الشريحة 1
... the superior temporal sulcus plays a role in both language processing and social attention . ...
... the superior temporal sulcus plays a role in both language processing and social attention . ...
Glossary of Genetic Terms 11Jul15
... Birth defect - A structural, functional or metabolic abnormality present at birth that results in physical or mental disability or is fatal. There are more than 4,000 know birth defects that may be caused by genetic or environmental factors. About 150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects ...
... Birth defect - A structural, functional or metabolic abnormality present at birth that results in physical or mental disability or is fatal. There are more than 4,000 know birth defects that may be caused by genetic or environmental factors. About 150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects ...
lec-09-forensic-dna-analysis-chem-195h-2017
... billion chance of error. This means there may be one other person on the planet that would be too similar to tell the difference. If all other satellite regions are also considered, the chances of error go way, way down… 1 in 53,581,500,000,000,000,000 ...
... billion chance of error. This means there may be one other person on the planet that would be too similar to tell the difference. If all other satellite regions are also considered, the chances of error go way, way down… 1 in 53,581,500,000,000,000,000 ...
Facts About Genetics and Neuromuscular Diseases
... and RNA, astute observers noticed that genetic traits, including many disorders, were passed from one generation to another in somewhat predictable patterns. These came to be known as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked recessive and X-linked dominant patterns of inheritance. ...
... and RNA, astute observers noticed that genetic traits, including many disorders, were passed from one generation to another in somewhat predictable patterns. These came to be known as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked recessive and X-linked dominant patterns of inheritance. ...
CENP-E Is a Plus End–Directed Kinetochore Motor Required for
... polar ejection forces, drive congression of chromosomes to the metaphase plate. A major question has been whether kinetochore-associated microtubule motors play an important role in congression. Using immunodepletion from and antibody addition to Xenopus egg extracts, we show that the kinetochore-as ...
... polar ejection forces, drive congression of chromosomes to the metaphase plate. A major question has been whether kinetochore-associated microtubule motors play an important role in congression. Using immunodepletion from and antibody addition to Xenopus egg extracts, we show that the kinetochore-as ...
HEREDITY
... look similar, but not identical, to their parents. However, the set of chromosomes that a child inherits from each parent is random. This is why siblings, other than identical twins, look similar to one another, but not identical. In the case of identical twins, they actually do both inherit the sam ...
... look similar, but not identical, to their parents. However, the set of chromosomes that a child inherits from each parent is random. This is why siblings, other than identical twins, look similar to one another, but not identical. In the case of identical twins, they actually do both inherit the sam ...
CHAPTER 16 Advanced Gene Mapping in Eukaryotes
... opposite mating types (mt+ and mt-) fuse to produce a zygote. ii. Meiosis of the zygote produces an unordered tetrad of haploid cells, two of type mt+ and two mt-. iii. Mitosis of each haploid cell results in new haploid algae cells. ...
... opposite mating types (mt+ and mt-) fuse to produce a zygote. ii. Meiosis of the zygote produces an unordered tetrad of haploid cells, two of type mt+ and two mt-. iii. Mitosis of each haploid cell results in new haploid algae cells. ...
PPT presentation - Yavapai College
... REMEMBER: A particular region of DNA that has the code to make a particular protein is called a “gene.” Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. Biology Department, Yavapai College ...
... REMEMBER: A particular region of DNA that has the code to make a particular protein is called a “gene.” Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. Biology Department, Yavapai College ...
Q1. A gardener took four cuttings from the same plant and put them
... Choose words from this list to complete the sentences below. body ...
... Choose words from this list to complete the sentences below. body ...
Isolation and characterization of a repeated sequence (RPS1) of
... were virtually identical; however, one or two chromosomes were variable in size (Asakura et al., 1991). In virtually all cases, the chromosome that varied in size was chromosome 2. This suggested that chromosome 2 is too variable to be useful for distinguishing between strains. A similar variable ch ...
... were virtually identical; however, one or two chromosomes were variable in size (Asakura et al., 1991). In virtually all cases, the chromosome that varied in size was chromosome 2. This suggested that chromosome 2 is too variable to be useful for distinguishing between strains. A similar variable ch ...
A FURTHER ANALYSIS OF LOCI IN THE SO
... That “block B,” or a t any rate two blocks, are contained in the tiny section between the righthand breaks of scute-4 and scute-8, was shown by another experiment. In this a cytological study of the mitotic chromosomes was made in the case of a mutual translocation between the scute-8 chromosome and ...
... That “block B,” or a t any rate two blocks, are contained in the tiny section between the righthand breaks of scute-4 and scute-8, was shown by another experiment. In this a cytological study of the mitotic chromosomes was made in the case of a mutual translocation between the scute-8 chromosome and ...
Lecture 4
... chromosomes have a special kind of linkage called sex-linkage. Because there are two such chromosomes in humans and many other animals this linkage can be separated into X-linkage and Y-linkage. Y chromosome has very few genes that cause an observable phenotype, therefore most sex-linkage is in fact ...
... chromosomes have a special kind of linkage called sex-linkage. Because there are two such chromosomes in humans and many other animals this linkage can be separated into X-linkage and Y-linkage. Y chromosome has very few genes that cause an observable phenotype, therefore most sex-linkage is in fact ...
