AB AB ab AB
... 5. Determine the order of genes on chromosome if you know that p=5% for genes A and B, p=3% for genes B and C and p=2% for genes A and C. 6. Dominant allele D is coding for Rh+ factor, recessive genotype dd is coding for Rh- phenotype (absence of Rh factor on the surface of erythrocytes). Elliptic ...
... 5. Determine the order of genes on chromosome if you know that p=5% for genes A and B, p=3% for genes B and C and p=2% for genes A and C. 6. Dominant allele D is coding for Rh+ factor, recessive genotype dd is coding for Rh- phenotype (absence of Rh factor on the surface of erythrocytes). Elliptic ...
Partnership
... which this is feasible have been developed, but the frequencies by which the events can be obtained are still too low for routine application. The methods that have been developed rely largely on the natural process of homologous recombination, which cells use for DNA repair and for meiosis. In yeas ...
... which this is feasible have been developed, but the frequencies by which the events can be obtained are still too low for routine application. The methods that have been developed rely largely on the natural process of homologous recombination, which cells use for DNA repair and for meiosis. In yeas ...
X inactivation Xplained
... chaotic choice results if Tsix is disrupted on both Xic alleles [24]. Surprisingly, this can result in viable female mice, albeit with a low frequency [24] (Figure 2e). Therefore, chaotic choice may represent the basic mechanism underlying the XCI counting and choice process. Currently, the molecula ...
... chaotic choice results if Tsix is disrupted on both Xic alleles [24]. Surprisingly, this can result in viable female mice, albeit with a low frequency [24] (Figure 2e). Therefore, chaotic choice may represent the basic mechanism underlying the XCI counting and choice process. Currently, the molecula ...
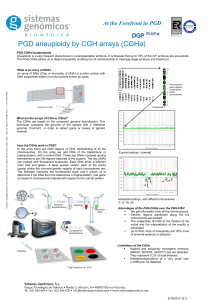
At the Forefront in PGD
... altered embryos (unbalanced) for a specific chromosomal rearrangement. However, the main limitation is that it does not provide information of the rest of chromosomes. Combined chromosomal PGD is based on CGH arrays technology. It allows to identify the altered embryos (unbalanced) in relation to th ...
... altered embryos (unbalanced) for a specific chromosomal rearrangement. However, the main limitation is that it does not provide information of the rest of chromosomes. Combined chromosomal PGD is based on CGH arrays technology. It allows to identify the altered embryos (unbalanced) in relation to th ...
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... These homologous regions allow the X and Y chromosomes in males to pair and behave like homologous chromosomes during meiosis in the testes. In mammalian testes and ovaries, the two sex chromosomes segregate during meiosis, and each gamete receives one. Each egg contains one X chromosome. In contras ...
... These homologous regions allow the X and Y chromosomes in males to pair and behave like homologous chromosomes during meiosis in the testes. In mammalian testes and ovaries, the two sex chromosomes segregate during meiosis, and each gamete receives one. Each egg contains one X chromosome. In contras ...
Fruit Flies
... the genetic differences among individuals of the same species. For example, offspring could either be left or right handed. These traits are passed through chromosomes. Chromosomes come in homologous pairs called autosomes, and one non-homologous pair called sex chromosomes. The number of chromosome ...
... the genetic differences among individuals of the same species. For example, offspring could either be left or right handed. These traits are passed through chromosomes. Chromosomes come in homologous pairs called autosomes, and one non-homologous pair called sex chromosomes. The number of chromosome ...
Microdeletions on the long arm of the Y chromosome
... A number of candidate genes for AZF have been described. However, only a few genes or gene families have been studied in detail. These include the ‘deleted in azoospermia’ (DAZ), 16 RNA-binding motif for Y-located RNA (RBMY1A1)—formerly known as Y-chromosome RNA recognition motif (YRRM),42 and the Y ...
... A number of candidate genes for AZF have been described. However, only a few genes or gene families have been studied in detail. These include the ‘deleted in azoospermia’ (DAZ), 16 RNA-binding motif for Y-located RNA (RBMY1A1)—formerly known as Y-chromosome RNA recognition motif (YRRM),42 and the Y ...
Swine Genetic Abnormalities
... Most cases of tremors in pigs are congenital (present at birth), but certain forms are often first expressed at later ages. The condition is also known as myoclonia congenita, trembles, shivers, shakers, or jumpy pig disease. The symptoms generally are present within a few hours of birth and are cha ...
