Untitled Document Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows
... Which process and type of resulting cells are represented in the diagram? ...
... Which process and type of resulting cells are represented in the diagram? ...
RADical new findings for some with features like CdLS Guest
... growth and facial features that look a bit like CdLS, their intellectual development can be normal. We are hopeful that by understanding more about RAD21, we will gain insight about how we might ...
... growth and facial features that look a bit like CdLS, their intellectual development can be normal. We are hopeful that by understanding more about RAD21, we will gain insight about how we might ...
Chromosome mapping of the sweet potato little leaf
... for the taxonomy of mollicutes (Neimark & Lange, 1990). Physical and genetic mapping of mollicute genomes has enabled inter- and intra-specific comparisons to be made. When both physical and genetic maps are known, genomes can be analysed for rearrangements, deletions, insertions or mutations. The f ...
... for the taxonomy of mollicutes (Neimark & Lange, 1990). Physical and genetic mapping of mollicute genomes has enabled inter- and intra-specific comparisons to be made. When both physical and genetic maps are known, genomes can be analysed for rearrangements, deletions, insertions or mutations. The f ...
Tricamy 21 (Down Syndrome)
... •Smaller head than average •Abnormally shaped head •Never fully reach their average adult height ...
... •Smaller head than average •Abnormally shaped head •Never fully reach their average adult height ...
Did sex chromosome turnover promote divergence of the major
... within the small group; matings between this group and the original population suffered from hybrid infertility. However, evidence that chromosome rearrangement is important in speciation was fragmentary, and modelling has been less than convincing (reviewed [4]). Views on the mechanisms of speciati ...
... within the small group; matings between this group and the original population suffered from hybrid infertility. However, evidence that chromosome rearrangement is important in speciation was fragmentary, and modelling has been less than convincing (reviewed [4]). Views on the mechanisms of speciati ...
Leaving Certificate Higher Level Genetics Questions
... (a) Explain each of the following: centrosome, genotype, hybrid. (b) Explain Mendel’s second law of inheritance using a suitable dihybrid cross. ...
... (a) Explain each of the following: centrosome, genotype, hybrid. (b) Explain Mendel’s second law of inheritance using a suitable dihybrid cross. ...
lecture 3
... 2% of genome (dinucleotides - 0.5%) Used as genetic markers (especially for disease mapping) ...
... 2% of genome (dinucleotides - 0.5%) Used as genetic markers (especially for disease mapping) ...
Chapter 13 - ScienceToGo
... Concept 13.3: Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from diploid to haploid • Like mitosis, meiosis is preceded by the replication of chromosomes • Meiosis takes place in two sets of cell divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II • The two cell divisions result in four daughter cells, rath ...
... Concept 13.3: Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from diploid to haploid • Like mitosis, meiosis is preceded by the replication of chromosomes • Meiosis takes place in two sets of cell divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II • The two cell divisions result in four daughter cells, rath ...
The diagrams below show two different scenarios for a pair of
... This answer suggests the student may understand that independent assortment allows for the segregation of different alleles in many dihybrid crosses, but does not understand that the data do not support the model of independent assortment because almost all of the offspring show the two sets of alle ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that independent assortment allows for the segregation of different alleles in many dihybrid crosses, but does not understand that the data do not support the model of independent assortment because almost all of the offspring show the two sets of alle ...
Gene Linkage and Genetic Mapping 4
... The data include 59 + 52 = 111 progeny with either both mutations or neither, and 46 + 43 = 89 with one mutation or the other. One of these groups consists of parental chromosomes and the other of recombinant chromosomes, and so the appropriate chi-square test compares the ratio 111:89 against an ex ...
... The data include 59 + 52 = 111 progeny with either both mutations or neither, and 46 + 43 = 89 with one mutation or the other. One of these groups consists of parental chromosomes and the other of recombinant chromosomes, and so the appropriate chi-square test compares the ratio 111:89 against an ex ...
