Output Stages Class A, AB, and B Power Stages Laboratory
... Given is a triple darlington push pull output stage using the small-signal transistors BC546/BC556, the medium power transistors BD139/BD140, and the power transistors BD809 and BD810. The triple is most often used in power stages delivering more than app. 10W of signal power into a load. It allows ...
... Given is a triple darlington push pull output stage using the small-signal transistors BC546/BC556, the medium power transistors BD139/BD140, and the power transistors BD809 and BD810. The triple is most often used in power stages delivering more than app. 10W of signal power into a load. It allows ...
Neon Sign Transformer
... used to convert mains voltages to those suitable for powering neon signs. They are also known as Luminous Tube Transformers or Gaseous Tube Transformers. Neon Sign Transformers come in different shapes and sizes. They are distinguished by being current limited centre grounded. Center grounded means ...
... used to convert mains voltages to those suitable for powering neon signs. They are also known as Luminous Tube Transformers or Gaseous Tube Transformers. Neon Sign Transformers come in different shapes and sizes. They are distinguished by being current limited centre grounded. Center grounded means ...
Infra Red Door Monitor System
... module will recognize there is no more infrared signal and it will produce a constant high voltage (+5V) as the input of the receiver circuit. ...
... module will recognize there is no more infrared signal and it will produce a constant high voltage (+5V) as the input of the receiver circuit. ...
RF6280 Preliminary
... DC-DC buck converter operation involves the stepping down of a higher battery voltage to a lower output voltage by the alternate switching of a PFET and NFET pair through an external LC filter. The desired output voltage, together with the battery voltage, primarily determine the duty cycle of the P ...
... DC-DC buck converter operation involves the stepping down of a higher battery voltage to a lower output voltage by the alternate switching of a PFET and NFET pair through an external LC filter. The desired output voltage, together with the battery voltage, primarily determine the duty cycle of the P ...
Figure 1.1 A telephone system.
... 1) Turn off (replace voltage source with short and current source with open) all independent sources except one source. Find the output (voltage or current) due to that active source. 2) Repeat step 1 for each of the other independent sources. 3) Find the total contribution by adding algebraically a ...
... 1) Turn off (replace voltage source with short and current source with open) all independent sources except one source. Find the output (voltage or current) due to that active source. 2) Repeat step 1 for each of the other independent sources. 3) Find the total contribution by adding algebraically a ...
What is an Avalanche Diode?
... When an inductive load is switched off, the collapsing magnetic field is converted into electrical energy • The transient takes the form of a double exponential transient • The heavier the inductive load, the bigger the transient These transients can be as large as hundreds of volts and hundreds of ...
... When an inductive load is switched off, the collapsing magnetic field is converted into electrical energy • The transient takes the form of a double exponential transient • The heavier the inductive load, the bigger the transient These transients can be as large as hundreds of volts and hundreds of ...
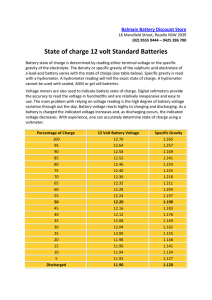
State of charge 12 volt Standard Batteries
... Battery state of charge is determined by reading either terminal voltage or the specific gravity of the electrolyte. The density or specific gravity of the sulphuric acid electrolyte of a lead-acid battery varies with the state of charge (see table below). Specific gravity is read with a hydrometer. ...
... Battery state of charge is determined by reading either terminal voltage or the specific gravity of the electrolyte. The density or specific gravity of the sulphuric acid electrolyte of a lead-acid battery varies with the state of charge (see table below). Specific gravity is read with a hydrometer. ...
Electronic Devices Conventional Current Version Thomas L. Floyd
... In the previous chapters, dc quantities were identified by nonitalic uppercase (capital) subscripts such as IC, IE, VC, and VCE. Lowercase italic subscripts are used to indicate ac quantities of rms, peak, and peak-to-peak currents and voltages: for example, Ic, Ie, Ib, Vc, and Vce (rms values are a ...
... In the previous chapters, dc quantities were identified by nonitalic uppercase (capital) subscripts such as IC, IE, VC, and VCE. Lowercase italic subscripts are used to indicate ac quantities of rms, peak, and peak-to-peak currents and voltages: for example, Ic, Ie, Ib, Vc, and Vce (rms values are a ...
PX3515 Sychronous Rectified Buck MOSFET Driver IC Applications Description
... Printed in the USA/1002/PDF/TK/PS This document contains characteristic data and other specifications that are subject to change without notice. Customers are advised to confirm information in this datasheet prior to using the information herein or placing an order. Primarion does not assume any lia ...
... Printed in the USA/1002/PDF/TK/PS This document contains characteristic data and other specifications that are subject to change without notice. Customers are advised to confirm information in this datasheet prior to using the information herein or placing an order. Primarion does not assume any lia ...
resonance
... function generator. example: if the frequency is 1k Hz, then f = 1 msec, and you might want to choose the 0.5 msec/div scale, or less so that you can see at least an entire wave on the screen. Trigger: The trigger tells you which wave you are using to time your display. In this case you want to use ...
... function generator. example: if the frequency is 1k Hz, then f = 1 msec, and you might want to choose the 0.5 msec/div scale, or less so that you can see at least an entire wave on the screen. Trigger: The trigger tells you which wave you are using to time your display. In this case you want to use ...
LT1671 - 60ns, Low Power,Single Supply, Ground-Sensing Comparator
... The LT1671 is designed for improved speed and stability for a wide range of operating conditions. The output stage provides active drive in both directions for maximum speed into TTL, CMOS or passive loads with minimal cross-conduction current. Unlike other fast comparators, the LT1671 remains stabl ...
... The LT1671 is designed for improved speed and stability for a wide range of operating conditions. The output stage provides active drive in both directions for maximum speed into TTL, CMOS or passive loads with minimal cross-conduction current. Unlike other fast comparators, the LT1671 remains stabl ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.