... Most cases of tremors in pigs are congenital (present at birth), but certain forms are often first expressed at later ages. The condition is also known as myoclonia congenita, trembles, shivers, shakers, or jumpy pig disease. The symptoms generally are present within a few hours of birth and are cha ...
Understanding human disease via randomized mice
... • Phenotype mechanism • Need not know anything in advance. ...
... • Phenotype mechanism • Need not know anything in advance. ...
Signed Reversal Distance
... on chromosome 3 had been inverted in one of the species. His discovery provided the first substantial evidence of a specific mutation occurring at some point during the evolutionary history of an entire species. A decade later, Theophilus Painter suggested the investigation of polytene chromosomes t ...
... on chromosome 3 had been inverted in one of the species. His discovery provided the first substantial evidence of a specific mutation occurring at some point during the evolutionary history of an entire species. A decade later, Theophilus Painter suggested the investigation of polytene chromosomes t ...
SCI 30 UA CH 2.1 What is Genetics
... In order to grow and to replace cells that are dead or damaged, your body must constantly make new cells. Skin cells, for example, need to be frequently replaced by new cells. A body cell, or an autosomal cell, divides by growing large and making extra copies of all its parts and then splitting into ...
... In order to grow and to replace cells that are dead or damaged, your body must constantly make new cells. Skin cells, for example, need to be frequently replaced by new cells. A body cell, or an autosomal cell, divides by growing large and making extra copies of all its parts and then splitting into ...
Genetic Causes of Infertility: Chromosomal Abnormalities in Couples
... in the blood. Y Chromosome deletions (missing genetic information on the Y chromosome) In most cases, the cause of severe male factor infertility is unknown. However, recent work from the laboratories of several scientists have reported that about 10-15% of men with severe male factor infertility ...
... in the blood. Y Chromosome deletions (missing genetic information on the Y chromosome) In most cases, the cause of severe male factor infertility is unknown. However, recent work from the laboratories of several scientists have reported that about 10-15% of men with severe male factor infertility ...
FISH, flexible joints and panic: are anxiety disorders really
... which is a very unusual finding. Mosiacism occurs when different cells of the body contain functionally different DNA, usually because of DNA sequence changes occurring during normal mitotic cell division. In any one person, the DUP25 duplication is found in only about 60% of cells, whereas the rema ...
... which is a very unusual finding. Mosiacism occurs when different cells of the body contain functionally different DNA, usually because of DNA sequence changes occurring during normal mitotic cell division. In any one person, the DUP25 duplication is found in only about 60% of cells, whereas the rema ...
SALIVARY CHROMOSOME ANALYSIS OF THE WHITE
... the region between 3E2 and 3E4. None of the deficiencies mentioned here includes ec, therefore, this locus must lie to the right of the right end of the longest of them, which is the 264-38; its righthand limit follows 3E2. Notch 264-8 presents an interesting case of a genetical deficiency without a ...
... the region between 3E2 and 3E4. None of the deficiencies mentioned here includes ec, therefore, this locus must lie to the right of the right end of the longest of them, which is the 264-38; its righthand limit follows 3E2. Notch 264-8 presents an interesting case of a genetical deficiency without a ...
Forensics and Probability
... • Two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents. • All humans arise from the joining of 1 egg and 1 sperm cell • 100% of a person’s DNA is the same within and throughout a human being’s body. • Whether you look at the cells of a person’s blo ...
... • Two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents. • All humans arise from the joining of 1 egg and 1 sperm cell • 100% of a person’s DNA is the same within and throughout a human being’s body. • Whether you look at the cells of a person’s blo ...
Genetic and Molecular Abnormalities in Tumors of the Bone and Soft
... tumors of difficult histologic classification and strong genetic predisposition. This article provides a comprehensive review of the cytogenetic abnormalities observed in bone and soft-tissue tumors, emphasizing known downstream molecular changes that may play a role in oncogenesis. Methods: The dat ...
... tumors of difficult histologic classification and strong genetic predisposition. This article provides a comprehensive review of the cytogenetic abnormalities observed in bone and soft-tissue tumors, emphasizing known downstream molecular changes that may play a role in oncogenesis. Methods: The dat ...
