exam 5 practice questions answers
... How many chromatids are present? 46 How many chromosomes are present? 46 Are these chromosomes duplicated, or unduplicated? Unduplicated How many pairs of homologous chromosomes are present? 23 What makes these chromosomes homologous? The fact that they exhibit the exact same banding in the same loc ...
... How many chromatids are present? 46 How many chromosomes are present? 46 Are these chromosomes duplicated, or unduplicated? Unduplicated How many pairs of homologous chromosomes are present? 23 What makes these chromosomes homologous? The fact that they exhibit the exact same banding in the same loc ...
Genetics Study Guide Chapter 11, 13, 14
... How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY? If a guinea pig that is heterozygous for black, short hair (BbSs) is crossed with a guinea pig that is homozygous for black hair but heterozygous for short hair (BBSs), how many diff ...
... How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY? If a guinea pig that is heterozygous for black, short hair (BbSs) is crossed with a guinea pig that is homozygous for black hair but heterozygous for short hair (BBSs), how many diff ...
First sex determining genes appeared in mammals 180 million years
... between males and females. hours! A gigantic task, which could not have been But this has not always been the case. A very long performed without important technical means: the high-throughput DNA sequencers of the genomics time ago, the X and Y were identical, until the Y started to differentiate f ...
... between males and females. hours! A gigantic task, which could not have been But this has not always been the case. A very long performed without important technical means: the high-throughput DNA sequencers of the genomics time ago, the X and Y were identical, until the Y started to differentiate f ...
Use of wild-wheat resources - UC Agriculture and Natural Resources
... genus Aegilops. In contrast, chromosomes of the B genome pair little, or not a t all, with those of any known diploid species. Consequently, a s a result of recombinations between the pairing chromosomes, genes from the diploid wheats and Aegilops species can readily be transferred t o the A, but no ...
... genus Aegilops. In contrast, chromosomes of the B genome pair little, or not a t all, with those of any known diploid species. Consequently, a s a result of recombinations between the pairing chromosomes, genes from the diploid wheats and Aegilops species can readily be transferred t o the A, but no ...
Dominant or Recessive - UNT's College of Education
... Genes for traits are encoded and arranged linearly on structures called chromosomes found in the nuclei of most cells. When organisms reproduce, the resulting offspring should receive an equal number of chromosomes from the mother and the father. In this activity you use the chromosomes and Bug Trai ...
... Genes for traits are encoded and arranged linearly on structures called chromosomes found in the nuclei of most cells. When organisms reproduce, the resulting offspring should receive an equal number of chromosomes from the mother and the father. In this activity you use the chromosomes and Bug Trai ...
sex linked genes - The Biology Corner
... Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: simply states that chromosomes are carriers of genetic information (Walter Sutton) Every organism has sex chromosomes (that determine sex) and the rest of the chromosomes are called autosomes Humans have 22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes (see karyoty ...
... Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: simply states that chromosomes are carriers of genetic information (Walter Sutton) Every organism has sex chromosomes (that determine sex) and the rest of the chromosomes are called autosomes Humans have 22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes (see karyoty ...
biology final review sheet answers
... 40. What is the diploid number of cells in the human body? 46 41. What is the haploid number of cells in the human body? 23 42. How many total chromosomes are in a gamete (sperm cell or egg cell)? 23 43. Mitosis produces two genetically (identical) (diploid) daughter cells. 44. Meiosis produces four ...
... 40. What is the diploid number of cells in the human body? 46 41. What is the haploid number of cells in the human body? 23 42. How many total chromosomes are in a gamete (sperm cell or egg cell)? 23 43. Mitosis produces two genetically (identical) (diploid) daughter cells. 44. Meiosis produces four ...
Introduction to Genetics
... You get 23 chromosomes from each parent. 1 of the 23 chromosomes determines whether you are male or female. The other 22 chromosomes (Autosomal DNA) pretty much determine your genetic profile. You get Autosomal DNA 50-50 from both parents. The two germ cells, male sperm and female egg, have chromos ...
... You get 23 chromosomes from each parent. 1 of the 23 chromosomes determines whether you are male or female. The other 22 chromosomes (Autosomal DNA) pretty much determine your genetic profile. You get Autosomal DNA 50-50 from both parents. The two germ cells, male sperm and female egg, have chromos ...
