LIMITED DNA SYNTHESIS IN THE ABSENCE OF PROTEIN
... D N A synthesis between treated and control plasm o d i a is questionable, because " r a t e s " of synthesis as defined by pulse-labeling procedures are subject to u n c e r t a i n t y owing to the undefined status of the metabolic pool of t h y m i n e derivatives. I t should be noted t h a t the ...
... D N A synthesis between treated and control plasm o d i a is questionable, because " r a t e s " of synthesis as defined by pulse-labeling procedures are subject to u n c e r t a i n t y owing to the undefined status of the metabolic pool of t h y m i n e derivatives. I t should be noted t h a t the ...
! Mendel`s Law of Independent Assortment
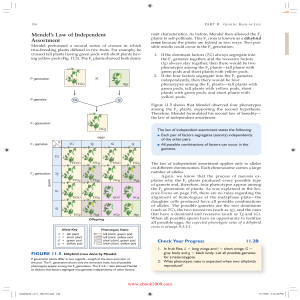
... see that each of these is ¼ of the total number of squares. How do we get the phenotypic results? The sum rule of probability tells us that when the same event can occur in more than one way, we can add the results. Because 1, 2, and 3 all result in unattached earlobes, we add them up to know that t ...
... see that each of these is ¼ of the total number of squares. How do we get the phenotypic results? The sum rule of probability tells us that when the same event can occur in more than one way, we can add the results. Because 1, 2, and 3 all result in unattached earlobes, we add them up to know that t ...
Informed Consent for Prenatal Diagnosis by
... 5) I understand that there is less than a 1 in 100 (1%) chance that the doctor may not be able to get enough amniotic fluid from the first try and may have to try a second time. Sometimes even the second time is not successful. It is my choice whether or not to have a second amniocentesis. 6) I unde ...
... 5) I understand that there is less than a 1 in 100 (1%) chance that the doctor may not be able to get enough amniotic fluid from the first try and may have to try a second time. Sometimes even the second time is not successful. It is my choice whether or not to have a second amniocentesis. 6) I unde ...
PowerPoint-presentatie
... progressive, hereditary, neuromuscular disorder which makes an individual very susceptible to nerve injury from pressure, stretch or repetitive use. When injured, the nerves demyelinate or lose their insulating covering. This causes episodes of numbness and weakness in the injured area, which are re ...
... progressive, hereditary, neuromuscular disorder which makes an individual very susceptible to nerve injury from pressure, stretch or repetitive use. When injured, the nerves demyelinate or lose their insulating covering. This causes episodes of numbness and weakness in the injured area, which are re ...
15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome - Unique The Rare Chromosome
... right amount of material – not too much and not too little. Even a tiny piece of missing material can disturb development, although it doesn’t always do so. ...
... right amount of material – not too much and not too little. Even a tiny piece of missing material can disturb development, although it doesn’t always do so. ...
Genetic Inheritance in Humans | Principles of Biology from Nature
... principles of Mendelian inheritance still provide an important foundation for understanding these more complex patterns. Mendelian patterns in human genetics. Human eye color is a trait that has often been described as a simple Mendelian trait, with brown eye color being dominant over green or blue ...
... principles of Mendelian inheritance still provide an important foundation for understanding these more complex patterns. Mendelian patterns in human genetics. Human eye color is a trait that has often been described as a simple Mendelian trait, with brown eye color being dominant over green or blue ...
Review
... during development, such as the temperature control of sex in alligators and crocodiles. the situation when alleles or alternative types of a particular linkage group (such as a Y or W chromosome) influence the probability of developing as a male or a female. the absence (or lack of function) of Y-l ...
... during development, such as the temperature control of sex in alligators and crocodiles. the situation when alleles or alternative types of a particular linkage group (such as a Y or W chromosome) influence the probability of developing as a male or a female. the absence (or lack of function) of Y-l ...
03 Inheritance booklet for.2015
... 10. If a pea plant with constricted seed pods is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for inflated seed pods, what are the chances of the offspring having constricted seed pods? You will need the pea plant chart on the next page to complete this problem. ...