No Slide Title
... – Genes found on the X chromosome are X-linked genes. – A sex-linked trait is a trait whose allele is located on a sex chromosome. – Because males have only one X chromosome, a male who carries a recessive allele on the X chromosome will exhibit the sex-linked trait. • Linked Genes – Pairs of genes ...
... – Genes found on the X chromosome are X-linked genes. – A sex-linked trait is a trait whose allele is located on a sex chromosome. – Because males have only one X chromosome, a male who carries a recessive allele on the X chromosome will exhibit the sex-linked trait. • Linked Genes – Pairs of genes ...
In Plant Cells
... number of chromosomes ….called the “Diploid” number (the symbol is 2n). Examples would be … skin cells, brain cells, etc. 2. Gametes are the “sex” cells and contain only ½ the normal number of chromosomes…. called the “Haploid” number (the symbol is n)….. Sperm cells and ova are gametes. n = number ...
... number of chromosomes ….called the “Diploid” number (the symbol is 2n). Examples would be … skin cells, brain cells, etc. 2. Gametes are the “sex” cells and contain only ½ the normal number of chromosomes…. called the “Haploid” number (the symbol is n)….. Sperm cells and ova are gametes. n = number ...
Meiosis is the process by which the number of
... Meiosis is the process by which the number of chromosomes per sex cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell. In other words, meiosis is the division of sex cells that results in the production of eggs (in females) and sperm (in males). The GOAL of meiosis ...
... Meiosis is the process by which the number of chromosomes per sex cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell. In other words, meiosis is the division of sex cells that results in the production of eggs (in females) and sperm (in males). The GOAL of meiosis ...
Physical location of 18S-28S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes
... parasitica. Utilizing American chestnut trees (mostly stump sprouts) still found in the wild, The American Chestnut Foundation (TACF) is transferring resistance from Chinese chestnut into American chestnut through backcross breeding. To facilitate this work our lab has teamed up with TACF to carryou ...
... parasitica. Utilizing American chestnut trees (mostly stump sprouts) still found in the wild, The American Chestnut Foundation (TACF) is transferring resistance from Chinese chestnut into American chestnut through backcross breeding. To facilitate this work our lab has teamed up with TACF to carryou ...
12.3 Laws of Inheritance
... Alleles do not always behave in dominant and recessive patterns. Incomplete dominance describes situations in which the heterozygote exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate between the homozygous phenotypes. ...
... Alleles do not always behave in dominant and recessive patterns. Incomplete dominance describes situations in which the heterozygote exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate between the homozygous phenotypes. ...
Slcyt, a Newly Identified Sex-Linked Gene, Has
... Jolla, CA). We refer to this as the TS library. Candidate sex-linked genes in S. latifolia were identified using a combination of segregation analysis of intron size variants (ISVS), using a universal primer (5#-GGTTGGAGCTAGTGTTGTG-3#) labeled with 6-FAM or VIC (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA), ...
... Jolla, CA). We refer to this as the TS library. Candidate sex-linked genes in S. latifolia were identified using a combination of segregation analysis of intron size variants (ISVS), using a universal primer (5#-GGTTGGAGCTAGTGTTGTG-3#) labeled with 6-FAM or VIC (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA), ...
Faster-Z Evolution Is Predominantly Due to Genetic Drift Research
... Genes linked to sex chromosomes may show different levels of functional change than autosomal genes due to different evolutionary pressures. We used whole-genome data from zebra finch–chicken orthologs to test for Faster-Z evolution, finding that Z-linked genes evolve up to 50% more rapidly than aut ...
... Genes linked to sex chromosomes may show different levels of functional change than autosomal genes due to different evolutionary pressures. We used whole-genome data from zebra finch–chicken orthologs to test for Faster-Z evolution, finding that Z-linked genes evolve up to 50% more rapidly than aut ...
Human Genetic Disorders - Virtual Learning Environment
... A genetic disorder refers to the problem arising due to an abnormality or change in the genome of an organism. Cytochemical studies provide an insight into the pattern of their inheritance in the future generations. Majority of genetic disorders are a result of genetic mutations. These are sudden he ...
... A genetic disorder refers to the problem arising due to an abnormality or change in the genome of an organism. Cytochemical studies provide an insight into the pattern of their inheritance in the future generations. Majority of genetic disorders are a result of genetic mutations. These are sudden he ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)