Faithful meiotic chromosome segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans
... We use the genetic model system C. elegans to identify genes that are essential for proper meiotic prophase cell cycle progression and faithful meiotic chromosome segregation. Characterization of the encoded factors, their interaction partners and identification of mammalian (human) homologues will ...
... We use the genetic model system C. elegans to identify genes that are essential for proper meiotic prophase cell cycle progression and faithful meiotic chromosome segregation. Characterization of the encoded factors, their interaction partners and identification of mammalian (human) homologues will ...
Period 4 Spring Exam Review Sheet
... 2. Mitosis has one division which makes 2 cells, while Meiosis has 2 divisions to make four cells. 3. Mitosis’s end product is two diploid cells, while Meiosis ends with four haploid cells. 4. Mitosis’ purpose is to make somatic cells. Meiosis is for gametes. Stages of Mitosis: see terms In Interpha ...
... 2. Mitosis has one division which makes 2 cells, while Meiosis has 2 divisions to make four cells. 3. Mitosis’s end product is two diploid cells, while Meiosis ends with four haploid cells. 4. Mitosis’ purpose is to make somatic cells. Meiosis is for gametes. Stages of Mitosis: see terms In Interpha ...
Chapter 11.2
... One form of the trait (white) disappears in the first generation offspring (F1), only to show up in the second generation (F2) We know that all members of the F1 offspring are heterozygous (Aa) because one parent could only produce an A gamete and the other could produce only an a gamete ...
... One form of the trait (white) disappears in the first generation offspring (F1), only to show up in the second generation (F2) We know that all members of the F1 offspring are heterozygous (Aa) because one parent could only produce an A gamete and the other could produce only an a gamete ...
Study Guide Part II
... 23. A carrier of a genetic disorder who does not show symptoms is most likely to be __________ to transmit it to offspring. 24. Dr. Smith's parents have normal hearing. However, Dr. Smith has an inherited form of deafness. Deafness is a recessive trait that is associated with the abnormal allele d. ...
... 23. A carrier of a genetic disorder who does not show symptoms is most likely to be __________ to transmit it to offspring. 24. Dr. Smith's parents have normal hearing. However, Dr. Smith has an inherited form of deafness. Deafness is a recessive trait that is associated with the abnormal allele d. ...
Chapter 4 Genetics: The Science of Heredity C4S1 `Mendel`s Work
... ii. One allele come from the male, and the other allele comes from the female iii. Sutton’s idea came to be known as the chromosome theory of inheritance Meiosis The process in which sex cells produce which have ½ the number of chromosomes a. What Happens During Meiosis i. Chromosome pairs separate ...
... ii. One allele come from the male, and the other allele comes from the female iii. Sutton’s idea came to be known as the chromosome theory of inheritance Meiosis The process in which sex cells produce which have ½ the number of chromosomes a. What Happens During Meiosis i. Chromosome pairs separate ...
PGS: 274 – 284
... A. This term refers to genes found on the sex chromosomes; 95% of the time it mainly refers to the X chromosome. (Think X when it is seX linked.) 1. This is because both sexes have at least one X chromosome in their genome. 2. XX (Female and homologous) ; XY (Male and heterologous) B. Sex chromosome ...
... A. This term refers to genes found on the sex chromosomes; 95% of the time it mainly refers to the X chromosome. (Think X when it is seX linked.) 1. This is because both sexes have at least one X chromosome in their genome. 2. XX (Female and homologous) ; XY (Male and heterologous) B. Sex chromosome ...
Mitosis I. Introduction II. MitosisHow Your Body
... are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes. Essentially, it is is the process of making exact copies of a cell. ...
... are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes. Essentially, it is is the process of making exact copies of a cell. ...
Non - Mendelian Genetics
... Some alleles are neither __________ nor ___________, and many ______ are controlled by __________ alleles or genes. ...
... Some alleles are neither __________ nor ___________, and many ______ are controlled by __________ alleles or genes. ...
