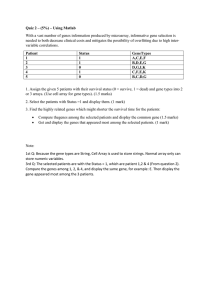
Quiz 2 – (5%) – Using Matlab With a vast number of genes
... 1st Q: Because the gene types are String, Cell Array is used to store strings. Normal array only can store numeric variables. 3rd Q: The selected patients are with the Status = 1, which are patient 1,2 & 4 (From question 2). Compare the genes among 1, 2, & 4, and display the same gene, for example: ...
... 1st Q: Because the gene types are String, Cell Array is used to store strings. Normal array only can store numeric variables. 3rd Q: The selected patients are with the Status = 1, which are patient 1,2 & 4 (From question 2). Compare the genes among 1, 2, & 4, and display the same gene, for example: ...
Document
... • some RNA’s are active and can function in the cell on their own • some RNA’s are incorporated into protein complexes to function * The main functions of non-coding RNA’s are in protein production and regulation of gene expression ...
... • some RNA’s are active and can function in the cell on their own • some RNA’s are incorporated into protein complexes to function * The main functions of non-coding RNA’s are in protein production and regulation of gene expression ...
Word file
... Figure SI 1. An early map of the mouse genome. Presented by The Roscoe B. Jackson Memorial Laboratory at the Tenth International Congress of Genetics, McGill University, Montreal, Canada, 1958, the map was sparse, but rich in visual impact. This remarkable exhibit showed the linkage groups of the mo ...
... Figure SI 1. An early map of the mouse genome. Presented by The Roscoe B. Jackson Memorial Laboratory at the Tenth International Congress of Genetics, McGill University, Montreal, Canada, 1958, the map was sparse, but rich in visual impact. This remarkable exhibit showed the linkage groups of the mo ...
Genetic Disorders Project
... Age at which the symptoms begin Slide 6 Prognosis: What is the outlook for the future of that person’s life? Treatment Options: Slide 7 Prevention: Are their certain risk factors for this disorder? Like being an older mother or being a recessive carrier of the trait? Slide 8 Personal Spin: ...
... Age at which the symptoms begin Slide 6 Prognosis: What is the outlook for the future of that person’s life? Treatment Options: Slide 7 Prevention: Are their certain risk factors for this disorder? Like being an older mother or being a recessive carrier of the trait? Slide 8 Personal Spin: ...
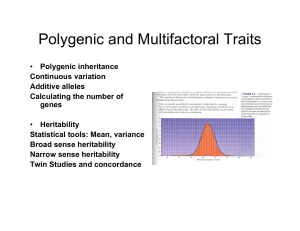
Polygenic and Multifactoral Traits
... phenotypes • Predisposition is caused by a number of genes in an additive way • Will develop the genetic disorder if exposed to proper environmental conditions. ...
... phenotypes • Predisposition is caused by a number of genes in an additive way • Will develop the genetic disorder if exposed to proper environmental conditions. ...
Chapter 3 Overview
... rare but severe form of Alzheimer disease. 7. In fragile X syndrome, part of the X chromosome is attached by such a thin string of molecules that it seems about to break off. Although there is considerable variation in its effects, some mental deficiency is common (more so in males than in females). ...
... rare but severe form of Alzheimer disease. 7. In fragile X syndrome, part of the X chromosome is attached by such a thin string of molecules that it seems about to break off. Although there is considerable variation in its effects, some mental deficiency is common (more so in males than in females). ...
Chapter 3: Heredity and Environment Chapter Preview Much is
... rare but severe form of Alzheimer disease. 7. In fragile X syndrome, part of the X chromosome is attached by such a thin string of molecules that it seems about to break off. Although there is considerable variation in its effects, some mental deficiency is common (more so in males than in females). ...
... rare but severe form of Alzheimer disease. 7. In fragile X syndrome, part of the X chromosome is attached by such a thin string of molecules that it seems about to break off. Although there is considerable variation in its effects, some mental deficiency is common (more so in males than in females). ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint.ppt
... from the sex chromosomes even though females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
... from the sex chromosomes even though females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint
... from the sex chromosomes even though females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
... from the sex chromosomes even though females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 11What type of organism was used in the first genetic studies done by Gregor Mendel? 12What is a karyotype? 13The two genes for a trait represented by capital & lower case letters are called __________. 14How many traits are involved in a dihybrid cross? 15Which of Mendel's laws states that the domi ...
... 11What type of organism was used in the first genetic studies done by Gregor Mendel? 12What is a karyotype? 13The two genes for a trait represented by capital & lower case letters are called __________. 14How many traits are involved in a dihybrid cross? 15Which of Mendel's laws states that the domi ...
Lecture
... Gene: A basic unit, which represents one characteristic of the individual. The value of each gene is called an allele Chromosome: A string of genes; it represents an individual i.e. a possible solution of a problem. Each chromosome represents a point in the search space Population: A collection of c ...
... Gene: A basic unit, which represents one characteristic of the individual. The value of each gene is called an allele Chromosome: A string of genes; it represents an individual i.e. a possible solution of a problem. Each chromosome represents a point in the search space Population: A collection of c ...
Genetics of MD - Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation
... Distinctive genetic mechanisms in DM Myotonic dystrophy is one of the most complex disorders known. In addition to the incredible variability of clinical symptoms, the disease also has several unique mechanistic features: • Autosomal dominant inheritance. The genes for DM1 and DM2 are dominant, mean ...
