CHAPTER 4 Study Guide
... 8. Why are sex-linked traits more common in males than in females? a. All alleles on the X chromosome are dominant. b. All alleles on the Y chromosome are recessive. c. A recessive allele on the X chromosome will produce the trait in a male. d. Any allele on the Y chromosome will be codominant with ...
... 8. Why are sex-linked traits more common in males than in females? a. All alleles on the X chromosome are dominant. b. All alleles on the Y chromosome are recessive. c. A recessive allele on the X chromosome will produce the trait in a male. d. Any allele on the Y chromosome will be codominant with ...
Cytogenetics
... the spindle, thereby arresting cell division during metaphase, the time when the chromosomes are maximally condensed and therefore most ...
... the spindle, thereby arresting cell division during metaphase, the time when the chromosomes are maximally condensed and therefore most ...
Variation
... people in the world would eventually be regulated by famine, disease and war. 1858: Darwin and Wallace – read Malthus’s essay and with their own observations produced the “theory of evolution by natural selection” 1st observation ...
... people in the world would eventually be regulated by famine, disease and war. 1858: Darwin and Wallace – read Malthus’s essay and with their own observations produced the “theory of evolution by natural selection” 1st observation ...
HMIVT
... 1. Homologous duplicated chromosomes pair up. Intimate contact encourages crossovers at various intervals along length of non-sister chromatids. Non-sister chromatids exchange segments at cross over site. Crossing over breaks up old combinations of alleles and puts new ones together in homologous ch ...
... 1. Homologous duplicated chromosomes pair up. Intimate contact encourages crossovers at various intervals along length of non-sister chromatids. Non-sister chromatids exchange segments at cross over site. Crossing over breaks up old combinations of alleles and puts new ones together in homologous ch ...
Base –sugar
... In human chromosomes are mostly studied in peripheral blood lymphocyte , any growing tissue including : bone marrow ,skin fibroblast or cells from amniotic fluid or choronic villi . In normal human nucleated cells contain 46 chromosomes arranged in 22 homologous pairs of autosomal chromosomes and on ...
... In human chromosomes are mostly studied in peripheral blood lymphocyte , any growing tissue including : bone marrow ,skin fibroblast or cells from amniotic fluid or choronic villi . In normal human nucleated cells contain 46 chromosomes arranged in 22 homologous pairs of autosomal chromosomes and on ...
Chromosomes Notes
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
CONNECT!
... # of chromosomes in a body cell? • What mistake occurred in the middle cell? • The gametes should all be haploid, which means a chromosome # of ___ for this species. • How many of the gametes have the proper # of chromosomes? • What is this type of mistake called? ...
... # of chromosomes in a body cell? • What mistake occurred in the middle cell? • The gametes should all be haploid, which means a chromosome # of ___ for this species. • How many of the gametes have the proper # of chromosomes? • What is this type of mistake called? ...
Activity 5
... Introduction: Have you ever wonder why a litter of cats looks so different or how none are the same color of the mom or the opposite how maybe a litter of bunnies look so alike? Are you interested in breeding your own project animals? In this activity we are going to look at inheritance and why it i ...
... Introduction: Have you ever wonder why a litter of cats looks so different or how none are the same color of the mom or the opposite how maybe a litter of bunnies look so alike? Are you interested in breeding your own project animals? In this activity we are going to look at inheritance and why it i ...
Cross-dressing or Crossing-over: Sex Testing of Women Athletes
... •Gel Electrophoresis – analyzes a sample for the presence of the SRY (male determining gene) located on the Y chromosome ...
... •Gel Electrophoresis – analyzes a sample for the presence of the SRY (male determining gene) located on the Y chromosome ...
Part 1 – Genetics 101
... depend on whether the pathological gene comes from the mother or the father. Ex. : Prader-Willi Syndrome or Angelman Syndrome Prader Willi Syndrome is caused by a microdeletion on the chromosome 15, that is inherited from the father (or more rarely when there are two copies of the gene from the moth ...
... depend on whether the pathological gene comes from the mother or the father. Ex. : Prader-Willi Syndrome or Angelman Syndrome Prader Willi Syndrome is caused by a microdeletion on the chromosome 15, that is inherited from the father (or more rarely when there are two copies of the gene from the moth ...
01 - wcusd15
... 9. Identifying Relationships Put the following in order of smallest to largest: chromosome, gene, and cell. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 10. Applying Concepts A pea plant has purple flowers. What allel ...
... 9. Identifying Relationships Put the following in order of smallest to largest: chromosome, gene, and cell. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 10. Applying Concepts A pea plant has purple flowers. What allel ...