... 10. If a pea plant with constricted seed pods is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for inflated seed pods, what are the chances of the offspring having constricted seed pods? You will need the pea plant chart on the next page to complete this problem. ...
A QTL Study of Cattle Behavioral Traits in Embryo Transfer Families
... which they found a QTL, is homologous to cattle chromosome 14 in the region where a QTL was found in this study. From the Department of Animal and Poultry Science (Schmutz, Winkelman-Sim, and Buchanan) and the Department of Herd Medicine and Theriogenology (Stookey and Waltz), University of Saskatch ...
... which they found a QTL, is homologous to cattle chromosome 14 in the region where a QTL was found in this study. From the Department of Animal and Poultry Science (Schmutz, Winkelman-Sim, and Buchanan) and the Department of Herd Medicine and Theriogenology (Stookey and Waltz), University of Saskatch ...
Idic(15)
... a third of those who took part in the Unique survey suffered from constipation although most children outgrew it (Unique). Many older babies and toddlers with idic(15) have trouble chewing and can choke or gag on lumps in food so may continue to eat puréed food for longer than their peers and the s ...
... a third of those who took part in the Unique survey suffered from constipation although most children outgrew it (Unique). Many older babies and toddlers with idic(15) have trouble chewing and can choke or gag on lumps in food so may continue to eat puréed food for longer than their peers and the s ...
Lesson Plan - Colorado FFA
... chromosome pair. The transmission of genes from parents to offspring depends entirely on the transmission of chromosomes from parents to offspring. Genes are what cause traits to be expressed. For each inherited trait an individual has, there are two genes for that specific trait, one from each pare ...
... chromosome pair. The transmission of genes from parents to offspring depends entirely on the transmission of chromosomes from parents to offspring. Genes are what cause traits to be expressed. For each inherited trait an individual has, there are two genes for that specific trait, one from each pare ...
Mendel and Genetics
... chromosome pair. The transmission of genes from parents to offspring depends entirely on the transmission of chromosomes from parents to offspring. Genes are what cause traits to be expressed. For each inherited trait an individual has, there are two genes for that specific trait, one from each pare ...
... chromosome pair. The transmission of genes from parents to offspring depends entirely on the transmission of chromosomes from parents to offspring. Genes are what cause traits to be expressed. For each inherited trait an individual has, there are two genes for that specific trait, one from each pare ...
Sex chromosomes and gender
... a region that was spatially linked to Sry to diverge from the X chromosome, leading to a loss of homology and recombination of those portions of the two chromosomes. The loss of recombination was important because it led to progressive degeneration of the Y chromosome and the subsequent evolution of ...
... a region that was spatially linked to Sry to diverge from the X chromosome, leading to a loss of homology and recombination of those portions of the two chromosomes. The loss of recombination was important because it led to progressive degeneration of the Y chromosome and the subsequent evolution of ...
CB3 - Homework
... When DNA is being extracted from cells, detergent is added to remove membranes. Protease enzymes (which digest proteins) are also used. Explain why detergent and protease enzymes are needed in order to collect pure samples of DNA. ...
... When DNA is being extracted from cells, detergent is added to remove membranes. Protease enzymes (which digest proteins) are also used. Explain why detergent and protease enzymes are needed in order to collect pure samples of DNA. ...
SEX CHROMOSOMES AND BRAIN GENDER
... a region that was spatially linked to Sry to diverge from the X chromosome, leading to a loss of homology and recombination of those portions of the two chromosomes. The loss of recombination was important because it led to progressive degeneration of the Y chromosome and the subsequent evolution of ...
... a region that was spatially linked to Sry to diverge from the X chromosome, leading to a loss of homology and recombination of those portions of the two chromosomes. The loss of recombination was important because it led to progressive degeneration of the Y chromosome and the subsequent evolution of ...
Gestation
... ends when the zygote implants into the wall of the mother's uterus. from two to eight weeks following conception the major organs and bodily systems form ...
