11-2 Genetics and Probability
... chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis – Abnormal number of chromosomes find their way into gametes ...
... chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis – Abnormal number of chromosomes find their way into gametes ...
Biology Name_____________________________________
... In order to survive, the cancer cell has learned to either spread its proteins to other cells (metastasizing) or rebuild new blood vessels into the tumor (angiogenesis). ...
... In order to survive, the cancer cell has learned to either spread its proteins to other cells (metastasizing) or rebuild new blood vessels into the tumor (angiogenesis). ...
Research News
... we are composed more of bacterial cells than human cells, that our bacterial profiles may define our individuality and influence our health as much as our own genes, must have left the average mycologist wondering, “What about the human Mycobiome?” The latest on-line issue of Nature includes an arti ...
... we are composed more of bacterial cells than human cells, that our bacterial profiles may define our individuality and influence our health as much as our own genes, must have left the average mycologist wondering, “What about the human Mycobiome?” The latest on-line issue of Nature includes an arti ...
sex-linked genes
... • PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME AND ANGELMAN SYDROME-SAME DELETION ON #15; SYMPTOMS DIFFER DEPENDING ON WHICH PARENT GAVE THE GENE • FRAGILE-X SYNDROME - AN ABNORMAL X CHROMOSOME, THE TIP HANGS ON THE REST OF THE CHROMOSOME BY A THIN DNA THREAD; MOST COMMON GENETIC CAUSE OF MENTAL RETARDATION; MORE LIKELY T ...
... • PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME AND ANGELMAN SYDROME-SAME DELETION ON #15; SYMPTOMS DIFFER DEPENDING ON WHICH PARENT GAVE THE GENE • FRAGILE-X SYNDROME - AN ABNORMAL X CHROMOSOME, THE TIP HANGS ON THE REST OF THE CHROMOSOME BY A THIN DNA THREAD; MOST COMMON GENETIC CAUSE OF MENTAL RETARDATION; MORE LIKELY T ...
biol b242 chromosomal evolution
... Across the whole Lepidoptera, a group of similar age to the mammals, there is quite a bit of variability (10-100s!), but ...
... Across the whole Lepidoptera, a group of similar age to the mammals, there is quite a bit of variability (10-100s!), but ...
Cell characteristics
... anaphase. The cell membrane starts to constrict around the middle. The ring of spindles pinches and separtates the two newly formed nuclei and half of organelles go into different cells. The newly formed cells may have different size and number of organelles but the same number of chromosomes. ...
... anaphase. The cell membrane starts to constrict around the middle. The ring of spindles pinches and separtates the two newly formed nuclei and half of organelles go into different cells. The newly formed cells may have different size and number of organelles but the same number of chromosomes. ...
Biology Midterm Exam Review Guide
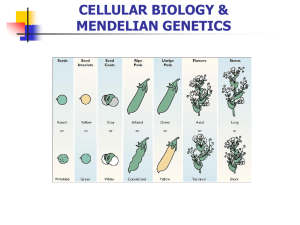
... 16. In certain species of rabbit, when a black rabbit is crossed with a white rabbit, a grey rabbit is produced. Show the results of a cross between a white rabbit and a grey rabbit. Include the genotypes of the parents, the punnett square, and genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring (including %) ...
... 16. In certain species of rabbit, when a black rabbit is crossed with a white rabbit, a grey rabbit is produced. Show the results of a cross between a white rabbit and a grey rabbit. Include the genotypes of the parents, the punnett square, and genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring (including %) ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH11.QXD
... b. The two daughter cells produced by meiosis I still have the two complete sets of chromosomes, as does a diploid cell. c. During anaphase II, the paired chromatids separate. d. After meiosis II, the four daughter cells contain the diploid number of chromosomes. ...
... b. The two daughter cells produced by meiosis I still have the two complete sets of chromosomes, as does a diploid cell. c. During anaphase II, the paired chromatids separate. d. After meiosis II, the four daughter cells contain the diploid number of chromosomes. ...
Lecture: Mendelian Genetics
... Monogenic = Trait coded for by a single gene (ex. Taster trait for “PTC”) Polygenic = Trait coded for by more than one gene (ex. Skin color) ...
... Monogenic = Trait coded for by a single gene (ex. Taster trait for “PTC”) Polygenic = Trait coded for by more than one gene (ex. Skin color) ...
Cellular Reproduction - Genomic DNA
... called a nucleoid. Some prokaryotes also have smaller loops of DNA called plasmids that are not essential for normal growth. Bacteria can exchange these plasmids with other bacteria, sometimes receiving bene cial new genes that the recipient can add to their chromosomal DNA. Antibiotic resistance is ...
... called a nucleoid. Some prokaryotes also have smaller loops of DNA called plasmids that are not essential for normal growth. Bacteria can exchange these plasmids with other bacteria, sometimes receiving bene cial new genes that the recipient can add to their chromosomal DNA. Antibiotic resistance is ...
