colorado State University Extension
... The crop developers then begin a long series of evaluations to determine that the gene has been incorporated successfully, that it is inherited in a stable and predictable manner, that the desired trait is expressed to the expected level, and that the plant does not show any negative effects. Evalua ...
... The crop developers then begin a long series of evaluations to determine that the gene has been incorporated successfully, that it is inherited in a stable and predictable manner, that the desired trait is expressed to the expected level, and that the plant does not show any negative effects. Evalua ...
DNA: The Hereditary Molecule
... exciting opportunity to capture the interest of your students in what is undeniably one of the most active and important aspects of modern biology: the study of our genes and the ways they influence our lives from conception to death. We will begin, not with stories of a monk puttering around with p ...
... exciting opportunity to capture the interest of your students in what is undeniably one of the most active and important aspects of modern biology: the study of our genes and the ways they influence our lives from conception to death. We will begin, not with stories of a monk puttering around with p ...
Genetics - Max Appeal!
... chromosome deletion and the second most common cause of congenital heart defects. The frequency of diagnosis has increased enormously over the past decade or so and many individuals are now found to have the deletion that only have very mild symptoms. Also a baby may be diagnosed and then as a resul ...
... chromosome deletion and the second most common cause of congenital heart defects. The frequency of diagnosis has increased enormously over the past decade or so and many individuals are now found to have the deletion that only have very mild symptoms. Also a baby may be diagnosed and then as a resul ...
U Unit: Heredity (Meiosis and Gametogenesis
... This occurs in early prophase when homologous chromosomes pair loosely along their lengths. Each gene is aligned precisely with the corresponding gene on the other homologue. The DNA molecules of one maternal and one paternal chromatid of a homologous pair are broken at the same place and then joine ...
... This occurs in early prophase when homologous chromosomes pair loosely along their lengths. Each gene is aligned precisely with the corresponding gene on the other homologue. The DNA molecules of one maternal and one paternal chromatid of a homologous pair are broken at the same place and then joine ...
Gene Section FOXC1 (forkhead box C1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... (F112S) transition within the forkhead domain. Mirzayans et al. (2000) found that Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome (RIEG3) was associated with a 67C-T transition in the FOXC1 gene, predicted to cause a gln23-to-ter (E23X) substitution upstream of the forkhead domain. Nishimura et al. (2001) found a 22-bp in ...
... (F112S) transition within the forkhead domain. Mirzayans et al. (2000) found that Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome (RIEG3) was associated with a 67C-T transition in the FOXC1 gene, predicted to cause a gln23-to-ter (E23X) substitution upstream of the forkhead domain. Nishimura et al. (2001) found a 22-bp in ...
Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
... DNA is the basis of life. It contains a set of instructions for building all of the proteins and RNA found in a cell. Those instructions are written in a code called the genetic code. The code consists of 4 bases, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine, often referred to as A, C, G, and T. The 4 ba ...
... DNA is the basis of life. It contains a set of instructions for building all of the proteins and RNA found in a cell. Those instructions are written in a code called the genetic code. The code consists of 4 bases, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine, often referred to as A, C, G, and T. The 4 ba ...
DOCX format - 27 KB - Office of the Gene Technology Regulator
... Food Standards Australia New Zealand has approved the use of material derived from these GM cottons in food. The GM cottons would also be subject to regulation by the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA), which assesses all herbicides and insecticidal products used in Aus ...
... Food Standards Australia New Zealand has approved the use of material derived from these GM cottons in food. The GM cottons would also be subject to regulation by the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA), which assesses all herbicides and insecticidal products used in Aus ...
Ch 13 outline
... In asexual reproduction, a single individual is the sole parent to donate genes to its offspring. Single-celled eukaryotes can reproduce asexually by mitotic cell division to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. ...
... In asexual reproduction, a single individual is the sole parent to donate genes to its offspring. Single-celled eukaryotes can reproduce asexually by mitotic cell division to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. ...
09_01.jpg
... Human Genome Project -- “Why sequence junk?!” • 90% of human genome (3.3x109) in finished status, ie 99% of euchromatin. • 45% of the genome are repeat sequences. • 5% of the genome encodes genes (1.5% is coding). • 35,000 ~ 40,000 genes with multiple splicing products per gene (build 34). • Finish ...
... Human Genome Project -- “Why sequence junk?!” • 90% of human genome (3.3x109) in finished status, ie 99% of euchromatin. • 45% of the genome are repeat sequences. • 5% of the genome encodes genes (1.5% is coding). • 35,000 ~ 40,000 genes with multiple splicing products per gene (build 34). • Finish ...
Gene Flow - nslc.wustl.edu
... identical, we can use a molecule genetic distance to measure the degree of non-identity • Then you can perform a standard fst analysis using not identity/non-identity, but rather a quantitative measure of identity and non-identity. Such an analysis is called AMOVA (Analysis of MOlecular VAriation) ...
... identical, we can use a molecule genetic distance to measure the degree of non-identity • Then you can perform a standard fst analysis using not identity/non-identity, but rather a quantitative measure of identity and non-identity. Such an analysis is called AMOVA (Analysis of MOlecular VAriation) ...
Ch14_Genetics
... Summary of Mendel’s Ideas • Genes are passed from parents to their offspring • If two or more forms (alleles) of the gene for a single trait exist, some forms of the gene may be dominant and others may be recessive (Law of Dominance) • In most organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene and t ...