Chapter 24
... allele. This can be seen in sickle cell disease. In codominance, the different alleles are both expressed. This can be seen in ABO blood types. The most drastic upset in chromosome number is an entire extra set, a condition called polyploidy. This results from formation of a diploid (rather than a n ...
... allele. This can be seen in sickle cell disease. In codominance, the different alleles are both expressed. This can be seen in ABO blood types. The most drastic upset in chromosome number is an entire extra set, a condition called polyploidy. This results from formation of a diploid (rather than a n ...
Chromosomes and Sex
... 8. How is a sex-linked gene different from a linked gene? How are sex-linked alleles represented? ...
... 8. How is a sex-linked gene different from a linked gene? How are sex-linked alleles represented? ...
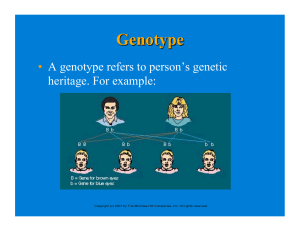
• A genotype refers to person`s genetic heritage. For example:
... • Recessive genes exert influence only if two genes of a pair are recessive. ...
... • Recessive genes exert influence only if two genes of a pair are recessive. ...
Molecular biology
... biochemistry and biophysics • Biochemistry – study of chemical substances and their vital processes in living organisms • Genetics – study of the effect of genetic differences in organisms • Molecular biology – study of molecular emphasizing the process of replication, transcription and translation ...
... biochemistry and biophysics • Biochemistry – study of chemical substances and their vital processes in living organisms • Genetics – study of the effect of genetic differences in organisms • Molecular biology – study of molecular emphasizing the process of replication, transcription and translation ...
Document
... product of the probabilities of each individual crossover therefore, the classes of offspring with the lowest numbers represent the double crossovers and allow the gene order to be determined ...
... product of the probabilities of each individual crossover therefore, the classes of offspring with the lowest numbers represent the double crossovers and allow the gene order to be determined ...
Gen.1303 The Scientific Basis of Human Genetics In the 19th
... The members of each pair of autosomes are said to be homologous, because their DNA is very similar. The X and Y chromosomes are not homologous of one another. Somatic cells, having two of each chromosome, are termed diploid cells. Human gametes have ...
... The members of each pair of autosomes are said to be homologous, because their DNA is very similar. The X and Y chromosomes are not homologous of one another. Somatic cells, having two of each chromosome, are termed diploid cells. Human gametes have ...
Sex Linked Traits - Thomas Hunt Morgan Fruit Fly Experiment
... child when neither parent is color blind. What are the genotypes of the parents and what is the sex of the child. ...
... child when neither parent is color blind. What are the genotypes of the parents and what is the sex of the child. ...
Chapter 14: Human Heredity Thomas Hunt Morgan: studied
... Genetic Engineering: cutting and splicing of genes and DNA from different sources. Insert new genes into almost any organism, including humans. Transgenic: organisms that have been transformed with genes from other organisms. Transgenic bacteria engineered to produce amounts insulin (a human protein ...
... Genetic Engineering: cutting and splicing of genes and DNA from different sources. Insert new genes into almost any organism, including humans. Transgenic: organisms that have been transformed with genes from other organisms. Transgenic bacteria engineered to produce amounts insulin (a human protein ...
Gene Linkage
... offspring (humans) 2. X-O: number of sex chromosomes determines sex; females have 2; males have 1; males produce two types of gametes & determine sex (many insects) 3. Z-W: female gamete determines sex of offspring (birds, butterflies, fish) 4. Haplo-diploid: female is a fertilized gamete; male unfe ...
... offspring (humans) 2. X-O: number of sex chromosomes determines sex; females have 2; males have 1; males produce two types of gametes & determine sex (many insects) 3. Z-W: female gamete determines sex of offspring (birds, butterflies, fish) 4. Haplo-diploid: female is a fertilized gamete; male unfe ...
Chapter 6.1 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
... units called genes A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA molecule. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. Genes determine how a body develops and functions. When genes are being used, the DNA is stretched out in the form of chromatin so that the information it contains ...
... units called genes A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA molecule. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. Genes determine how a body develops and functions. When genes are being used, the DNA is stretched out in the form of chromatin so that the information it contains ...
CHAPTER 8 (CHOMOSOME MUTATION: CHANGES IN
... A. Chromosomal mutations are processes that result in rearranged chromosome parts, abnormal numbers of individual chromosomes, or abnormal numbers of chromosome sets. The resulting products are also known as chromosomal mutations. B. For our purposes here, we will be talking about alterations in lar ...
... A. Chromosomal mutations are processes that result in rearranged chromosome parts, abnormal numbers of individual chromosomes, or abnormal numbers of chromosome sets. The resulting products are also known as chromosomal mutations. B. For our purposes here, we will be talking about alterations in lar ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)