Light Study Guide
... The only thing we can really ________ is __________. Because of this, it has been studied for many years. Some of the ancients, thought that light was made up of tiny __________________ that entered the eye. Others, like P________, S______________ and E__________, thought that vision resulted from s ...
... The only thing we can really ________ is __________. Because of this, it has been studied for many years. Some of the ancients, thought that light was made up of tiny __________________ that entered the eye. Others, like P________, S______________ and E__________, thought that vision resulted from s ...
Polarization of light II
... unpolarised beam is made to incident at an interface at Brewster angle. The reflected beam will contain the s component only. In this experiment , you will study the variation of intensity as a function of angle of incidence for p as well s polarized light and will measure the Brewster angle for air ...
... unpolarised beam is made to incident at an interface at Brewster angle. The reflected beam will contain the s component only. In this experiment , you will study the variation of intensity as a function of angle of incidence for p as well s polarized light and will measure the Brewster angle for air ...
Lecture 21 - Lehigh University
... The main factor which reduces image quality of an objective lens is the double dependence of its parameters on wavelength and temperature. Thus, in addition to spherical aberrations, both chromatic and temperature aberrations need to be carefully corrected in high performance optical systems. For e ...
... The main factor which reduces image quality of an objective lens is the double dependence of its parameters on wavelength and temperature. Thus, in addition to spherical aberrations, both chromatic and temperature aberrations need to be carefully corrected in high performance optical systems. For e ...
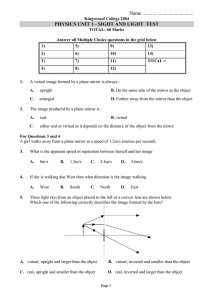
Wave Light Test
... Draw two rays from the light source to the points A and B. Continue these rays to show their path after reflection. Show any construction. ...
... Draw two rays from the light source to the points A and B. Continue these rays to show their path after reflection. Show any construction. ...
CT_optics
... A group of sprinters gather at point P on a parking lot bordering a beach. They must run across the parking lot to a point Q on the beach as quickly as possible. Which path from P to Q takes the least time? You should consider the relative speeds of the sprinters on the hard surface of the parking ...
... A group of sprinters gather at point P on a parking lot bordering a beach. They must run across the parking lot to a point Q on the beach as quickly as possible. Which path from P to Q takes the least time? You should consider the relative speeds of the sprinters on the hard surface of the parking ...
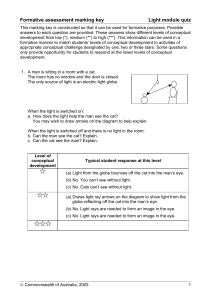
Formative assessment marking key: Light Module Quiz
... answers to each question are provided. These answers show different levels of conceptual development from low (*), medium (**) to high (***). This information can be used in a formative manner to match students’ levels of conceptual development to activities of appropriate conceptual challenge desig ...
... answers to each question are provided. These answers show different levels of conceptual development from low (*), medium (**) to high (***). This information can be used in a formative manner to match students’ levels of conceptual development to activities of appropriate conceptual challenge desig ...
Design technique for all-dielectric non
... advantage of a wider non−polarizing spectral band, but there are other applications such as systems that use high power densities of light (e.g. focused laser beam) or systems that are used in unfavorable environmental conditions (e.g. excessive humidity or salinity), when all−dielectric package coa ...
... advantage of a wider non−polarizing spectral band, but there are other applications such as systems that use high power densities of light (e.g. focused laser beam) or systems that are used in unfavorable environmental conditions (e.g. excessive humidity or salinity), when all−dielectric package coa ...
Critical angle - Kelso High School
... 2. What is meant by the frequency of a wave and give its unit? 3. Define the period of a wave? 4. Give two equations to calculate the velocity of a wave. 5. What is refraction? 6. Draw a diagram of a light wave being refracted, going from air into glass. Mark on the normal, the incident and refracte ...
... 2. What is meant by the frequency of a wave and give its unit? 3. Define the period of a wave? 4. Give two equations to calculate the velocity of a wave. 5. What is refraction? 6. Draw a diagram of a light wave being refracted, going from air into glass. Mark on the normal, the incident and refracte ...
Liquid Crystals
... Twisted Nematics and Light • The two components will experience different refraction indices, because both the two indices of refraction are perpendicular to one another and the two components of the wave are perpendicular to one another. • Therefore, by the very definition of refraction indices, o ...
... Twisted Nematics and Light • The two components will experience different refraction indices, because both the two indices of refraction are perpendicular to one another and the two components of the wave are perpendicular to one another. • Therefore, by the very definition of refraction indices, o ...
concave lens
... The transparent glass allows objects to be seen through it (a). The translucent lamp shade allows light to pass through, although the lightbulb source itself is not visible (b). The opaque tarp covers the statue, preventing the statue from being seen (c). ...
... The transparent glass allows objects to be seen through it (a). The translucent lamp shade allows light to pass through, although the lightbulb source itself is not visible (b). The opaque tarp covers the statue, preventing the statue from being seen (c). ...
revision_foundation_..
... The transmission of light through a glass fibre is one of the most important applications of total internal reflection. There is no energy lost at the reflecting surface, therefore it is possible to send a light wave along a glass fibre and for the light to be reflected millions of times without an ...
... The transmission of light through a glass fibre is one of the most important applications of total internal reflection. There is no energy lost at the reflecting surface, therefore it is possible to send a light wave along a glass fibre and for the light to be reflected millions of times without an ...
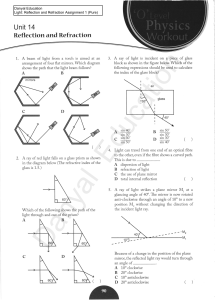
Assignment 1A
... photographer wishes to take pictures without being noticed. He sets up two plane mirrors together with his camera. Which arrangement of mirrors will allow the photographer to take pictures of someone behind the camera? ...
