Single Slit Diffraction & Gratings
... Optical activity occurs in a material because of an asymmetry in the shape of its constituent materials ...
... Optical activity occurs in a material because of an asymmetry in the shape of its constituent materials ...
Exemption Renewal Request Form
... of light used to illuminate samples will have a different wavelength to the fluorescent light emitted by the dyes, but these two wavelengths are usually similar. If a white light source is used, steep-edge cut off filters are needed to remove light of wavelengths that are not required for inducing f ...
... of light used to illuminate samples will have a different wavelength to the fluorescent light emitted by the dyes, but these two wavelengths are usually similar. If a white light source is used, steep-edge cut off filters are needed to remove light of wavelengths that are not required for inducing f ...
A transparent material like glass allows light to pass
... the two blunt corners of the crystal. Blunt corner is the corner at which three parallelograms meet with obtuse angles. There will be two blunt corners. In a uniaxial crystal there is only one optic axis. There some other crystals with more than one optic axis and they may be called biaxial crystals ...
... the two blunt corners of the crystal. Blunt corner is the corner at which three parallelograms meet with obtuse angles. There will be two blunt corners. In a uniaxial crystal there is only one optic axis. There some other crystals with more than one optic axis and they may be called biaxial crystals ...
Seminar ON SMART SENSOR
... Many a times it is required to alter the sensor excitation over the operating range of a SENSOR. an example of this is SILICON Wheatstone bridge, where the drive voltage is increased with increasing temperature ANALOG INPUT • Multiplexing of inputs can be done to avoid duplication of circuits in m ...
... Many a times it is required to alter the sensor excitation over the operating range of a SENSOR. an example of this is SILICON Wheatstone bridge, where the drive voltage is increased with increasing temperature ANALOG INPUT • Multiplexing of inputs can be done to avoid duplication of circuits in m ...
TIE-41 Large Optical Glass Blanks
... Even though large transmitting lenses and prisms have been produced in the past, this cannot be taken for granted. The optical elements in the future will be even larger and the specifications will be much more stringent, reflecting the ambitious scientific goals of the new telescope generations. Th ...
... Even though large transmitting lenses and prisms have been produced in the past, this cannot be taken for granted. The optical elements in the future will be even larger and the specifications will be much more stringent, reflecting the ambitious scientific goals of the new telescope generations. Th ...
Optical Basicity and Polarizability of Nd3+
... upon exposure to intense light beams, polarizability is the most important properties which govern the nonlinearity response of the glass. That is why knowledge of the state of polarization of ions in different crystalline and amorphous materials is of significant interest. The aim of the present st ...
... upon exposure to intense light beams, polarizability is the most important properties which govern the nonlinearity response of the glass. That is why knowledge of the state of polarization of ions in different crystalline and amorphous materials is of significant interest. The aim of the present st ...
System for observing interference phenomenon: In the previous
... thickness of the film, refractive index of material etc. We shall be discussing some of these systems and their applications in the following sections. The major systems for observing interference phenomenon are as follows. ...
... thickness of the film, refractive index of material etc. We shall be discussing some of these systems and their applications in the following sections. The major systems for observing interference phenomenon are as follows. ...
BEST OF - Edmund Optics
... or oils on your hands, Compressed Air effectively removes surface dust without directly contacting any coating an optic may have, Cotton-Tipped Swabs and Lens Tissue offer an effective means to wipe away any dirt without scratching an optic, and Lens Cleaners, Reagent-Grade Isopropyl Alcohol and Ace ...
... or oils on your hands, Compressed Air effectively removes surface dust without directly contacting any coating an optic may have, Cotton-Tipped Swabs and Lens Tissue offer an effective means to wipe away any dirt without scratching an optic, and Lens Cleaners, Reagent-Grade Isopropyl Alcohol and Ace ...
worksheet
... F. The bending of light when it passes through a liquid G. The circular opening in the iris of the eye that controls how much light enters the eye. ...
... F. The bending of light when it passes through a liquid G. The circular opening in the iris of the eye that controls how much light enters the eye. ...
Laser Refraction and Diffraction
... composed of numerous small wave sources. These sources produce additional waves at the position of the wavefront, which leads to subsequent wavefronts that produce more subsequent wavefronts according to the assumptions of this principle. Various phenomena of diffraction and interference can be qual ...
... composed of numerous small wave sources. These sources produce additional waves at the position of the wavefront, which leads to subsequent wavefronts that produce more subsequent wavefronts according to the assumptions of this principle. Various phenomena of diffraction and interference can be qual ...
freshman engineering laboratory
... related molecules. Liquid crystals are another state of matter in addition to the most commonly encountered phases (gas, liquid, solid); they have greater ordering than more normal liquids but less ordering than crystalline solids. All phase changes have a characteristic phase transition temperature ...
... related molecules. Liquid crystals are another state of matter in addition to the most commonly encountered phases (gas, liquid, solid); they have greater ordering than more normal liquids but less ordering than crystalline solids. All phase changes have a characteristic phase transition temperature ...
PDF
... stabilizing the optical performance with respect to temperature. Any temperature changes experienced by the optics may be with respect to time or space or both. Time refers to a uniform heat soak across all the optics, and space refers to a gradient across the optics resulting in each lens (and hous ...
... stabilizing the optical performance with respect to temperature. Any temperature changes experienced by the optics may be with respect to time or space or both. Time refers to a uniform heat soak across all the optics, and space refers to a gradient across the optics resulting in each lens (and hous ...
document
... The index of refraction of a medium is usually a function of the wavelength of the light. It is larger at shorter wavelengths. Consequently, a light beam consisting of rays of different wavelength (e.g., sun light) will be refracted at different angles at the interface of two different media. This s ...
