Meiosis and Mendel`s Law of Segregation
... the process of meiosis. Meiosis is the process in which a diploid germ cell, diploid meaning that the cell has two sets of chromosomes – one from each parent, first replicates its DNA and then undergoes two rounds of division to produce four haploid gametes. The resulting products of meiosis, or gam ...
... the process of meiosis. Meiosis is the process in which a diploid germ cell, diploid meaning that the cell has two sets of chromosomes – one from each parent, first replicates its DNA and then undergoes two rounds of division to produce four haploid gametes. The resulting products of meiosis, or gam ...
A detailed gene map of pig chromosome 4, where the first
... affecting growth, carcass traits and fat deposition. The first QTL on SSC4, denoted FAT1, was identified in a European wild boar – Large White intercross. SSC4 has previously been shown to share homology with human chromosomes 1 (HSA1) and 8 (HSA8). SSC4 is divided into two chromosomal blocks where ...
... affecting growth, carcass traits and fat deposition. The first QTL on SSC4, denoted FAT1, was identified in a European wild boar – Large White intercross. SSC4 has previously been shown to share homology with human chromosomes 1 (HSA1) and 8 (HSA8). SSC4 is divided into two chromosomal blocks where ...
Chromosome Locations of the MYB Related Genes, AMYB and
... Thus, it seemed important to determine if other members of idiogram of grain distribution after in situ hybridization with radiolabeled AMYB the MYB gene family map to chromosome regions indicating probe. For the AMYB probe a total of 100 grains were counted on 75 metaphases, direct involvement in n ...
... Thus, it seemed important to determine if other members of idiogram of grain distribution after in situ hybridization with radiolabeled AMYB the MYB gene family map to chromosome regions indicating probe. For the AMYB probe a total of 100 grains were counted on 75 metaphases, direct involvement in n ...
Insect Karyotype Analysis 1617 - Natomas Unified School District
... have been traced to specific visible abnormalities of the chromosomes. ...
... have been traced to specific visible abnormalities of the chromosomes. ...
INDIAN LEARNERS OWN ACADEMY, KUWAIT CHAPTER
... 6. A test is performed to know whether the given plant is homozygous dominant or heterozygous. Name the test and phenotypic ratio of this test for a monohybrid cross. 7. Identify the sex of organism as male or female in which the sex chromosome are found as (i) ZW in bird (ii) XY in Drosophila (iii) ...
... 6. A test is performed to know whether the given plant is homozygous dominant or heterozygous. Name the test and phenotypic ratio of this test for a monohybrid cross. 7. Identify the sex of organism as male or female in which the sex chromosome are found as (i) ZW in bird (ii) XY in Drosophila (iii) ...
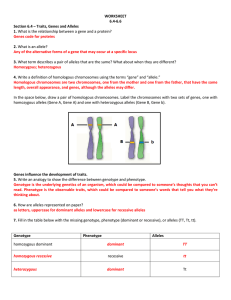
WORKSHEET 6.4-6.6 Section 6.4 – Traits, Genes and Alleles 1
... No. The two genes are unlikely to be separated by crossing over, so they will be inherited together. 4. Which does sexual reproduction create; new alleles or new combinations of alleles? New combinations of alleles 5. How is the production of unique genetic combinations an advantage to organisms and ...
... No. The two genes are unlikely to be separated by crossing over, so they will be inherited together. 4. Which does sexual reproduction create; new alleles or new combinations of alleles? New combinations of alleles 5. How is the production of unique genetic combinations an advantage to organisms and ...
Section 10.2 Summary – pages 263-273
... Homologous chromosomes • The two chromosomes of each pair in a diploid cell are called homologous chromosomes. • Each pair of homologous chromosomes has genes for the same traits. ...
... Homologous chromosomes • The two chromosomes of each pair in a diploid cell are called homologous chromosomes. • Each pair of homologous chromosomes has genes for the same traits. ...
An Introduction to Metabolism
... 8. State Mendel’s law of independent assortment in your own words. 9. Predict the results of a dihybrid cross and state the genotype and phenotypic ratios of the F2 generation using a Punnett square. 10. Cite examples of incomplete dominance and codominance 11. Explain how the phenotypic expression ...
... 8. State Mendel’s law of independent assortment in your own words. 9. Predict the results of a dihybrid cross and state the genotype and phenotypic ratios of the F2 generation using a Punnett square. 10. Cite examples of incomplete dominance and codominance 11. Explain how the phenotypic expression ...
