Park, chapter 3 (Evolutionary Genetics)
... If Mendel possessed neither the technology nor the background knowledge to understand DNA and the genome, what then did he discover about the processes of genetics? We refer to his contribution as Mendelian genetics. It involves the basic laws of inheritance, which we will take up in the next sectio ...
... If Mendel possessed neither the technology nor the background knowledge to understand DNA and the genome, what then did he discover about the processes of genetics? We refer to his contribution as Mendelian genetics. It involves the basic laws of inheritance, which we will take up in the next sectio ...
Genetics Concept Inventory
... Composition of DNA Nature of linked genes Products of translation are proteins Nature of the genetic code Cellular structure that contain DNA Nature of allele Composition of chromosomes Identification of drawing with two alleles on chromosomes within a diploid cell Where DNA is found in animal cells ...
... Composition of DNA Nature of linked genes Products of translation are proteins Nature of the genetic code Cellular structure that contain DNA Nature of allele Composition of chromosomes Identification of drawing with two alleles on chromosomes within a diploid cell Where DNA is found in animal cells ...
practice exam 3_answer key
... a. Genetic diversity increases due to random fertilization. b. Genetic diversity increases due to independent orientation of chromosomes at metaphase I. c. Genetic diversity increases by mitosis. d. Genetic diversity increases by crossing over during meiosis. e. Genetic diversity increases by recomb ...
... a. Genetic diversity increases due to random fertilization. b. Genetic diversity increases due to independent orientation of chromosomes at metaphase I. c. Genetic diversity increases by mitosis. d. Genetic diversity increases by crossing over during meiosis. e. Genetic diversity increases by recomb ...
Chapter 19-Population Genetics and Speciation
... SYMPATRIC SPECIATION: production of new species within a single population, usually not in species that reproduce sexually b/c reprod barrier must be formed; usu change in # of chromosomes. New species thus can be formed: ...
... SYMPATRIC SPECIATION: production of new species within a single population, usually not in species that reproduce sexually b/c reprod barrier must be formed; usu change in # of chromosomes. New species thus can be formed: ...
AP Study Guide Exam 3
... activates cellular proteins) MPF= used for G2 checkpoint (maturation/mitosis promoting factor), APC= used for M checkpoint( Anaphase promoting complex) 21. CDK’s and Cyclin drive cell from one phase to the next in cell cycle. These proteins have been highly conserved through evolution. See same gene ...
... activates cellular proteins) MPF= used for G2 checkpoint (maturation/mitosis promoting factor), APC= used for M checkpoint( Anaphase promoting complex) 21. CDK’s and Cyclin drive cell from one phase to the next in cell cycle. These proteins have been highly conserved through evolution. See same gene ...
procedure
... Sordaria fimicola is an ascomycete fungus that can be used to demonstrate the results of crossing over during meiosis. Sordaria is a haploid organism for most of its life cycle. It becomes diploid only when the fusion of the mycelia of two different strains results in the fusion of the two different ...
... Sordaria fimicola is an ascomycete fungus that can be used to demonstrate the results of crossing over during meiosis. Sordaria is a haploid organism for most of its life cycle. It becomes diploid only when the fusion of the mycelia of two different strains results in the fusion of the two different ...
cell cycle - Montville.net
... chromosomes are stretched out very thin to allow surfaces for the various chemical reactions that involve chromosomes to take place. When the nucleus is stained and examined, it appears uniformly colored and the chromosomes collectively are termed chromatin. It is critical to remember that even thou ...
... chromosomes are stretched out very thin to allow surfaces for the various chemical reactions that involve chromosomes to take place. When the nucleus is stained and examined, it appears uniformly colored and the chromosomes collectively are termed chromatin. It is critical to remember that even thou ...
lab 10 - genetics
... • Your body produces antibodies to any protein that you don’t have the gene for ...
... • Your body produces antibodies to any protein that you don’t have the gene for ...
File
... A burglar broke into a house. The burglar cut his hand on some broken glass. Scientists extracted DNA from the blood on the broken glass. The scientists analysed the DNA from the glass and DNA from three suspects, A, B and C. The scientists used a method called DNA fingerprinting. Figure 2 shows the ...
... A burglar broke into a house. The burglar cut his hand on some broken glass. Scientists extracted DNA from the blood on the broken glass. The scientists analysed the DNA from the glass and DNA from three suspects, A, B and C. The scientists used a method called DNA fingerprinting. Figure 2 shows the ...
Amoeba Sisters: Video Recap
... 9. Suzy knows that an individual’s sex is determined by sex chromosomes. She knows that females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y chromosome. She creates the Punnett square cross below to show sex inheritance. She wants to know which parent determines the sex of a baby---is it th ...
... 9. Suzy knows that an individual’s sex is determined by sex chromosomes. She knows that females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y chromosome. She creates the Punnett square cross below to show sex inheritance. She wants to know which parent determines the sex of a baby---is it th ...
Multiple Alleles, Polygenic and Sex
... - The human Y chromosome is much smaller and appears to contain only few genes. - Father determines the sex of the offspring - The chance is always 50-50 for either sex - A recessive gene has no matching gene on the Y - More Sex linked disorders are found in males Sex linked disorders: 1. Colorblind ...
... - The human Y chromosome is much smaller and appears to contain only few genes. - Father determines the sex of the offspring - The chance is always 50-50 for either sex - A recessive gene has no matching gene on the Y - More Sex linked disorders are found in males Sex linked disorders: 1. Colorblind ...
