PH 481 - Physics | Oregon State University
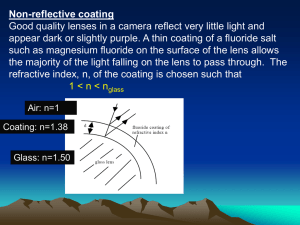
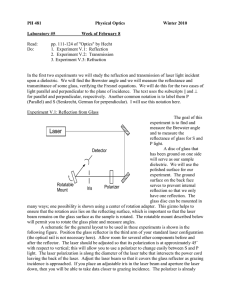
... In order to do this and to find the Brewster angle B, rotate the reflector so that the incident angle i ≈ 55˚ and view the reflected beam on a card. Adjust the polarizer so as to minimize the brightness of the reflected beam. Change the angle of incidence and plane of polarization alternately to a ...
... In order to do this and to find the Brewster angle B, rotate the reflector so that the incident angle i ≈ 55˚ and view the reflected beam on a card. Adjust the polarizer so as to minimize the brightness of the reflected beam. Change the angle of incidence and plane of polarization alternately to a ...
Sample Problems for Final
... intensity, are incident on the slit: yellow light of wavelength 480 nm and red light of wavelength 640 nm. The central (m=0) maxima for both colors occur on the screen straight ahead of the slits. How far away from this do you need to go to see purely yellow light? Purely red light? The first point ...
... intensity, are incident on the slit: yellow light of wavelength 480 nm and red light of wavelength 640 nm. The central (m=0) maxima for both colors occur on the screen straight ahead of the slits. How far away from this do you need to go to see purely yellow light? Purely red light? The first point ...
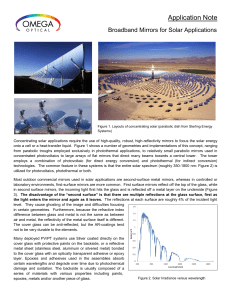
Broadband Mirrors for Solar Applications
... they do not heat up with intense illumination. The light that is not reflected does get absorbed by the glass substrate at low wavelengths (<340 nm or so) and is transmitted through the part at higher wavelengths. The transition between transmission and reflection can be optimized by changing the nu ...
... they do not heat up with intense illumination. The light that is not reflected does get absorbed by the glass substrate at low wavelengths (<340 nm or so) and is transmitted through the part at higher wavelengths. The transition between transmission and reflection can be optimized by changing the nu ...
Light Hits Near Infinite Speed in Silver-Coated Glass
... glass. It is the first with a refractive index below 0.1, which means that light passes through it at almost infinite speed, says Albert Polman at the FOM Institute AMOLF in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. But the speed of light has not, technically, been broken. The wave is moving quickly, but its "gro ...
... glass. It is the first with a refractive index below 0.1, which means that light passes through it at almost infinite speed, says Albert Polman at the FOM Institute AMOLF in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. But the speed of light has not, technically, been broken. The wave is moving quickly, but its "gro ...
Soliton Propagation in Optical Fibers
... Bell intend to connect Boston and Cambridge...with a line of sunbeams hung on telegraph posts, and, if so, what diameter are the sunbeams to be...?...will it be necessary to insulate them against the weather...?...until (the public) sees a man going through the streets with a coil of No. 12 sunbeams ...
... Bell intend to connect Boston and Cambridge...with a line of sunbeams hung on telegraph posts, and, if so, what diameter are the sunbeams to be...?...will it be necessary to insulate them against the weather...?...until (the public) sees a man going through the streets with a coil of No. 12 sunbeams ...
tutorial #10 [wave nature of light] .quiz
... 1) A beam of light is sent directly down onto a glass plate, ng = 1.5, and a plastic plate, np = 1.2, that form a thin wedge of air as shown in fig. 1. An observer looking down through the glass plate sees the fringe pattern shown in the lower part of the drawing, with the dark fringes at the ends A ...
... 1) A beam of light is sent directly down onto a glass plate, ng = 1.5, and a plastic plate, np = 1.2, that form a thin wedge of air as shown in fig. 1. An observer looking down through the glass plate sees the fringe pattern shown in the lower part of the drawing, with the dark fringes at the ends A ...
Nikon Glass News Winter 2015
... When natural light passes through a triangular prism, the light is divided into seven colors similar to a rainbow. This is because of a phenomenon known as dispersion. This demonstrates that different wavelengths of light have a different refractive index. Engineers involved in optical design need t ...
... When natural light passes through a triangular prism, the light is divided into seven colors similar to a rainbow. This is because of a phenomenon known as dispersion. This demonstrates that different wavelengths of light have a different refractive index. Engineers involved in optical design need t ...
Document
... physical reason for this is that the velocity of light is different inside the dielectric. We are used to this happening in water or glass but in crystals the situation can be more complex when crystals are anisotropic. We have seen that the value of n is a function of λ. It normally decreases as λ ...
... physical reason for this is that the velocity of light is different inside the dielectric. We are used to this happening in water or glass but in crystals the situation can be more complex when crystals are anisotropic. We have seen that the value of n is a function of λ. It normally decreases as λ ...
Aspheric Lenses
... says "these lenses use special optical technologies [such as] Ultra-low Dispersion UD glass, Super Low Dispersion glass, Fluorite elements, and Aspherical elements to truly push the optical envelope." The truth is long lenses may use ULD and Fluorite glass, but wide angles and lenses of shorter than ...
... says "these lenses use special optical technologies [such as] Ultra-low Dispersion UD glass, Super Low Dispersion glass, Fluorite elements, and Aspherical elements to truly push the optical envelope." The truth is long lenses may use ULD and Fluorite glass, but wide angles and lenses of shorter than ...
The page, which you have just visited, was created for students of
... forming a thick syrup and eventually an amorphous solid. The molecules then have a disordered arrangement, but sufficient cohesion to maintain some rigidity. In this state it is often called an amorphous solid or easily and commonly glass. There is a conviction, that glass is actually a supercooled ...
... forming a thick syrup and eventually an amorphous solid. The molecules then have a disordered arrangement, but sufficient cohesion to maintain some rigidity. In this state it is often called an amorphous solid or easily and commonly glass. There is a conviction, that glass is actually a supercooled ...
Facts About Ultra Violet (UV) Lights
... Closing the view screen of the biological safety cabinets (BSC) because all silicatebased glass does not permit UV light to penetrate. ...
... Closing the view screen of the biological safety cabinets (BSC) because all silicatebased glass does not permit UV light to penetrate. ...
Document
... Crown glass is type of optical glass used in lenses and other optical components. Crown glass is produced from alkali-lime silicates containing approximately 10% potassium oxide. It has low n (≈1.52) and low despersion (with Abbe Number around 60). Generally, this is any glass with Abbe numbers in t ...
... Crown glass is type of optical glass used in lenses and other optical components. Crown glass is produced from alkali-lime silicates containing approximately 10% potassium oxide. It has low n (≈1.52) and low despersion (with Abbe Number around 60). Generally, this is any glass with Abbe numbers in t ...


![tutorial #10 [wave nature of light] .quiz](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/020410144_1-db052accb2aa8cded167524d89755606-300x300.png)