CrossingOver - sciencewithskinner
... in the pictures to the right. These alleles code for 3 different traits. What is the genotype of this person for each trait? ______________________ 3. Use the figure to the right as a guide in joining and labeling these model chromatids. Although there are four chromatids, assume that they started o ...
... in the pictures to the right. These alleles code for 3 different traits. What is the genotype of this person for each trait? ______________________ 3. Use the figure to the right as a guide in joining and labeling these model chromatids. Although there are four chromatids, assume that they started o ...
why care
... Mitosis retains genetic information because it maintains chromosome number through nuclear division. ...
... Mitosis retains genetic information because it maintains chromosome number through nuclear division. ...
Non - Mendelian Genetics
... – _________ allele forms • Both alleles can _______ , meaning both _____ at the ______ time • More than _____ possible alleles exist in a population – Speckled sussex chickens, black and white feathers ...
... – _________ allele forms • Both alleles can _______ , meaning both _____ at the ______ time • More than _____ possible alleles exist in a population – Speckled sussex chickens, black and white feathers ...
genes notes
... Can be arranged in an infinite number of ways. Within these molecules is the genetic code that determines all the characteristics of an organism. Different segments of the chromosomes control different traits that are expressed in the organism. ...
... Can be arranged in an infinite number of ways. Within these molecules is the genetic code that determines all the characteristics of an organism. Different segments of the chromosomes control different traits that are expressed in the organism. ...
File - Mr Andrews` Science Space!
... 8 Biological concepts and processes relating to variation in phenotypes as adaptive features will be selected from: • inheritable and non-inheritable variations that exist within a group of living organisms • differing rates of survival by various members of a group may depend on their phenotype • t ...
... 8 Biological concepts and processes relating to variation in phenotypes as adaptive features will be selected from: • inheritable and non-inheritable variations that exist within a group of living organisms • differing rates of survival by various members of a group may depend on their phenotype • t ...
Heredity Inherited Traits - Saint Mary Catholic School
... Sex Cells are Haploid or Half • The gametes are the sex cells of the parents. When formed they undergo meiosis. In the process, the chromosomes are duplicated, then separated and packaged as separate sets in the sex cells. • If this were not the case, the number of chromosomes would double every ti ...
... Sex Cells are Haploid or Half • The gametes are the sex cells of the parents. When formed they undergo meiosis. In the process, the chromosomes are duplicated, then separated and packaged as separate sets in the sex cells. • If this were not the case, the number of chromosomes would double every ti ...
ap-biology-big-idea-3-review-answers
... bad? Provide an example of a good mutation for bacteria (consider hand sanitizer usage). Environment. ...
... bad? Provide an example of a good mutation for bacteria (consider hand sanitizer usage). Environment. ...
File
... Amniocentesis in 2nd trimester sample of embryo cells from fluid stain & photograph chromosomes ...
... Amniocentesis in 2nd trimester sample of embryo cells from fluid stain & photograph chromosomes ...
GENERAL ZOOLOGY LECTURE EXAM 2
... 4. In order for DNA polymerase to function on a single strand of DNA, it requires a short piece of ribonucleic acid referred to as a: a. mRNA b. tRNA c. rRNA d. small subunit of the ribosome e. primer 5. During which phase do the centrosomes of a cell duplicate? a. G1 of interphase b. S of interphas ...
... 4. In order for DNA polymerase to function on a single strand of DNA, it requires a short piece of ribonucleic acid referred to as a: a. mRNA b. tRNA c. rRNA d. small subunit of the ribosome e. primer 5. During which phase do the centrosomes of a cell duplicate? a. G1 of interphase b. S of interphas ...
Ch8 Cell Reproduction
... reforms around each set of chromosomes • Four haploid (n) cells – each about ¼ the size of original cell ...
... reforms around each set of chromosomes • Four haploid (n) cells – each about ¼ the size of original cell ...
What distinguishes a plant cell from other cells?
... BASIC DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MEIOSIS & MITOSIS Chromosome number is reduced: diploid to haploid ...
... BASIC DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MEIOSIS & MITOSIS Chromosome number is reduced: diploid to haploid ...
Mukai, T.
... are produced in crosses of Girardot with 13 geographical strains of D. equinoxialis. However, crosses with three otlier D. equinoxialis strains (Belem 0, Iana, and Puerto Rico) produce offspring which are sterile - both males and females. The second strain, called Belem K, was collected in Belem, No ...
... are produced in crosses of Girardot with 13 geographical strains of D. equinoxialis. However, crosses with three otlier D. equinoxialis strains (Belem 0, Iana, and Puerto Rico) produce offspring which are sterile - both males and females. The second strain, called Belem K, was collected in Belem, No ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.