Application of Molecular Technologies in Beef Production
... • Any chromosome contains many genes, but parts of the chromosome may contain no genes • The precise locations of most genes are unknown • Current estimates place the number of human genes at 50,000; bovine, perhaps ...
... • Any chromosome contains many genes, but parts of the chromosome may contain no genes • The precise locations of most genes are unknown • Current estimates place the number of human genes at 50,000; bovine, perhaps ...
CHAPTER 12 GENETICS
... – Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes (1n) – Meiosis occurs in the sex organs (testes and ovaries) producing gametes (sperm and eggs) Fertilization is the union of sperm and egg – The zygote has a diploid chromosome number, one set ...
... – Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes (1n) – Meiosis occurs in the sex organs (testes and ovaries) producing gametes (sperm and eggs) Fertilization is the union of sperm and egg – The zygote has a diploid chromosome number, one set ...
Lect 7 JF 12
... 2. Evolution would also not be possible without variants 3. Variants are sometimes referred to as mutants especially if they have been deliberately produced in the laboratory 4. How do variants or mutants arise? changes in the genetic information (DNA) that occur due to a process called mutation ...
... 2. Evolution would also not be possible without variants 3. Variants are sometimes referred to as mutants especially if they have been deliberately produced in the laboratory 4. How do variants or mutants arise? changes in the genetic information (DNA) that occur due to a process called mutation ...
Biology Test: Chapter 6 Introduction to Genetics 1. _____ What type
... 8.__________Chromosomes lined up at the equator is not in a tetrad. 9.__________ Homologous chromosomes BEGIN to pair up. 10.__________ Sister chromatids, still joined, move toward the poles. ...
... 8.__________Chromosomes lined up at the equator is not in a tetrad. 9.__________ Homologous chromosomes BEGIN to pair up. 10.__________ Sister chromatids, still joined, move toward the poles. ...
Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
... This type of error in cell division causes about 3 to 4 percent of the cases of Down syndrome. In about half of all translocation Down cases, one of the parents is carrying the rearrangement of chromosome 21, called a balanced translocation. The parent may be unaware that he or she is a carrier of t ...
... This type of error in cell division causes about 3 to 4 percent of the cases of Down syndrome. In about half of all translocation Down cases, one of the parents is carrying the rearrangement of chromosome 21, called a balanced translocation. The parent may be unaware that he or she is a carrier of t ...
Nature and Nurture
... Heritability varies from one group to another Environment changes the heritability of a trait Genetic factors matter less when a characteristic is largely determined by environment Inherited traits lead to different characteristics in different contexts Reaction range – inherited traits as a ...
... Heritability varies from one group to another Environment changes the heritability of a trait Genetic factors matter less when a characteristic is largely determined by environment Inherited traits lead to different characteristics in different contexts Reaction range – inherited traits as a ...
Final Exam Review - Genetics Concepts
... 26. One parent with AB blood marries another person with B blood. Which of the following child CANNOT be theirs? a. A b. B c. O d. AB ...
... 26. One parent with AB blood marries another person with B blood. Which of the following child CANNOT be theirs? a. A b. B c. O d. AB ...
Review - BrandtBRC
... • c. He cross-pollinated plants. • d. He cross-pollinated both plants and animals. ...
... • c. He cross-pollinated plants. • d. He cross-pollinated both plants and animals. ...
Human Genetic Disorders - Effingham County Schools
... affects a person's ability to think, talk, and move. ...
... affects a person's ability to think, talk, and move. ...
CHAPTER 15
... Sturtevant used the testcross design to map the relative positions of three fruit fly genes: body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). o Cinnabar (cn), one of many Drosophila genes affecting eye color, results in a bright red eye. o The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. o The ...
... Sturtevant used the testcross design to map the relative positions of three fruit fly genes: body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). o Cinnabar (cn), one of many Drosophila genes affecting eye color, results in a bright red eye. o The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. o The ...
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... Sturtevant used the testcross design to map the relative positions of three fruit fly genes: body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). o Cinnabar (cn), one of many Drosophila genes affecting eye color, results in a bright red eye. o The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. o The ...
... Sturtevant used the testcross design to map the relative positions of three fruit fly genes: body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). o Cinnabar (cn), one of many Drosophila genes affecting eye color, results in a bright red eye. o The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. o The ...
Meiosis activity
... TO START: Take out the contents of one cell. There should be 4 chromosomes: 2 yellow and 2 orange or 2 green and 2 pink. Take out the chromosomes labeled 1 and 3 (for example: one pink #1, one green #1, one pink #3, and one green #3). The different chromosomes are indicated both by the number at th ...
... TO START: Take out the contents of one cell. There should be 4 chromosomes: 2 yellow and 2 orange or 2 green and 2 pink. Take out the chromosomes labeled 1 and 3 (for example: one pink #1, one green #1, one pink #3, and one green #3). The different chromosomes are indicated both by the number at th ...
What are genomes and how are they studied
... Interspersed repeats or Transposon-derived repeats. They constitute 45% of genome and arise mainly as a result of transposition either through a DNA/RNA intermediate. They can be divided into 4 main types ...
... Interspersed repeats or Transposon-derived repeats. They constitute 45% of genome and arise mainly as a result of transposition either through a DNA/RNA intermediate. They can be divided into 4 main types ...
