Genetic Disorders - Sarah E. Goode STEM Academy
... The mutation may have little or no effect. It also may result in a birth defect or may increase the person’s likelihood of developing a disease. ...
... The mutation may have little or no effect. It also may result in a birth defect or may increase the person’s likelihood of developing a disease. ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Mentally retarded, round head, flat nasal bridge, protruding tounge, small ...
... Mentally retarded, round head, flat nasal bridge, protruding tounge, small ...
the title overview
... MS-LS3-2. Develop and use a model to describe why asexual reproduction results in offspring with identical genetic information and sexual reproduction results in offspring with genetic variation. MS-LS4-5. Gather and synthesize information about the technologies that have changed the way humans infl ...
... MS-LS3-2. Develop and use a model to describe why asexual reproduction results in offspring with identical genetic information and sexual reproduction results in offspring with genetic variation. MS-LS4-5. Gather and synthesize information about the technologies that have changed the way humans infl ...
Untitled - Pearson
... and many associated phenomena. In the process, we found many opportunities to consider the methods and reasoning by which much of this information was acquired. What answers would you propose to the following fundamental questions? (a) How was it established experimentally that the frequency of reco ...
... and many associated phenomena. In the process, we found many opportunities to consider the methods and reasoning by which much of this information was acquired. What answers would you propose to the following fundamental questions? (a) How was it established experimentally that the frequency of reco ...
- Wiley Online Library
... Natural selection The most-fit individuals reproduce, passing their genetic information on to their offspring. Nelder-mead downhill simplex algorithm A nonderivative, robust local optimization method developed in 1965. Neural network An algorithm modeling biological nervous systems consisting of a l ...
... Natural selection The most-fit individuals reproduce, passing their genetic information on to their offspring. Nelder-mead downhill simplex algorithm A nonderivative, robust local optimization method developed in 1965. Neural network An algorithm modeling biological nervous systems consisting of a l ...
Presentation
... During meiosis, the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of A. daughter cells. B. homologous chromosomes. C. gametes. D. chromatids. ...
... During meiosis, the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of A. daughter cells. B. homologous chromosomes. C. gametes. D. chromatids. ...
Genetics
... environments. Greater variation within the species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
... environments. Greater variation within the species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
C17.2 PPT - Destiny High School
... The mutation may have little or no effect. It also may result in a birth defect or may increase the person’s likelihood of developing a disease. ...
... The mutation may have little or no effect. It also may result in a birth defect or may increase the person’s likelihood of developing a disease. ...
how meiosis reduces chromosome number
... Variation: is demonstrated by the differences in appearance that offspring show from parents and siblings ...
... Variation: is demonstrated by the differences in appearance that offspring show from parents and siblings ...
Mendel and His Peas
... With the formation of four cells, meiosis is over. Each of these prospective germ cells carries half the number of chromosomes of somatic cells. ...
... With the formation of four cells, meiosis is over. Each of these prospective germ cells carries half the number of chromosomes of somatic cells. ...
Human Genetics
... An individual carries a matched pair of chromosomes and thus has two alleles for the ABO blood groups. Two alleles may be expressed at the same time. If an individual has IA and IB, they will have type AB blood. Since both alleles are expressed, this is an example of codominance. The possible genoty ...
... An individual carries a matched pair of chromosomes and thus has two alleles for the ABO blood groups. Two alleles may be expressed at the same time. If an individual has IA and IB, they will have type AB blood. Since both alleles are expressed, this is an example of codominance. The possible genoty ...
7.4 Human Genetics and Pedigrees * Pedigree
... * Types of traits 1. single-gene traits = have 1 allele (dominant or recessive) that determines phenotype Ex: widow’s peak (dominant trait), straight ...
... * Types of traits 1. single-gene traits = have 1 allele (dominant or recessive) that determines phenotype Ex: widow’s peak (dominant trait), straight ...
1. Explain why organisms only reproduce their own
... It is a consequence of heredity, which results from the transmission of genes from parents to offspring Because they share similar genes, offspring more closely resemble their parents or close relatives than others ...
... It is a consequence of heredity, which results from the transmission of genes from parents to offspring Because they share similar genes, offspring more closely resemble their parents or close relatives than others ...