Name: Genetics 314 – Spring, 2008 Exam 3 – 100 points 1. You
... system worked to prevent recombination. You tell him it is too early to celebrate, why? Because formation of the synaptonemal complex, synapsis and/or homologous chromosome pairing and recombination only occur in meiosis so observing mitosis would not be of any use in determining if chromosome pairi ...
... system worked to prevent recombination. You tell him it is too early to celebrate, why? Because formation of the synaptonemal complex, synapsis and/or homologous chromosome pairing and recombination only occur in meiosis so observing mitosis would not be of any use in determining if chromosome pairi ...
Genetics PowerPoint
... hybrid will show a blend of the two traits. In humans, hair texture is such a trait. Because neither curly or straight hair is recessive, no lower case letters are used. ...
... hybrid will show a blend of the two traits. In humans, hair texture is such a trait. Because neither curly or straight hair is recessive, no lower case letters are used. ...
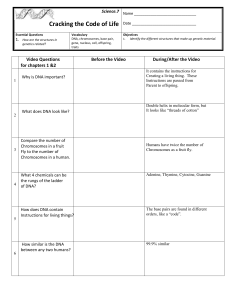
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
... Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
Unit 6: Genetics and Reproduction
... Polygenic Inheritance • Some characteristics, such as eye color, are controlled by several genes. • Sometimes the genes are on the same chromosome. • Sometimes they are found on different chromosomes. ...
... Polygenic Inheritance • Some characteristics, such as eye color, are controlled by several genes. • Sometimes the genes are on the same chromosome. • Sometimes they are found on different chromosomes. ...
Mitosis/Meiosis and Genetic Diseases
... This can cause altered gene activity, a loss of crossingover, or a duplication/deletion if crossing-over does occur. -Duplication – repetition of a segment within a chromosome; it can be due to unequal crossing over which produces a deletion on one chromosome and a duplication on the other. Often, m ...
... This can cause altered gene activity, a loss of crossingover, or a duplication/deletion if crossing-over does occur. -Duplication – repetition of a segment within a chromosome; it can be due to unequal crossing over which produces a deletion on one chromosome and a duplication on the other. Often, m ...
Practice Midterm 2
... 23) If the genes for seed color (Yellow/green) and seed shape (Round/wrinkled) are on the same chromosome, and no crossing over occurs between the two genes, what would your phenotypic ratios be for ...
... 23) If the genes for seed color (Yellow/green) and seed shape (Round/wrinkled) are on the same chromosome, and no crossing over occurs between the two genes, what would your phenotypic ratios be for ...
Principles of Genetics
... hybrid will show a blend of the two traits. In humans, hair texture is such a trait. Because neither curly or straight hair is recessive, no lower case letters are used. ...
... hybrid will show a blend of the two traits. In humans, hair texture is such a trait. Because neither curly or straight hair is recessive, no lower case letters are used. ...
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
... cytoplasmic division of immature reproductive cells in sexually-reproducing eukaryotic species ...
... cytoplasmic division of immature reproductive cells in sexually-reproducing eukaryotic species ...
Ploidy
Ploidy is the number of sets of chromosomes in a cell. Usually a gamete (sperm or egg, which fuse into a single cell during the fertilization phase of sexual reproduction) carries a full set of chromosomes that includes a single copy of each chromosome, as aneuploidy generally leads to severe genetic disease in the offspring. The gametic or haploid number (n) is the number of chromosomes in a gamete. Two gametes form a diploid zygote with twice this number (2n, the zygotic or diploid number) i.e. two copies of autosomal chromosomes. For humans, a diploid species, n = 23. A typical human somatic cell contains 46 chromosomes: 2 complete haploid sets, which make up 23 homologous chromosome pairs.Because chromosome number is generally reduced only by the specialized process of meiosis, the somatic cells of the body inherit and maintain the chromosome number of the zygote. However, in many situations somatic cells double their copy number by means of endoreduplication as an aspect of cellular differentiation. For example, the hearts of two-year-old children contain 85% diploid and 15% tetraploid nuclei, but by 12 years of age the proportions become approximately equal, and adults examined contained 27% diploid, 71% tetraploid and 2% octaploid nuclei.Cells are described according to the number of sets present (the ploidy level): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is frequently used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes (triploid or higher ploidy).