MCDB 1041 Activity 3: Thinking about how “linkage” affects the
... same chromosome. By looking at large pedigrees of families with genetic diseases, they were able to see some patterns (for example, finding that hemophilia and color blindness are both on the X chromosome). However, this turned out to be an inefficient way of “mapping” the locations of genes because ...
... same chromosome. By looking at large pedigrees of families with genetic diseases, they were able to see some patterns (for example, finding that hemophilia and color blindness are both on the X chromosome). However, this turned out to be an inefficient way of “mapping” the locations of genes because ...
Chapter 14 - The Biology Corner
... If a person with type AB is married to someone with type O blood, what blood types are possible in their children? ...
... If a person with type AB is married to someone with type O blood, what blood types are possible in their children? ...
Study Guide for Test
... phenotypes. Be able to identify types of mutations and events that may occur as a result of each type of mutation. Be able to explain the products of mitosis and how they compare to the original cell. ...
... phenotypes. Be able to identify types of mutations and events that may occur as a result of each type of mutation. Be able to explain the products of mitosis and how they compare to the original cell. ...
Lecture 7 - Brandeis Life Sciences
... male parent, it is expressed in the heart and no other tissue. If it is inherited from the female parent, it is not expressed at all. This pattern of expression correlates precisely with a parentally imprinted methylation state evident in all tissues. Methylation of the transgene is acquired by its ...
... male parent, it is expressed in the heart and no other tissue. If it is inherited from the female parent, it is not expressed at all. This pattern of expression correlates precisely with a parentally imprinted methylation state evident in all tissues. Methylation of the transgene is acquired by its ...
Evolution and Biology II
... times – varies by species – called the Hayflick limit, mice = 15, humans = 50, tortoise = 110 Telomeres at end of chromosomes are needed to reproduce successfully, but get shorter each time until gone Telomerase is an enzyme which will allow these to maintain length, but is usually switched off in c ...
... times – varies by species – called the Hayflick limit, mice = 15, humans = 50, tortoise = 110 Telomeres at end of chromosomes are needed to reproduce successfully, but get shorter each time until gone Telomerase is an enzyme which will allow these to maintain length, but is usually switched off in c ...
Supplemental material
... I, cells with more than three large DNA clumps; metaphase I, cells with more than one DNA clump; anaphase I, cells with unequal poles or one or more laggards. (C) Meiosis II. Sister chromatids separate precociously at metaphase II (MII) in soloZ2-0198/Df(2L)A267 spermatocytes and segregate unequally ...
... I, cells with more than three large DNA clumps; metaphase I, cells with more than one DNA clump; anaphase I, cells with unequal poles or one or more laggards. (C) Meiosis II. Sister chromatids separate precociously at metaphase II (MII) in soloZ2-0198/Df(2L)A267 spermatocytes and segregate unequally ...
powerpoint - Marric.us
... Mendel realized that there must be two sets of instructions for each characteristic and that each parent would donate one set of instructions to offspring Now we know that the sets of instructions are genes and that a fertilized egg would have two forms of the same gene for every characteristics and ...
... Mendel realized that there must be two sets of instructions for each characteristic and that each parent would donate one set of instructions to offspring Now we know that the sets of instructions are genes and that a fertilized egg would have two forms of the same gene for every characteristics and ...
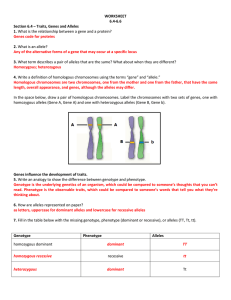
WORKSHEET 6.4-6.6 Section 6.4 – Traits, Genes and Alleles 1
... 9. The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes is called Crossing over 10. The tendency for two genes that are located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together is called. ...
... 9. The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes is called Crossing over 10. The tendency for two genes that are located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together is called. ...
Genetics
... of probability • Mendel’s laws reflect the laws of probability. • The probability scale ranged from zero (an event with no chance of occurring) to one (an event that is certain to occur). • The probability of tossing heads with a normal coin is ½. • The probability of rolling a 3 with a six-sided di ...
... of probability • Mendel’s laws reflect the laws of probability. • The probability scale ranged from zero (an event with no chance of occurring) to one (an event that is certain to occur). • The probability of tossing heads with a normal coin is ½. • The probability of rolling a 3 with a six-sided di ...
ANIMAL GENETICS
... An animals performance and analysis of ancestry and progeny are valuable tools in determining the animals use for breeding. This information is obtained through the use of data collection and ...
... An animals performance and analysis of ancestry and progeny are valuable tools in determining the animals use for breeding. This information is obtained through the use of data collection and ...
Biology Unit Review
... 123. In carnations, neither the allele for red flower colour nor the allele for white flower colour are dominant. If a purebred red carnation is crossed with a purebred white carnation, what are the offspring like? ______________________________________________________ 124. A homozygous red carnatio ...
... 123. In carnations, neither the allele for red flower colour nor the allele for white flower colour are dominant. If a purebred red carnation is crossed with a purebred white carnation, what are the offspring like? ______________________________________________________ 124. A homozygous red carnatio ...
Sex-linked disorder
... C. an increase in deciduous tree species. D. an increase in nighttime temperatures. ...
... C. an increase in deciduous tree species. D. an increase in nighttime temperatures. ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.