... photographer wishes to take pictures without being noticed. He sets up two plane mirrors together with his camera. Which arrangement of mirrors will allow the photographer to take pictures of someone behind the camera? ...
Interference 1 - schoolphysics
... beam reflects from the near end and part from the far end. When the two beams combine they show interference due to the path difference formed by travelling along the rod and back. The rod is now heated gently, the end nearest the laser being fixed and the other end being allowed to expand. It is fo ...
... beam reflects from the near end and part from the far end. When the two beams combine they show interference due to the path difference formed by travelling along the rod and back. The rod is now heated gently, the end nearest the laser being fixed and the other end being allowed to expand. It is fo ...
dec 2016_nature of light unit test review sheet answer key
... 2. If light is invisible as it travels, what do you need to do to detect light? - You need a form of matter to intercept the path of light and reflect it back to the observer’s eyes. 3. How long does it take for the sunlight to reach Earth? (Use the diagram on page 41 in the textbook to assist you i ...
... 2. If light is invisible as it travels, what do you need to do to detect light? - You need a form of matter to intercept the path of light and reflect it back to the observer’s eyes. 3. How long does it take for the sunlight to reach Earth? (Use the diagram on page 41 in the textbook to assist you i ...
Optics - Mr. Gallagher's Physics
... • Lenses: bend light in a specific way. ▫ Converging lens (convex): bends light to a point. ▫ Diverging lens (concave): Spreads light out. ...
... • Lenses: bend light in a specific way. ▫ Converging lens (convex): bends light to a point. ▫ Diverging lens (concave): Spreads light out. ...
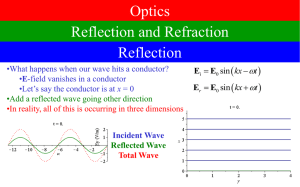
Reflect/Refract
... •The speed of light in a material can depend on frequency •Index of refraction n depends on frequency •Confusingly, its dependence is often given as a function of wavelength in vacuum •Called dispersion •This means that different types of light bend by different amounts in any given material •For mo ...
... •The speed of light in a material can depend on frequency •Index of refraction n depends on frequency •Confusingly, its dependence is often given as a function of wavelength in vacuum •Called dispersion •This means that different types of light bend by different amounts in any given material •For mo ...
Chapter 6: Polarization and Crystal Optics
... P6-7. A plane, linearly polarized light wave, with intensity I 0 , is transmitted through a system of perfect linear polarizers (we assume that all light is transmitted in the transmission direction but in the perpendicular direction all light is absorbed). Give for the following systems of polarize ...
... P6-7. A plane, linearly polarized light wave, with intensity I 0 , is transmitted through a system of perfect linear polarizers (we assume that all light is transmitted in the transmission direction but in the perpendicular direction all light is absorbed). Give for the following systems of polarize ...
Diffraction
... l Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time. When they pass through LIGO's L-shaped detector they will decrease the distance between the test masses in one arm of the L, while increasing it in the other. These changes are minute: just 10-16 centimeters, or one-hundredmillionth th ...
... l Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time. When they pass through LIGO's L-shaped detector they will decrease the distance between the test masses in one arm of the L, while increasing it in the other. These changes are minute: just 10-16 centimeters, or one-hundredmillionth th ...
File
... 3. A bi convex lens is made of glass of ref index 1.5.The radius of curvature of each face is 30 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens in air. 4. Explain why white light is dispersed when passing through a prism? 5. For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different me ...
... 3. A bi convex lens is made of glass of ref index 1.5.The radius of curvature of each face is 30 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens in air. 4. Explain why white light is dispersed when passing through a prism? 5. For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different me ...
Triple Refraction_and_Total_Internal_Reflection
... They slow down as they move from the light blue to the dark blue medium. 2. Do the waves change direction and what is this called? Yes, the waves do change direction. This is called refraction. 3. Where do the waves change direction? The waves change direction at the boundary. Then they travel in st ...
... They slow down as they move from the light blue to the dark blue medium. 2. Do the waves change direction and what is this called? Yes, the waves do change direction. This is called refraction. 3. Where do the waves change direction? The waves change direction at the boundary. Then they travel in st ...
Interference I - Galileo and Einstein
... of the magnifying glass discussed above. • The simplest compound microscope has two convex lenses: the first (objective) forms a real (inverted) image, the second (eyepiece) acts as a magnifying glass to examine that image. • The total magnification is a product of the two: the eyepiece is N/fe, N = ...
... of the magnifying glass discussed above. • The simplest compound microscope has two convex lenses: the first (objective) forms a real (inverted) image, the second (eyepiece) acts as a magnifying glass to examine that image. • The total magnification is a product of the two: the eyepiece is N/fe, N = ...
Document
... which it originally came. The reflector will be seen to be lit up from the point of view of the light source for example the driver of a car with its headlights on. ...
... which it originally came. The reflector will be seen to be lit up from the point of view of the light source for example the driver of a car with its headlights on. ...
Ref. “Optical Materials”
... Go the IMI webiste or contact Professor Jain for more informations! ...
... Go the IMI webiste or contact Professor Jain for more informations! ...
Chromatic Dispersion
... the phase consist of spherical droplets of one phase in the other. In fact, one will have droplets of each phase within the other. Because it’s unlikely that two liquids suited to this purpose will have the same density, one will typically sit atop the other. There will be an effective dispersion on ...
... the phase consist of spherical droplets of one phase in the other. In fact, one will have droplets of each phase within the other. Because it’s unlikely that two liquids suited to this purpose will have the same density, one will typically sit atop the other. There will be an effective dispersion on ...