Some chromosomal abnormalities that can be detected by
... making a protein that is involved in the development and maintenance of bone and brain tissue. Two specific mutations in the FGFR3 gene are responsible for almost all cases of achondroplasia. Researchers believe that these mutations cause the FGFR3 protein to be overly active, which interferes with ...
... making a protein that is involved in the development and maintenance of bone and brain tissue. Two specific mutations in the FGFR3 gene are responsible for almost all cases of achondroplasia. Researchers believe that these mutations cause the FGFR3 protein to be overly active, which interferes with ...
Cells and Chromosomes Note Sheet
... How are Sperm/Egg Cells Different From Other Cells In The Body o Most cells in the body have a full set of chromosomes, which means they have _______ chromosomes a piece. o However, two types of cells in the body do NOT have this usual number. These cells are either _____________ or ____________ c ...
... How are Sperm/Egg Cells Different From Other Cells In The Body o Most cells in the body have a full set of chromosomes, which means they have _______ chromosomes a piece. o However, two types of cells in the body do NOT have this usual number. These cells are either _____________ or ____________ c ...
Chapter 15 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... Sturtevant used the testcross design to map the relative position of three fruit fly genes, body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). ° The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. ° The recombination frequency between cn and vg is 9.5%. ° The recombination frequency between b and v ...
... Sturtevant used the testcross design to map the relative position of three fruit fly genes, body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). ° The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. ° The recombination frequency between cn and vg is 9.5%. ° The recombination frequency between b and v ...
Use case flow for use case: 2
... Use case flow for use case: 2 Query: Of those associations between gene expressions and SNP’s that are on the same chromosome (cis), are they preferentially 3’ or 5’? Precondition: The biomedical researcher has identified a set of correlations between expression levels and SNP’s: (Gene expressed, SN ...
... Use case flow for use case: 2 Query: Of those associations between gene expressions and SNP’s that are on the same chromosome (cis), are they preferentially 3’ or 5’? Precondition: The biomedical researcher has identified a set of correlations between expression levels and SNP’s: (Gene expressed, SN ...
Maurice Godfrey, Ph.D. University of Nebraska Medical Center
... “baby” pile. Now each Reebop baby will have 14 chromosomes just like Mom and Dad did. But half will be red and half green, indicating that half came from Mom and half came from Dad. 4. Line up the chromosomes contributed to the baby by the Mom and Dad in pairs of similar size, letter side up. You wi ...
... “baby” pile. Now each Reebop baby will have 14 chromosomes just like Mom and Dad did. But half will be red and half green, indicating that half came from Mom and half came from Dad. 4. Line up the chromosomes contributed to the baby by the Mom and Dad in pairs of similar size, letter side up. You wi ...
Essential Genetics for Horsemen
... present, whether a foal has one ‘E’ or two (Ee or EE). The ‘e’ allele produces a chestnut (red) base color, but if an ‘E’ allele is present with an ‘e’ the base coat color is black (Ee). For a chestnut color to be produced, the foal needs to have two copies of the ‘e’ allele (ee). So, a foal that r ...
... present, whether a foal has one ‘E’ or two (Ee or EE). The ‘e’ allele produces a chestnut (red) base color, but if an ‘E’ allele is present with an ‘e’ the base coat color is black (Ee). For a chestnut color to be produced, the foal needs to have two copies of the ‘e’ allele (ee). So, a foal that r ...
LP7 - Inheritance and Genetic Diseases
... Neurofibromatosis is an autosomal dominant disorder, which means only one copy of the affected gene is needed for the disorder to develop. Therefore, if only one parent has neurofibromatosis, his or her children have a 50% chance of developing the condition as well. The severity in affected individu ...
... Neurofibromatosis is an autosomal dominant disorder, which means only one copy of the affected gene is needed for the disorder to develop. Therefore, if only one parent has neurofibromatosis, his or her children have a 50% chance of developing the condition as well. The severity in affected individu ...
Chapter 15 – The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... Mary Lyon, a British geneticist, demonstrated that selection of which X chromosome will form the Barr body occurs randomly and independently in embryonic cells at the time of X inactivation. ...
... Mary Lyon, a British geneticist, demonstrated that selection of which X chromosome will form the Barr body occurs randomly and independently in embryonic cells at the time of X inactivation. ...