... Distinctive genetic mechanisms in DM Myotonic dystrophy is one of the most complex disorders known. In addition to the incredible variability of clinical symptoms, the disease also has several unique mechanistic features: • Autosomal dominant inheritance. The genes for DM1 and DM2 are dominant, mean ...
Lecture 10
... (2) Nearly all cases of Down’s Syndrome developed AD-like brain pathology (plaques and tangles) ...
... (2) Nearly all cases of Down’s Syndrome developed AD-like brain pathology (plaques and tangles) ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... An ultrasound probe scans the mother’s abdomen, while a transducer transmits high-frequency sound waves that are transformed into a picture on a video screen. Testing Fetal Cells For testing purposes, fetal cells may be obtained by amniocentesis, chorionic villi sampling, or from the mother’s blood. ...
... An ultrasound probe scans the mother’s abdomen, while a transducer transmits high-frequency sound waves that are transformed into a picture on a video screen. Testing Fetal Cells For testing purposes, fetal cells may be obtained by amniocentesis, chorionic villi sampling, or from the mother’s blood. ...
Human Heridity
... (lungs, pancreas, etc) Genetic Recessive -a person must inherit an allele from ________ of their parents -Huntington’s Disease- causes degeneration of brain cells -Sickle Cell Anemia-causes the shape of the red blood cells to change from circles to sickle (half-moon) shaped and they get caught in ve ...
... (lungs, pancreas, etc) Genetic Recessive -a person must inherit an allele from ________ of their parents -Huntington’s Disease- causes degeneration of brain cells -Sickle Cell Anemia-causes the shape of the red blood cells to change from circles to sickle (half-moon) shaped and they get caught in ve ...
Nedchromosnotes2jan2014NED 20 KB
... condition refer to what? Important terms you need to and should know but I do not have time to redefine because they should be hardwired by now are haploid, diploid, nucleosome, chromatin, histone, centromere, telomere, homologues, chromatids. Bacterial genomes = 4.6 Mb = 4.6 x 10^6 bp Human genome ...
... condition refer to what? Important terms you need to and should know but I do not have time to redefine because they should be hardwired by now are haploid, diploid, nucleosome, chromatin, histone, centromere, telomere, homologues, chromatids. Bacterial genomes = 4.6 Mb = 4.6 x 10^6 bp Human genome ...
Genetic Disorders
... Gene mutations can be either inherited from a parent or acquired. A hereditary mutation is a mistake that is present in the DNA of virtually all body cells. Hereditary mutations are also called germ line mutations because the gene change exists in the reproductive cells and can be passed from gene ...
... Gene mutations can be either inherited from a parent or acquired. A hereditary mutation is a mistake that is present in the DNA of virtually all body cells. Hereditary mutations are also called germ line mutations because the gene change exists in the reproductive cells and can be passed from gene ...
Finding Protein-Coding Genes
... course, please tell me what you did. The report from this exercise should be around two to four pages, including figures. Quantitative answers are preferable to qualitative ones. Describe your observations in your own words, and cite your sources for information. Pick a genetic locus (single gene or ...
... course, please tell me what you did. The report from this exercise should be around two to four pages, including figures. Quantitative answers are preferable to qualitative ones. Describe your observations in your own words, and cite your sources for information. Pick a genetic locus (single gene or ...
PowerPoint to accompany
... • missing a chromosome or having an extra chromosome • results from nondisjunction • trisomy is the condition of having an extra chomosome • monosomy is the condition of missing a chromosome Euploid is a normal chromosome number ...
... • missing a chromosome or having an extra chromosome • results from nondisjunction • trisomy is the condition of having an extra chomosome • monosomy is the condition of missing a chromosome Euploid is a normal chromosome number ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype KEY CONCEPT affect the expression of traits.
... The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. ...
... The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. ...
the maternal grandsire - Weimaraner Club of America
... generation and are passed along only by female offspring. Recently, however, an article documenting scientific evidence of the maternal-grandsire effect appeared in issue number 242 of Equus, an outstanding horse publication. I acknowledge that article for providing me with much of the information i ...
... generation and are passed along only by female offspring. Recently, however, an article documenting scientific evidence of the maternal-grandsire effect appeared in issue number 242 of Equus, an outstanding horse publication. I acknowledge that article for providing me with much of the information i ...
Questions 2011-engl
... (A) an unmodified transmission of genetic information from mother to child. (B) a modification of gene-activity by intragenic repeat-expansion. (C) an appearance of genetically caused signs in following generations not following the expected mode of inheritance. (D) a different gene-activity, accord ...
... (A) an unmodified transmission of genetic information from mother to child. (B) a modification of gene-activity by intragenic repeat-expansion. (C) an appearance of genetically caused signs in following generations not following the expected mode of inheritance. (D) a different gene-activity, accord ...
The Human Genome Chapter 14
... All human egg cells carry a single X chromosome (23,X). However, half of all sperm cells carry an X chromosome and half carry a Y chromosome (23,Y). This means that half of the zygotes will be 46,XX and half will be 46, XY. ...
... All human egg cells carry a single X chromosome (23,X). However, half of all sperm cells carry an X chromosome and half carry a Y chromosome (23,Y). This means that half of the zygotes will be 46,XX and half will be 46, XY. ...