Meiosis
... • Genes are the units of heredity, and are made up of segments of DNA • Genes are passed to the next generation through reproductive cells called gametes (sperm and eggs) • Each gene has a specific location called a locus on a certain chromosome • One set of chromosomes is inherited from each parent ...
... • Genes are the units of heredity, and are made up of segments of DNA • Genes are passed to the next generation through reproductive cells called gametes (sperm and eggs) • Each gene has a specific location called a locus on a certain chromosome • One set of chromosomes is inherited from each parent ...
Heredity and the Environment
... DNA strand that provides an instruction for a particular trait, tissue, or other structure. There are approximately 20,000 to 30,000 genes (depending on how they are identified and counted) aligned somewhere along the set of 46 chromosomes in each human cell (Human Genome Project, 2006). It is also ...
... DNA strand that provides an instruction for a particular trait, tissue, or other structure. There are approximately 20,000 to 30,000 genes (depending on how they are identified and counted) aligned somewhere along the set of 46 chromosomes in each human cell (Human Genome Project, 2006). It is also ...
Case Report Clinical Expression of an Inherited Unbalanced
... other autosomes or sex chromosomes [6–10]. Generally, the detection of unbalanced type of translocation in children with facial dysmorphism, mental retardation, and growth retardation led to retrospective detection of balanced translocations in their parents. In the present case, the child was detec ...
... other autosomes or sex chromosomes [6–10]. Generally, the detection of unbalanced type of translocation in children with facial dysmorphism, mental retardation, and growth retardation led to retrospective detection of balanced translocations in their parents. In the present case, the child was detec ...
Autism and maternally derived aberrations of chromosome 15q
... aberrations of chromosome 15 may be the single most common identifiable cause of autism. These aberrations include duplications and deletions involving the proximal long arm of chromosome 15. The Department of Disabilities and Special Needs (DDSN) is the public agency responsible for services for au ...
... aberrations of chromosome 15 may be the single most common identifiable cause of autism. These aberrations include duplications and deletions involving the proximal long arm of chromosome 15. The Department of Disabilities and Special Needs (DDSN) is the public agency responsible for services for au ...
Morgan and Linkage
... given that it contains an allele from the original chromosome of interest. The third unit is the centimorgan or cM. One centimorgan is defined as the physical distance corresponding to a value of ✓ equalling 0.01. In other words, it is the distance such that the probability is .01 that a gamete will ...
... given that it contains an allele from the original chromosome of interest. The third unit is the centimorgan or cM. One centimorgan is defined as the physical distance corresponding to a value of ✓ equalling 0.01. In other words, it is the distance such that the probability is .01 that a gamete will ...
Relationship between chromosome fragility, aneuploidy and
... monosomy was again very similar in FA patients and controls (P > 0.05). A tendency towards higher frequencies of monosomy 7 in FA patients was observed, but it did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.07). Similar non-significant results were obtained for other chromosome numerical abnormalitie ...
... monosomy was again very similar in FA patients and controls (P > 0.05). A tendency towards higher frequencies of monosomy 7 in FA patients was observed, but it did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.07). Similar non-significant results were obtained for other chromosome numerical abnormalitie ...
Completion of a parasexual cycle in Candida
... locus in 32 colonies picked at random from YEPD revealed that 31 of the 32 colonies were still tetra-allelic at MTL and one was tri-allelic, consistent with relatively stable propagation of the tetraploid on this medium. In comparison, analysis of 32 colonies randomly picked from pre-spo plates indi ...
... locus in 32 colonies picked at random from YEPD revealed that 31 of the 32 colonies were still tetra-allelic at MTL and one was tri-allelic, consistent with relatively stable propagation of the tetraploid on this medium. In comparison, analysis of 32 colonies randomly picked from pre-spo plates indi ...
File
... with long tails and cats with no tails are homozygous for their respective alleles. Cats with one long tail allele and one no tail allele have short tails. For each of the following construct a punnett square and give phenotypic and genotype ratios of the offspring. a) a long tail cat and a cat with ...
... with long tails and cats with no tails are homozygous for their respective alleles. Cats with one long tail allele and one no tail allele have short tails. For each of the following construct a punnett square and give phenotypic and genotype ratios of the offspring. a) a long tail cat and a cat with ...