Chapter 20
... Gender Verification • females who have Turner’s syndrome (a single X chromosome) will not exhibit Barr bodies • if these women were tested for Barr bodies to confirm gender (such as in the Olympics) they would test negative • in other cases, such as testicular feminization syndrome, XY individuals ...
... Gender Verification • females who have Turner’s syndrome (a single X chromosome) will not exhibit Barr bodies • if these women were tested for Barr bodies to confirm gender (such as in the Olympics) they would test negative • in other cases, such as testicular feminization syndrome, XY individuals ...
What makes us human?
... A. 1/4 would be tall; 1/2 intermediate height; 1/4 short B. All the offspring would be tall. C. 1/2 would be tall; 1/4 intermediate height; 1/4 short. D. All the offspring would be intermediate. E. 1/4 would be tall; 1/4 intermediate height; 1/2 short. ...
... A. 1/4 would be tall; 1/2 intermediate height; 1/4 short B. All the offspring would be tall. C. 1/2 would be tall; 1/4 intermediate height; 1/4 short. D. All the offspring would be intermediate. E. 1/4 would be tall; 1/4 intermediate height; 1/2 short. ...
Lab 7
... Be sure to use the SAME letter – either lowercase or uppercase – for each position on the chromosomes. These letters represent your alleles, they are either dominant (uppercase) or recessive (lowercase). All of these letters represent your fly’s genotype. 1. What is your fly’s starting genotype? ___ ...
... Be sure to use the SAME letter – either lowercase or uppercase – for each position on the chromosomes. These letters represent your alleles, they are either dominant (uppercase) or recessive (lowercase). All of these letters represent your fly’s genotype. 1. What is your fly’s starting genotype? ___ ...
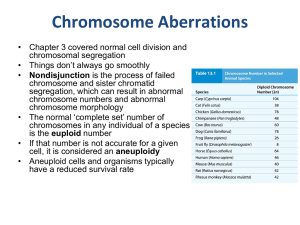
Chromosome Aberrations
... • Polyploidy – the presence of three or more complete sets of chromosomes in an organism’s nucleus • Autopolyploidy – duplication of chromosome sets within a species • Allopolyploidy – combining chromosome sets from different species • Tolerated much more readily in plants • Commercial cotton is the ...
... • Polyploidy – the presence of three or more complete sets of chromosomes in an organism’s nucleus • Autopolyploidy – duplication of chromosome sets within a species • Allopolyploidy – combining chromosome sets from different species • Tolerated much more readily in plants • Commercial cotton is the ...
File reebop
... 2. Using the information in the Reebop Genotype-Phenotype Conversion Table, list all the possible genotypes that would produce the phenotypes exhibited by Mom and Dad. ...
... 2. Using the information in the Reebop Genotype-Phenotype Conversion Table, list all the possible genotypes that would produce the phenotypes exhibited by Mom and Dad. ...
Unit III: GENETICS
... on the X chromosome. Note: In terms of gene expression , autosomal ( non-sex chromosomes) inheritance typically involves pairs of genes , with gender being irrelevant to gene expression. Most sex-linked traits are X-linked.Very few Ylinked traits are known. Sex-linked inheritance involves pair ...
... on the X chromosome. Note: In terms of gene expression , autosomal ( non-sex chromosomes) inheritance typically involves pairs of genes , with gender being irrelevant to gene expression. Most sex-linked traits are X-linked.Very few Ylinked traits are known. Sex-linked inheritance involves pair ...
Unit 11 Human Genetics
... Shana who had type A blood. Together, they had 2 children: Cherith (Type O) and Bryan (Type AB). Bryan married Ali (Type O) and they had 2 children: Christian (Type A) and Jon (who could not donate blood to Christian). Ali had an affair with Trent, who was homozygous for blood type A. Ali and Trent ...
... Shana who had type A blood. Together, they had 2 children: Cherith (Type O) and Bryan (Type AB). Bryan married Ali (Type O) and they had 2 children: Christian (Type A) and Jon (who could not donate blood to Christian). Ali had an affair with Trent, who was homozygous for blood type A. Ali and Trent ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 15 8thed
... In individuals with the SRY gene, the generic embryonic gonads develop into testes. o The SRY gene codes for a protein that regulates many other genes, triggering a cascade of biochemical, physiological, and anatomical features. In individuals lacking the SRY gene, the generic embryonic gonads devel ...
... In individuals with the SRY gene, the generic embryonic gonads develop into testes. o The SRY gene codes for a protein that regulates many other genes, triggering a cascade of biochemical, physiological, and anatomical features. In individuals lacking the SRY gene, the generic embryonic gonads devel ...
P Cross
... • Extra X chromosome interferes with meiosis and usually prevents these individuals from reproducing • Most common sex chromosome disorder, second most common disorder due to the presence of an extra chromosome ...
... • Extra X chromosome interferes with meiosis and usually prevents these individuals from reproducing • Most common sex chromosome disorder, second most common disorder due to the presence of an extra chromosome ...
BIOLOGY BINGO
... • A disease which causes mental retardation because the body can not metabolize the amino acid phenylalanine. This disorder is autosomal recessive. ...
... • A disease which causes mental retardation because the body can not metabolize the amino acid phenylalanine. This disorder is autosomal recessive. ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)