... Summary of Mendel’s Ideas • Genes are passed from parents to their offspring • If two or more forms (alleles) of the gene for a single trait exist, some forms of the gene may be dominant and others may be recessive (Law of Dominance) • In most organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene and t ...
Chapter 19. - Kenston Local Schools
... create sections of double-stranded mRNA “death” tag for mRNA triggers degradation of mRNA ...
... create sections of double-stranded mRNA “death” tag for mRNA triggers degradation of mRNA ...
Genetic Causes of Infertility: Chromosomal Abnormalities in Couples
... missing DNA in the sons, therefore, no evidence that the abnormality is getting worse with a subsequent generation. The Y chromosome is not essential for life and until recently most regions of it were assumed to be functionally inert. Sex determination (controlled by the SRY gene) has long been vie ...
... missing DNA in the sons, therefore, no evidence that the abnormality is getting worse with a subsequent generation. The Y chromosome is not essential for life and until recently most regions of it were assumed to be functionally inert. Sex determination (controlled by the SRY gene) has long been vie ...
Final Exam Study Guide - Tacoma Community College
... 48. Describe independent assortment and how it leads to genetic differences in gametes. Lecture 6: Mendelian Genetics – 13 questions 49. Differentiate between dominant and recessive traits. 50. Differentiate between parental (P), first filial (F1), and second filial (F2)generations. 51. Differentiat ...
... 48. Describe independent assortment and how it leads to genetic differences in gametes. Lecture 6: Mendelian Genetics – 13 questions 49. Differentiate between dominant and recessive traits. 50. Differentiate between parental (P), first filial (F1), and second filial (F2)generations. 51. Differentiat ...
Learned traits - Warren County Schools
... • An organism with two alleles that are the same is called homozygous. ...
... • An organism with two alleles that are the same is called homozygous. ...
presentation - Harlem Children Society
... Two separate ligations are done here; the first one is to insert the mut Hbraf into our constructed plasmid and the next ligation is to insert the wt Hbraf into our constructed plasmid without the mut Hbraf. Transformation is prepared with both newly constructed plasmids thus 62.1mod/oli/Trp2+mutH a ...
... Two separate ligations are done here; the first one is to insert the mut Hbraf into our constructed plasmid and the next ligation is to insert the wt Hbraf into our constructed plasmid without the mut Hbraf. Transformation is prepared with both newly constructed plasmids thus 62.1mod/oli/Trp2+mutH a ...
Visualize a simple recessive
... that sex chromosomes are not involved and that results are expected in equal frequencies for both genders. As a reminder, genes are the basic unit of genetic inheritance and are inherited singly, not as pairs. Genes are located on chromosomes. Cattle have 30 pairs of chromosomes. The sire contribute ...
... that sex chromosomes are not involved and that results are expected in equal frequencies for both genders. As a reminder, genes are the basic unit of genetic inheritance and are inherited singly, not as pairs. Genes are located on chromosomes. Cattle have 30 pairs of chromosomes. The sire contribute ...
Presentation #2 - UCLA Human Genetics
... e = unobserved random variable, which adds noise to the observed y (contributes to variation in y). Sometimes referred to as “error”, although it is not necessarily error ...
... e = unobserved random variable, which adds noise to the observed y (contributes to variation in y). Sometimes referred to as “error”, although it is not necessarily error ...
A
... tems that mold our form, we humans may be much more similar to our far distant worm and insect relatives than we might like to think. So similar, in fact, thatÑas our work has shownÑcurious experimenters can use some human and mouse Hox genes to guide the development of fruit-ßy embryos. The story o ...
... tems that mold our form, we humans may be much more similar to our far distant worm and insect relatives than we might like to think. So similar, in fact, thatÑas our work has shownÑcurious experimenters can use some human and mouse Hox genes to guide the development of fruit-ßy embryos. The story o ...
- Wiley Online Library
... features of CED (Table 1, Fig. 1B and C), they all had markedly lax skin with joint laxity fulfilling the clinical definition of cutis laxa, but none had evidence of retinal involvement and only the oldest patient developed end-stage renal failure. In addition, the two older siblings have confirmed ...
... features of CED (Table 1, Fig. 1B and C), they all had markedly lax skin with joint laxity fulfilling the clinical definition of cutis laxa, but none had evidence of retinal involvement and only the oldest patient developed end-stage renal failure. In addition, the two older siblings have confirmed ...
Biology in Society
... •Contra Galton, regression does not mean that mass selection will fail, it just means that selective breeding of tall couples will not lead to as great an increase in average heights as it would if the tall couples "bred true." •From the technical points above we can infer that, on a social level, G ...
... •Contra Galton, regression does not mean that mass selection will fail, it just means that selective breeding of tall couples will not lead to as great an increase in average heights as it would if the tall couples "bred true." •From the technical points above we can infer that, on a social level, G ...
Ontologies 2 - European Bioinformatics Institute
... • Where an individual gene product that is part of a complex can be annotated to terms that describe the action (function or process) of the whole complex • contributes_to is not needed to annotate a catalytic subunit. ...
... • Where an individual gene product that is part of a complex can be annotated to terms that describe the action (function or process) of the whole complex • contributes_to is not needed to annotate a catalytic subunit. ...