Characterization of sex chromosomes in rainbow trout and coho
... this marker in order to perform genetic analyzes in the progeny. On the other hand, in rainbow trout males with no morphological differences among X and Y chromosomes (XX males) the hybridization of the 5S rDNA marker in two subtelocentric chromosomes, which also show a bright DAPI band, indicates t ...
... this marker in order to perform genetic analyzes in the progeny. On the other hand, in rainbow trout males with no morphological differences among X and Y chromosomes (XX males) the hybridization of the 5S rDNA marker in two subtelocentric chromosomes, which also show a bright DAPI band, indicates t ...
Часть 1. - Ассоциация синдрома Ретта
... male to female mutations. By use of molecular markers, direct evidence for a sexual bias in the origin of mutations has been shown for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, haemophilia A, haemophilia B and the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. For example, in a study of 43 haemophilia B families, it was found ...
... male to female mutations. By use of molecular markers, direct evidence for a sexual bias in the origin of mutations has been shown for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, haemophilia A, haemophilia B and the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. For example, in a study of 43 haemophilia B families, it was found ...
Chapter 13 Practice Multiple Choice
... with an orange gene, she will produce which of the following egg types? a. Only blue gene eggs b. Only orange gene eggs c. 1/2 blue and 1/2 orange gene eggs d. 3/4 blue and 1/4 orange gene eggs e. An indeterminate frequency of blue and orange gene eggs ____ 21. A female with a paternal set of one or ...
... with an orange gene, she will produce which of the following egg types? a. Only blue gene eggs b. Only orange gene eggs c. 1/2 blue and 1/2 orange gene eggs d. 3/4 blue and 1/4 orange gene eggs e. An indeterminate frequency of blue and orange gene eggs ____ 21. A female with a paternal set of one or ...
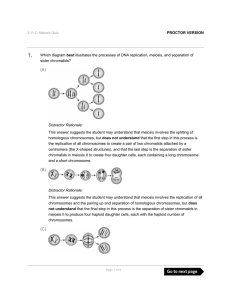
(A) (B) (C)
... indicated by “Y” on the pedigree below. Because the condition results from a unique sequence of nucleotides that is extremely rare in the human population, it is often used in paternity cases to determine if offspring are related to the potential parents. ...
... indicated by “Y” on the pedigree below. Because the condition results from a unique sequence of nucleotides that is extremely rare in the human population, it is often used in paternity cases to determine if offspring are related to the potential parents. ...
Document
... i lloss and d cataracts. t t O Onsett off this thi rare disorder commonly occurs during young adulthood. However, it can occur at any age and is extremely variable in degree of severity. The myotonic dystrophy gene gene, found on chromosome 19 19, codes for a protein kinase that is found in skelet ...
... i lloss and d cataracts. t t O Onsett off this thi rare disorder commonly occurs during young adulthood. However, it can occur at any age and is extremely variable in degree of severity. The myotonic dystrophy gene gene, found on chromosome 19 19, codes for a protein kinase that is found in skelet ...
Chapter 15 Multiple Choice Practice
... c. located far from each other on the same chromosome. d. Both A and B e. Both A and C ____ 14. The frequency of crossing over between any two linked genes will be which of the following? a. Higher if they are recessive b. Dependent on how many alleles there are c. Determined by their relative domin ...
... c. located far from each other on the same chromosome. d. Both A and B e. Both A and C ____ 14. The frequency of crossing over between any two linked genes will be which of the following? a. Higher if they are recessive b. Dependent on how many alleles there are c. Determined by their relative domin ...
Molecular-3
... mutations, mutant alleles lost through selection must be replaced by recurrent new mutations to maintain the observed disease incidence. If the incidence of a serious X-linked disease is not changing and selection is operating against, and only against, hemizygous males, the mutation rate, μ, must ...
... mutations, mutant alleles lost through selection must be replaced by recurrent new mutations to maintain the observed disease incidence. If the incidence of a serious X-linked disease is not changing and selection is operating against, and only against, hemizygous males, the mutation rate, μ, must ...
Understanding Patterns of Inheritance Through Pedigree
... books is to teach recognizable Mendelian patterns through Punnett square analysis, and introduce other, nonmendelian patterns later. After students have mastered Punnett squares, then they are introduced to pedigree analysis. All too often students associate pedigrees with the last Punnett square th ...