Incomplete Dominance
... gene (Xh) and the normal condition to the gene (XH). Show a cross between a hemophiliac man and a woman does not carry the trait. ...
... gene (Xh) and the normal condition to the gene (XH). Show a cross between a hemophiliac man and a woman does not carry the trait. ...
Biology 3A Laboratory Mendelian, Human and Population Genetics
... chromosome and may have several versions/forms called alleles. For example, in pea plants, height is governed by a single gene which can have two versions, T and t. Every diploid cell has two copies of one gene which make up the homologous pair of chromosomes that determine a particular trait. Thes ...
... chromosome and may have several versions/forms called alleles. For example, in pea plants, height is governed by a single gene which can have two versions, T and t. Every diploid cell has two copies of one gene which make up the homologous pair of chromosomes that determine a particular trait. Thes ...
human endogenous retroviral LTR
... endogenous retrovirus HERV-K (HML-2) long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences on human chromosome 21. We show that their distribution along the chromosome is not only nonrandom but also roughly correlated with the gene density. Amplification of orthologous LTR sites from a number of primate genomes prod ...
... endogenous retrovirus HERV-K (HML-2) long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences on human chromosome 21. We show that their distribution along the chromosome is not only nonrandom but also roughly correlated with the gene density. Amplification of orthologous LTR sites from a number of primate genomes prod ...
Document
... the occurrence of one crossover tends to inhibit additional crossovers in the same region of the chromosome, and so double crossovers are less frequent than expected. • The degree to which one crossover interferes with additional crossovers in the same region is termed the interference. To calculate ...
... the occurrence of one crossover tends to inhibit additional crossovers in the same region of the chromosome, and so double crossovers are less frequent than expected. • The degree to which one crossover interferes with additional crossovers in the same region is termed the interference. To calculate ...
A Large Pseudoautosomal Region on the Sex Chromosomes of the
... evolution in nonrecombining genomic regions, which is influenced by Muller’s ratchet, background selection, Hill– Robertson effects, and genetic hitchhiking of deleterious alleles with beneficial mutations (Charlesworth B and Charlesworth D 2000). Suppressed recombination between sex chromosomes thu ...
... evolution in nonrecombining genomic regions, which is influenced by Muller’s ratchet, background selection, Hill– Robertson effects, and genetic hitchhiking of deleterious alleles with beneficial mutations (Charlesworth B and Charlesworth D 2000). Suppressed recombination between sex chromosomes thu ...
Genetic Algorithms and Ant Colony Optimisation
... about GA used this type of encoding.In binary encoding every chromosome is a string of bits, 0 or 1. Example ...
... about GA used this type of encoding.In binary encoding every chromosome is a string of bits, 0 or 1. Example ...
7) NATURAL SELECTION: the process by which forms of life having
... 7) NATURAL SELECTION: the process by which forms of life having traits that better fit a specific environmental pressure, such as predators, changes in climate, or competition for food or mates, will tend to survive and reproduce in greater numbers than others of their kind, thus ensuring the contin ...
... 7) NATURAL SELECTION: the process by which forms of life having traits that better fit a specific environmental pressure, such as predators, changes in climate, or competition for food or mates, will tend to survive and reproduce in greater numbers than others of their kind, thus ensuring the contin ...
Read PDF - Hormones
... surrounding them is increased. Large, abnormal cytoplasmic vacuoles containing bone collagen fibrils were observed by ultrastructural examination. The conclusion is that although pycnodysostosis osteoclasts function normally in demineralizing bone, they do not adequately degrade the organic matrix. ...
... surrounding them is increased. Large, abnormal cytoplasmic vacuoles containing bone collagen fibrils were observed by ultrastructural examination. The conclusion is that although pycnodysostosis osteoclasts function normally in demineralizing bone, they do not adequately degrade the organic matrix. ...