Heredity - SPS186.org
... genetic information they inherit from their parents. Heredity is the passing on, or transmission, of biological traits from parent to child. People are similar to each of their parents in some ways but different from their parents in other ways. What determines the combination of traits that are pas ...
... genetic information they inherit from their parents. Heredity is the passing on, or transmission, of biological traits from parent to child. People are similar to each of their parents in some ways but different from their parents in other ways. What determines the combination of traits that are pas ...
Histone H3 phosphorylation is required for the initiation, but not
... To correlate the extent of H3 phosphorylation with OAinduced PCC, we exposed asynchronous cell populations to 0.5 µM OA for 2.5 hours. Under these conditions, over 70% of HeLa and IM cells appeared rounded up with compact nuclei characteristic of S-phase PCC. The nuclei of these cells displayed high ...
... To correlate the extent of H3 phosphorylation with OAinduced PCC, we exposed asynchronous cell populations to 0.5 µM OA for 2.5 hours. Under these conditions, over 70% of HeLa and IM cells appeared rounded up with compact nuclei characteristic of S-phase PCC. The nuclei of these cells displayed high ...
Depat.Anat. Genetic/Lec4 Dr.sarab H. Linkage
... * Heterozygous females are carriers; they do not show the trait but can pass it on. XR Xr * Males are never carriers but express the one allele on the X chromosome. Characteristics of Sex-linked Inheritance The X-linked genes exhibit following characteristic patterns of inheritance : 1. The differen ...
... * Heterozygous females are carriers; they do not show the trait but can pass it on. XR Xr * Males are never carriers but express the one allele on the X chromosome. Characteristics of Sex-linked Inheritance The X-linked genes exhibit following characteristic patterns of inheritance : 1. The differen ...
The Gene Encoding Peripheral Myelin Protein Zero Is Located on
... (1977) Abnormal myelination in transplanted trembler mouse Schwann cells. Nature 265: 73-75. Banerjee, U., P. J. Renfranz, J. A. Pollack, and S. Benzer (1987) Molecular characterization and expression of sevenless, a gene involved in neuronal pattern formation in the Drosophila eye. Cell 49: 281291. ...
... (1977) Abnormal myelination in transplanted trembler mouse Schwann cells. Nature 265: 73-75. Banerjee, U., P. J. Renfranz, J. A. Pollack, and S. Benzer (1987) Molecular characterization and expression of sevenless, a gene involved in neuronal pattern formation in the Drosophila eye. Cell 49: 281291. ...
Mendel and After - U3A Site Builder Home Page
... determined by the combination of alleles. Alleles may be dominant, co-dominant or recessive. ...
... determined by the combination of alleles. Alleles may be dominant, co-dominant or recessive. ...
Modern Genetics Jeopardy
... Professionals who help couples understand their chances of having a child with a particular genetic disorder are called ____________________. ...
... Professionals who help couples understand their chances of having a child with a particular genetic disorder are called ____________________. ...
Final Jeopardy - Lindbergh School District
... Professionals who help couples understand their chances of having a child with a particular genetic disorder are called ____________________. ...
... Professionals who help couples understand their chances of having a child with a particular genetic disorder are called ____________________. ...
Organisation of the human genome and our tools for
... polypeptide sequence (Venter et al., 2001; Lander et al., 2001). The human genome contains approximately 30 000 genes and the average amount of coding sequence in a gene is 2000 base pairs. The size of human genes varies from hundreds of bases to several megabases especially due to the large introni ...
... polypeptide sequence (Venter et al., 2001; Lander et al., 2001). The human genome contains approximately 30 000 genes and the average amount of coding sequence in a gene is 2000 base pairs. The size of human genes varies from hundreds of bases to several megabases especially due to the large introni ...
A gene for the suppression of anchorage independence is located in
... In these studies a major problem has been to distinguish unequivocally between the chromosomes of the abnormal and of the normal parental cells. In order to circumvent this problem various approaches have been attempted, such as utilizing translocation chromosomes, variations of C-bands among strain ...
... In these studies a major problem has been to distinguish unequivocally between the chromosomes of the abnormal and of the normal parental cells. In order to circumvent this problem various approaches have been attempted, such as utilizing translocation chromosomes, variations of C-bands among strain ...
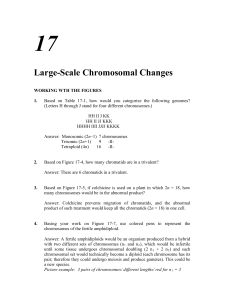
Large-Scale Chromosomal Changes
... an abnormal (mutant) phenotype. b. Cytologically, duplications lead to longer chromosomes and, depending on the type, unique pairing structures during meiosis when heterozygous. These may be simple unpaired loops or more complicated twisted loop structures. Genetically, duplications can lead to asym ...
... an abnormal (mutant) phenotype. b. Cytologically, duplications lead to longer chromosomes and, depending on the type, unique pairing structures during meiosis when heterozygous. These may be simple unpaired loops or more complicated twisted loop structures. Genetically, duplications can lead to asym ...
HCC Anthropology Lecture Chapter 1
... “anthropology” in order to provoke new modes of thought and to fulfill the “publish or perish” mentality when other issues cannot be examined ...
... “anthropology” in order to provoke new modes of thought and to fulfill the “publish or perish” mentality when other issues cannot be examined ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.