... books is to teach recognizable Mendelian patterns through Punnett square analysis, and introduce other, nonmendelian patterns later. After students have mastered Punnett squares, then they are introduced to pedigree analysis. All too often students associate pedigrees with the last Punnett square th ...
Brooker Chapter 4
... Heterozygosity at a locus produces a third 3 phenotype intermediate to the two homozygous phenotypes ...
... Heterozygosity at a locus produces a third 3 phenotype intermediate to the two homozygous phenotypes ...
Multiple Roles of the Y Chromosome in the Biology of
... It is generally accepted that the sex chromosomes of most animals arose from a couple of homologous autosomes after the acquisition of a dominant sex determination gene[17,18] and that the Y chromosome is the result of the degeneration of one of them[19,20,21]. Its degeneration would be a consequenc ...
... It is generally accepted that the sex chromosomes of most animals arose from a couple of homologous autosomes after the acquisition of a dominant sex determination gene[17,18] and that the Y chromosome is the result of the degeneration of one of them[19,20,21]. Its degeneration would be a consequenc ...
Genome partitioning of genetic variation for complex traits using
... The traits vWF and QTi were available in the ARIC cohort only. aWithout principal component adjustment. bAdjustment with the first 10 principal components from principal component analysis. Ng(C) are correlated (r = 0.628), we performed cEstimate of variance explained by all autosomal SNPs. dNarrow ...
... The traits vWF and QTi were available in the ARIC cohort only. aWithout principal component adjustment. bAdjustment with the first 10 principal components from principal component analysis. Ng(C) are correlated (r = 0.628), we performed cEstimate of variance explained by all autosomal SNPs. dNarrow ...
Heredity
... Genes – sequence of triplets on DNA Humans have about – 23,000 genes Each chromosome contains many genes Like the chromosomes they are part of, genes occur in pairs of two. – Alleles - alternate forms of a gene ...
... Genes – sequence of triplets on DNA Humans have about – 23,000 genes Each chromosome contains many genes Like the chromosomes they are part of, genes occur in pairs of two. – Alleles - alternate forms of a gene ...
Ineritance Packet inheritancepacket
... GAMETE- Egg and sperm cells (sex cells). They have half the chromosomes compared do other cells in the body (23 individual chromosomes for humans). SOMATIC CELLS- Cells in the body other than egg or sperm. They have a full set of DNA. For humans this is 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chro ...
... GAMETE- Egg and sperm cells (sex cells). They have half the chromosomes compared do other cells in the body (23 individual chromosomes for humans). SOMATIC CELLS- Cells in the body other than egg or sperm. They have a full set of DNA. For humans this is 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chro ...
The hitch-hiking effect of a favourable gene
... When a selectively favourable mutation occurs in a population and is subsequently fixed in that population, this process will alter the frequencies of alleles at closely linked loci. Alleles present on the chromosome on which the original mutation occurred will tend to increase in frequency, and oth ...
... When a selectively favourable mutation occurs in a population and is subsequently fixed in that population, this process will alter the frequencies of alleles at closely linked loci. Alleles present on the chromosome on which the original mutation occurred will tend to increase in frequency, and oth ...
Genome Biology - Institute for Applied Ecology
... for compensated and non-compensated genes in each tissue were unexpected if the genes were drawn at random from the set of all Z genes (p<0.02 in each case). The level of expression of Z genes in each tissue in males was significantly positively correlated with the M:F ratio of Z genes (Pearson corr ...
... for compensated and non-compensated genes in each tissue were unexpected if the genes were drawn at random from the set of all Z genes (p<0.02 in each case). The level of expression of Z genes in each tissue in males was significantly positively correlated with the M:F ratio of Z genes (Pearson corr ...
F 1 - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... • Particulate inheritance—each determinant was physically distinct and remained intact ...
... • Particulate inheritance—each determinant was physically distinct and remained intact ...
Sex Determination and Sex
... extensions to his basic principles of heredity. In this chapter, we explore one of the major extensions to Mendel’s principles: the inheritance of characteristics encoded by genes located on the sex chromosomes, which differ in males and females ( ◗ FIGURE 4.2). These characteristics and the genes t ...
... extensions to his basic principles of heredity. In this chapter, we explore one of the major extensions to Mendel’s principles: the inheritance of characteristics encoded by genes located on the sex chromosomes, which differ in males and females ( ◗ FIGURE 4.2). These characteristics and the genes t ...