Sex Determination and Sex
... Environmental Sex Determination • Limpets – stack position determines sex – Bottom of stack female, top male – But males then become females and new individuals on top settle as males ...
... Environmental Sex Determination • Limpets – stack position determines sex – Bottom of stack female, top male – But males then become females and new individuals on top settle as males ...
genetics
... environments. Greater variation within the species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
... environments. Greater variation within the species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
Bacterial Genetics
... • Important point: the closer 2 genes are to each other, the higher the co-transduction frequency. • We are just trying to get the order of the genes here, not put actual distances on the map. • Expt: donor strain is aziR leu+ thr+. Phage P1 is grown on the donor strain, and then the resulting phage ...
... • Important point: the closer 2 genes are to each other, the higher the co-transduction frequency. • We are just trying to get the order of the genes here, not put actual distances on the map. • Expt: donor strain is aziR leu+ thr+. Phage P1 is grown on the donor strain, and then the resulting phage ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Define the following: – Gamete – Gene – Chromatids – Zygote – Autosomes ...
... • Define the following: – Gamete – Gene – Chromatids – Zygote – Autosomes ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... Chromosomes consist of chromatin which is a combination of DNA and proteins. There are two types of chromatin, euchromatin and heterochromatin, which show different degrees of condensation. Euchromatin is the less condensed form, is generally rich in genes and is actively transcribed whereas heteroc ...
... Chromosomes consist of chromatin which is a combination of DNA and proteins. There are two types of chromatin, euchromatin and heterochromatin, which show different degrees of condensation. Euchromatin is the less condensed form, is generally rich in genes and is actively transcribed whereas heteroc ...
Chromosome Research, 8:319-334
... including interstitial deletions and/or translocations between human and host chromosomes, although the rearrangement frequencies were relatively low (Nakagawa et al. 1996). To characterize them more precisely, we used WCP probes to determine the frequency of cells that retained the human chromosome ...
... including interstitial deletions and/or translocations between human and host chromosomes, although the rearrangement frequencies were relatively low (Nakagawa et al. 1996). To characterize them more precisely, we used WCP probes to determine the frequency of cells that retained the human chromosome ...
ppt - Department of Plant Sciences
... Pure Line - a population that breeds true for a particular trait [this was an important innovation because any non-pure (segregating) generation would and did confuse the results of genetic experiments] Allele - one alternative form of a given allelic pair; tall and dwarf are the alleles for the hei ...
... Pure Line - a population that breeds true for a particular trait [this was an important innovation because any non-pure (segregating) generation would and did confuse the results of genetic experiments] Allele - one alternative form of a given allelic pair; tall and dwarf are the alleles for the hei ...
Morgan and Gene Recombination
... additive: 9% (b-cn) + 9.5% (cn-vg) > 17% (b-vg). • This results from multiple crossing over events. • A second crossing over “cancels out” the first and reduced the observed number of recombinant offspring. • Genes father apart (for example, b-vg) are more likely to experience multiple crossing over ...
... additive: 9% (b-cn) + 9.5% (cn-vg) > 17% (b-vg). • This results from multiple crossing over events. • A second crossing over “cancels out” the first and reduced the observed number of recombinant offspring. • Genes father apart (for example, b-vg) are more likely to experience multiple crossing over ...
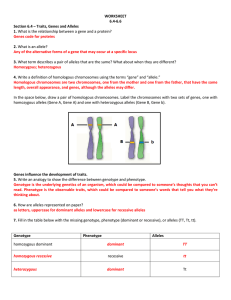
WORKSHEET 6.4-6.6 Section 6.4 – Traits, Genes and Alleles 1
... 9. The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes is called Crossing over 10. The tendency for two genes that are located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together is called. ...
... 9. The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes is called Crossing over 10. The tendency for two genes that are located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together is called. ...
Chapter 10 Meiosis
... – Because alleles for the same trait can vary, new combinations of genes in each chromosome can result; this is one source of genetic variation – After crossing over, the nonsister chromaids ...
... – Because alleles for the same trait can vary, new combinations of genes in each chromosome can result; this is one source of genetic variation – After crossing over, the nonsister chromaids ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)