... The index of refraction of a medium is usually a function of the wavelength of the light. It is larger at shorter wavelengths. Consequently, a light beam consisting of rays of different wavelength (e.g., sun light) will be refracted at different angles at the interface of two different media. This s ...
Optical and mechanical properties of soda lime glass
... their respective configurations is given in Table 1. Copper, glass, PMMA, and free surface are denoted by C, G, P, and F, respectively in this table. If more than one discs of soda lime glass were used in an experiment, each disc is represented by GX, where X is a numeral. Numeral 1 indicates that t ...
... their respective configurations is given in Table 1. Copper, glass, PMMA, and free surface are denoted by C, G, P, and F, respectively in this table. If more than one discs of soda lime glass were used in an experiment, each disc is represented by GX, where X is a numeral. Numeral 1 indicates that t ...
Calibration, Size bin choices, Mie scattering theory
... size. We don’t precisely know the illumination and detector efficiency, so an empirical calibration is required to assign sizes to each of the pulse height thresholds that have been set in the instruments. If we have calibration particles whose size we can strictly control, then we can sample these ...
... size. We don’t precisely know the illumination and detector efficiency, so an empirical calibration is required to assign sizes to each of the pulse height thresholds that have been set in the instruments. If we have calibration particles whose size we can strictly control, then we can sample these ...
Halogen Lamp Ultraviolet Output
... The small bulb of the tungsten halogen lamp operates at a very high temperature, often several hundred degrees Celsius. If this bulb were to be shattered for any reason while operating, the hot fragments could cause burns. Proper use of this lamp requires it to be operated within light fixtures that ...
... The small bulb of the tungsten halogen lamp operates at a very high temperature, often several hundred degrees Celsius. If this bulb were to be shattered for any reason while operating, the hot fragments could cause burns. Proper use of this lamp requires it to be operated within light fixtures that ...
Total Reflection
... angle dependent phase shift between the reflected and incident light. Mathematically this means that the Fresnel reflection coefficient becomes a complex rather than a real number. This phase shift is polarization dependent and grows as the incidence angle deviates further from the critical angle ...
... angle dependent phase shift between the reflected and incident light. Mathematically this means that the Fresnel reflection coefficient becomes a complex rather than a real number. This phase shift is polarization dependent and grows as the incidence angle deviates further from the critical angle ...
A History of Imaging
... renaissance, it is puzzling that the development of the first multi-element optical instrument was so long delayed. In 1590, the father and son team of Hans and Zacharias Janssen introduced the compound microscope, a two-element optical system. Apparently society was ready. Within 20 years of the mic ...
... renaissance, it is puzzling that the development of the first multi-element optical instrument was so long delayed. In 1590, the father and son team of Hans and Zacharias Janssen introduced the compound microscope, a two-element optical system. Apparently society was ready. Within 20 years of the mic ...
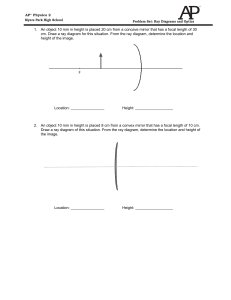
AP® Physics 2 Myers Park High School Problem Set: Ray Diagrams
... b. vacuum c. air d. glass 2. Refraction, as light goes from air to glass, results from differences in light's _____. a. frequency in air and glass b. incident angle c. speed in air and glass d. all of the above. 3. Light refracts when traveling from air into glass because light _____. a. intensity i ...
... b. vacuum c. air d. glass 2. Refraction, as light goes from air to glass, results from differences in light's _____. a. frequency in air and glass b. incident angle c. speed in air and glass d. all of the above. 3. Light refracts when traveling from air into glass because light _____. a. intensity i ...
Worksheets for Unit 4 Light and Matter
... 1. Connect up the light source to a 6 to 8 V DC power supply. 2. View the 35 mm slide through a magnifying glass and draw a sketch of the slide to illustrate the group of narrow slits that appear on the slide 3. Using a blue filter in front of the light filament, view the light passing through each ...
... 1. Connect up the light source to a 6 to 8 V DC power supply. 2. View the 35 mm slide through a magnifying glass and draw a sketch of the slide to illustrate the group of narrow slits that appear on the slide 3. Using a blue filter in front of the light filament, view the light passing through each ...
Materialanalytik Praktikum Ellipsometry B508
... of this lab course, we will give a qualitative description of the processes to give a better understanding of the experiment and to point out how this gained knowledge should influence the execution of our experiments. Fig. 4 shows a schematic view of the light propagation in an ellipsometer experim ...
... of this lab course, we will give a qualitative description of the processes to give a better understanding of the experiment and to point out how this gained knowledge should influence the execution of our experiments. Fig. 4 shows a schematic view of the light propagation in an ellipsometer experim ...
Lect03_Bi177_MicroscopeOptics
... • Velocity (or speed) at which a wave travels can be calculated from the wavelength and frequency. ...
... • Velocity (or speed) at which a wave travels can be calculated from the wavelength and frequency. ...
blOEmhOf An example of a generic structure design
... for an attractive city. But it is reality. Urban developers and architects have the responsibility to develop a sustainable perspective for these areas, for which there are no overarching plans, and to create new typologies for the less compact city. D’Hooghe sees three important themes in this: fir ...
... for an attractive city. But it is reality. Urban developers and architects have the responsibility to develop a sustainable perspective for these areas, for which there are no overarching plans, and to create new typologies for the less compact city. D’Hooghe sees three important themes in this: fir ...