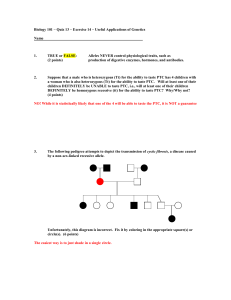
Biology 101 – Quiz 13 – Exercise 14 – Useful Applications of Genetics
... Edna will be a hemophiliac? What are the chances that Edna will be a carrier of the hemophilia trait? (5 points) Since Billy Bob is not a hemophiliac, Edna will receive an X chromosome with the dominant healthy allele from him. Thus there is no chance of her being a hemophiliac. However, she has a 5 ...
... Edna will be a hemophiliac? What are the chances that Edna will be a carrier of the hemophilia trait? (5 points) Since Billy Bob is not a hemophiliac, Edna will receive an X chromosome with the dominant healthy allele from him. Thus there is no chance of her being a hemophiliac. However, she has a 5 ...
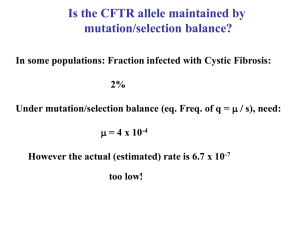
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
Chromosomes, Chromosome Anomalies
... miscarriage. The only autosomal monosomy in humans which might be compatible with life is monosomy 21, but this is still a debatable situation. Non-disjunction can affect each pair of chromosomes and rarely more than one pair may be involved in the same meiotic cell (multiple non-disjunction most of ...
... miscarriage. The only autosomal monosomy in humans which might be compatible with life is monosomy 21, but this is still a debatable situation. Non-disjunction can affect each pair of chromosomes and rarely more than one pair may be involved in the same meiotic cell (multiple non-disjunction most of ...
Genetic Explanation 2: the role a specific gene defect
... more prevalent in men; women are protected from the faulty gene by their other X chromosome. The warrior gene is simply a shorter, less active version of a gene allele (an alternative form of a gene caused by a mutation) on the X chromosome known as the MAO-A gene. If people inherit the warrior gene ...
... more prevalent in men; women are protected from the faulty gene by their other X chromosome. The warrior gene is simply a shorter, less active version of a gene allele (an alternative form of a gene caused by a mutation) on the X chromosome known as the MAO-A gene. If people inherit the warrior gene ...
here
... b) Using the data in Figure 5, calculate the probability that a mother of 40 years of age will give birth to a child with a chromosomal abnormality other than trisomy 21. The probability is approximately 0.8%. 3) Only a small number of possible chromosomal abnormalities are ever found among live bir ...
... b) Using the data in Figure 5, calculate the probability that a mother of 40 years of age will give birth to a child with a chromosomal abnormality other than trisomy 21. The probability is approximately 0.8%. 3) Only a small number of possible chromosomal abnormalities are ever found among live bir ...
Test (1) If there are four children in a family with a different blood
... recombination frequency of 11% between the loci. The two alleles at the ALK locus will be denoted A and a. The three alleles at the ABO blood group locus will be denoted I A, IB and i. The parent has blood type 0 and alkaptonuria, another – blood type A and normal (heterozygous for both loci). What ...
... recombination frequency of 11% between the loci. The two alleles at the ALK locus will be denoted A and a. The three alleles at the ABO blood group locus will be denoted I A, IB and i. The parent has blood type 0 and alkaptonuria, another – blood type A and normal (heterozygous for both loci). What ...
Chapter 18
... • What is meiosis used for and in what cells? • Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis. • Compare and contrast spermatogenesis and oogenesis. • What are trisomy and monosomy? • What most often causes these changes in chromosome number? • What are the syndromes associated with changes in sex chromo ...
... • What is meiosis used for and in what cells? • Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis. • Compare and contrast spermatogenesis and oogenesis. • What are trisomy and monosomy? • What most often causes these changes in chromosome number? • What are the syndromes associated with changes in sex chromo ...
Chapter 9 - Personal
... – Shows the inheritance of a trait in a family through multiple generations – Demonstrates dominant or recessive inheritance – Can also be used to deduce genotypes of family members ...
... – Shows the inheritance of a trait in a family through multiple generations – Demonstrates dominant or recessive inheritance – Can also be used to deduce genotypes of family members ...