Chapter 02: Operating System Overview
... • Processor must wait for I/O instruction to complete before proceeding ...
... • Processor must wait for I/O instruction to complete before proceeding ...
Operating Systems Design
... As you can imagine, batching was a big pain You submit a job, you twiddle your thumbs for a while, you get the output, see a bug, try to figure out what went wrong, resubmit the job, etc. Even running production programs was difficult in this environment ...
... As you can imagine, batching was a big pain You submit a job, you twiddle your thumbs for a while, you get the output, see a bug, try to figure out what went wrong, resubmit the job, etc. Even running production programs was difficult in this environment ...
Syllabus - Marwadi University
... Study of Basic commands of Linux/UNIX. Study of Advance commands and filters of Linux/UNIX. Write a shell script to reverse a number supplied by a user. Write a shell script to find the smallest of three numbers. Write a shell script to find the largest among the 3 given numbers. Write Shell script ...
... Study of Basic commands of Linux/UNIX. Study of Advance commands and filters of Linux/UNIX. Write a shell script to reverse a number supplied by a user. Write a shell script to find the smallest of three numbers. Write a shell script to find the largest among the 3 given numbers. Write Shell script ...
Chapter 8: Operating Systems and Utility Programs
... – The operating system assigned a portion of storage medium, i.e. a hard disk, to function as additional RAM – Slower than RAM – Swap file • The part of the hard disk used for virtual memory • Paging is the technique of swapping items between memory and storage – It’s a time consuming process ...
... – The operating system assigned a portion of storage medium, i.e. a hard disk, to function as additional RAM – Slower than RAM – Swap file • The part of the hard disk used for virtual memory • Paging is the technique of swapping items between memory and storage – It’s a time consuming process ...
Operating System Overview
... • Processor must wait for I/O instruction to complete before preceding ...
... • Processor must wait for I/O instruction to complete before preceding ...
08 Operating System Support
... When working with a large process execution may be confined to a small section of a program (subroutine) It is better use of memory to load in just a few pages If the program references data or branches to an instruction on a page not in main memory, a page fault is triggered which tells the OS to b ...
... When working with a large process execution may be confined to a small section of a program (subroutine) It is better use of memory to load in just a few pages If the program references data or branches to an instruction on a page not in main memory, a page fault is triggered which tells the OS to b ...
Southeastern University
... –operating system code is executed as a separate entity that operates in privileged mode Execution Within User Processes –operating system software within context of a user process –process executes in privileged mode when executing operating system code Process-Based Operating System –major ker ...
... –operating system code is executed as a separate entity that operates in privileged mode Execution Within User Processes –operating system software within context of a user process –process executes in privileged mode when executing operating system code Process-Based Operating System –major ker ...
Operating Systems
... concerning the modern operating systems design. More specifically, the operating system most important functions and their main associated concepts are presented - process management, process communication, deadlocks, memory management, file systems and input/output management. Practical knowledge o ...
... concerning the modern operating systems design. More specifically, the operating system most important functions and their main associated concepts are presented - process management, process communication, deadlocks, memory management, file systems and input/output management. Practical knowledge o ...
System Structures
... Protection and security - The owners of information stored in a multiuser or networked computer system may want to control use of that information, concurrent processes should not interfere with each other ...
... Protection and security - The owners of information stored in a multiuser or networked computer system may want to control use of that information, concurrent processes should not interfere with each other ...
2005-07.pdf
... memory manager and the file system manager, and the operating system kernel. The system task is allowed to modify kernel-level data structures, such as the memory map. However, thses structures are actually maintained by user-level processes. The latter cannot directly modify kernel-level data, and ...
... memory manager and the file system manager, and the operating system kernel. The system task is allowed to modify kernel-level data structures, such as the memory map. However, thses structures are actually maintained by user-level processes. The latter cannot directly modify kernel-level data, and ...
390aLecture01_15au
... • output: goes to console • errors can also be printed (by default, sent to console like output) • parameters vs. input parameters: before Enter is pressed; sent in by shell input: after Enter is pressed; sent in by user ...
... • output: goes to console • errors can also be printed (by default, sent to console like output) • parameters vs. input parameters: before Enter is pressed; sent in by shell input: after Enter is pressed; sent in by user ...