- NRC Research Press
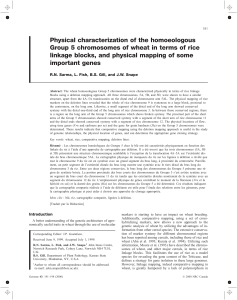
... Abstract: The wheat homoeologous Group 5 chromosomes were characterized physically in terms of rice linkage blocks using a deletion mapping approach. All three chromosomes, 5A, 5B, and 5D, were shown to have a similar structure, apart from the 4A–5A translocation on the distal end of chromosome arm ...
... Abstract: The wheat homoeologous Group 5 chromosomes were characterized physically in terms of rice linkage blocks using a deletion mapping approach. All three chromosomes, 5A, 5B, and 5D, were shown to have a similar structure, apart from the 4A–5A translocation on the distal end of chromosome arm ...
Living things inherit traits in patterns.
... various forms of the same gene are called alleles (uh-LEELZ). Thus, the homolog from one parent might have an allele for regular height at site A, while the gene from the other parent might have an allele for short height at site A. The alleles on a pair of homologs may or may not be different. Thou ...
... various forms of the same gene are called alleles (uh-LEELZ). Thus, the homolog from one parent might have an allele for regular height at site A, while the gene from the other parent might have an allele for short height at site A. The alleles on a pair of homologs may or may not be different. Thou ...
revised Elements of Genetics
... The most vigorous promoter of Mendelism in Europe was William Bateson, who coined the term "genetics", "gene", and "allele" to describe many of its tenets. The model of heredity was highly contested by other biologists because it implied that heredity was discontinuous, in opposition to the apparent ...
... The most vigorous promoter of Mendelism in Europe was William Bateson, who coined the term "genetics", "gene", and "allele" to describe many of its tenets. The model of heredity was highly contested by other biologists because it implied that heredity was discontinuous, in opposition to the apparent ...
Living things inherit traits in patterns.
... various forms of the same gene are called alleles (uh-LEELZ). Thus, the homolog from one parent might have an allele for regular height at site A, while the gene from the other parent might have an allele for short height at site A. The alleles on a pair of homologs may or may not be different. Thou ...
... various forms of the same gene are called alleles (uh-LEELZ). Thus, the homolog from one parent might have an allele for regular height at site A, while the gene from the other parent might have an allele for short height at site A. The alleles on a pair of homologs may or may not be different. Thou ...
Lesson 1: Non-Mendelian Inheritance Patterns Introduction The
... the A protein. A father with B type blood has blood cells with the B protein. Their child with AB type blood has blood cells that have both the A and the B protein. Finally, sex-linked inheritance refers to the genes that are carried on the sex chromosomes. Females are XX and males are XY. The X chr ...
... the A protein. A father with B type blood has blood cells with the B protein. Their child with AB type blood has blood cells that have both the A and the B protein. Finally, sex-linked inheritance refers to the genes that are carried on the sex chromosomes. Females are XX and males are XY. The X chr ...
6.1 Chromosomes and Meiosis
... • In the reproductive organs: The ovaries in women and the testes in men. 2. Do you think that Y chromosomes contain genes that are critical for an organism’s survival? Explain. • No, a Y chromosome is not necessary for survival. Females do not have a Y chromosome, and they are able to survive. ...
... • In the reproductive organs: The ovaries in women and the testes in men. 2. Do you think that Y chromosomes contain genes that are critical for an organism’s survival? Explain. • No, a Y chromosome is not necessary for survival. Females do not have a Y chromosome, and they are able to survive. ...
Genetics 101 - VHL Alliance
... Chromosomes contain sections of DNA called genes that tell our body how to grow and develop. We all have two copies of each chromosome and two copies of each gene. There is a 50% chance of inheriting an individual gene from a parent. Some genes are dominant. A single gene might be responsibl ...
... Chromosomes contain sections of DNA called genes that tell our body how to grow and develop. We all have two copies of each chromosome and two copies of each gene. There is a 50% chance of inheriting an individual gene from a parent. Some genes are dominant. A single gene might be responsibl ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)