390aLecture01_15sp
... • output: goes to console • errors can also be printed (by default, sent to console like output) • parameters vs. input parameters: before Enter is pressed; sent in by shell input: after Enter is pressed; sent in by user ...
... • output: goes to console • errors can also be printed (by default, sent to console like output) • parameters vs. input parameters: before Enter is pressed; sent in by shell input: after Enter is pressed; sent in by user ...
Intro to UNIX - Regis University: Academic Web Server for Faculty
... • More than one user can run at the same time and each user can run more than one task at the same time • In Unix, each program is started as a process. – A process is a program in execution. • Usually only one copy of a program, but there may be many processes running the same program. • Each inter ...
... • More than one user can run at the same time and each user can run more than one task at the same time • In Unix, each program is started as a process. – A process is a program in execution. • Usually only one copy of a program, but there may be many processes running the same program. • Each inter ...
Unix – Linux
... • The Operating System – Acts as the interface to all software, hardware, and users of a computer. – Requires a file system for organizing files – Must maintain its viability to prevent other programs, hardware, users, etc, from impeding its operation. Unix and its variants will accomplish the above ...
... • The Operating System – Acts as the interface to all software, hardware, and users of a computer. – Requires a file system for organizing files – Must maintain its viability to prevent other programs, hardware, users, etc, from impeding its operation. Unix and its variants will accomplish the above ...
2.01
... loaders, linkage editors, and overlay-loaders, debugging systems for higher-level and machine language Communications - Provide the mechanism for creating virtual connections among processes, users, and computer systems Allow users to send messages to one another’s screens, browse web pages, sen ...
... loaders, linkage editors, and overlay-loaders, debugging systems for higher-level and machine language Communications - Provide the mechanism for creating virtual connections among processes, users, and computer systems Allow users to send messages to one another’s screens, browse web pages, sen ...
CHAP10
... • Correctness of the system depends not only on the logical result of the computation but also on the time at which the results are produced ...
... • Correctness of the system depends not only on the logical result of the computation but also on the time at which the results are produced ...
Homework 1 Solutions
... 10. On all current computers, at least part of the interrupt handlers are written in assembly language. Why? There are actions (such as saving registers) that happen while an interrupt is being handled. These actions need to be written in assembly because they cannot be expressed in higher level lan ...
... 10. On all current computers, at least part of the interrupt handlers are written in assembly language. Why? There are actions (such as saving registers) that happen while an interrupt is being handled. These actions need to be written in assembly because they cannot be expressed in higher level lan ...
ppt
... • v2.2 (v2.2.14 in Fossil lab) • 1,000,000 lines of code • 7-10 million users • Estimated growth 25%/year through 2003 – all others, 10% combined ...
... • v2.2 (v2.2.14 in Fossil lab) • 1,000,000 lines of code • 7-10 million users • Estimated growth 25%/year through 2003 – all others, 10% combined ...
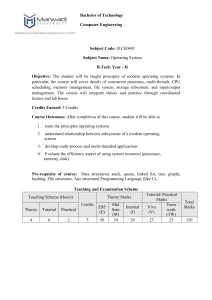
Course objectives: 1. To learn the fundamentals of Operating
... Case Study: Linux system, Design Principles, kernel modules, process management, scheduling, memory management, file system, input and output, inter process communication, network structure, security ...
... Case Study: Linux system, Design Principles, kernel modules, process management, scheduling, memory management, file system, input and output, inter process communication, network structure, security ...
Ch-1_3431
... User (protected) Mode: CPU is executing user-level application Kernel (supervisor, system, privileged) Mode: ...
... User (protected) Mode: CPU is executing user-level application Kernel (supervisor, system, privileged) Mode: ...
Lecture for Chapter 2.3 (Fall 09)
... Resource allocation must be properly done when multiple users or multiple jobs running concurrently. ...
... Resource allocation must be properly done when multiple users or multiple jobs running concurrently. ...
Chapter 1 Computer System Overview
... memory divided by the page size - Page frame = size of memory/page size • How many bits does the system use to maintain the displacement = as much as page size • Ex: contains 128MB of main memory and has a page size of 8KB ...
... memory divided by the page size - Page frame = size of memory/page size • How many bits does the system use to maintain the displacement = as much as page size • Ex: contains 128MB of main memory and has a page size of 8KB ...