... ends when the zygote implants into the wall of the mother's uterus. from two to eight weeks following conception the major organs and bodily systems form ...
by Attila Mokanszki Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Eva Olah
... most of them are macroscopic structural aberrations of chromosome Y. It can occur that the short arm of chromosome Y translocates to chromosome X or any autosomes. In cases of Y to X translocation male phenotype develops with 46,XX karyotype. This can explain by the presence of SRY (sex determinatio ...
... most of them are macroscopic structural aberrations of chromosome Y. It can occur that the short arm of chromosome Y translocates to chromosome X or any autosomes. In cases of Y to X translocation male phenotype develops with 46,XX karyotype. This can explain by the presence of SRY (sex determinatio ...
The dual nature of homologous recombination in plants
... Box 1. Homologous recombination and plant breeding Genetic improvement of crop plants, executed for many thousands of years, depends on HR. The classical breeding procedure involves crossing of chosen parental lines and subsequently selecting the offspring for the desired trait. An understanding of ...
... Box 1. Homologous recombination and plant breeding Genetic improvement of crop plants, executed for many thousands of years, depends on HR. The classical breeding procedure involves crossing of chosen parental lines and subsequently selecting the offspring for the desired trait. An understanding of ...
Genetic Diseases - American Society of Cytopathology
... • Sorted by size and labeled from 1-22, X and Y • Banding patterns after staining by Giemsa results in the following subclassifications: • p arm is the shorter segment from the centromere outward, q is the longer ...
... • Sorted by size and labeled from 1-22, X and Y • Banding patterns after staining by Giemsa results in the following subclassifications: • p arm is the shorter segment from the centromere outward, q is the longer ...
one
... different alleles. Both copies of a gene can affect phenotype. Much of what has been learned about human genes comes from studies of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, ...
... different alleles. Both copies of a gene can affect phenotype. Much of what has been learned about human genes comes from studies of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, ...
UP-CPMT - 2007 Paper-1
... 3) nephron 4) both (1) and (2) 41. Regeneration in Hydra will be faster if it is cut off from 1) tentacles 2) hypostome 3) base 4) all of these 42. First mammal occur in which era-period? ...
... 3) nephron 4) both (1) and (2) 41. Regeneration in Hydra will be faster if it is cut off from 1) tentacles 2) hypostome 3) base 4) all of these 42. First mammal occur in which era-period? ...
Sir John B. Gurdon - Nobel Lecture: The Egg and
... In addition to the rapid DNA replication and cell division enforced on a transplanted somatic nucleus, there are other ways in which we may account for the progressively decreasing success rate of nuclear transfers from differentiating and differentiated cells. One of these is that there may be a me ...
... In addition to the rapid DNA replication and cell division enforced on a transplanted somatic nucleus, there are other ways in which we may account for the progressively decreasing success rate of nuclear transfers from differentiating and differentiated cells. One of these is that there may be a me ...
REVIEWS - Ken Wolfe`s
... Box 1 | Paleopolyploidy in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome Analyses of the yeast genome sequence indicated that it contained duplicated chromosomal regions, in which a group of genes on one chromosome had a group of homologues on another chromosome32,36,48,49 (FIG. 3). Of yeast’s 5,800 genes, ~9 ...
... Box 1 | Paleopolyploidy in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome Analyses of the yeast genome sequence indicated that it contained duplicated chromosomal regions, in which a group of genes on one chromosome had a group of homologues on another chromosome32,36,48,49 (FIG. 3). Of yeast’s 5,800 genes, ~9 ...
B1 SHA - you and your genes
... True of False • Chromosomes are found in the nucleus. • Sperm and egg cells have the same amount of information as other body cells. • When we are adults our cells stop dividing. • Everyone in this room in unique. • Genes are joined up into chains called chromosomes. • The environment we grow up in ...
... True of False • Chromosomes are found in the nucleus. • Sperm and egg cells have the same amount of information as other body cells. • When we are adults our cells stop dividing. • Everyone in this room in unique. • Genes are joined up into chains called chromosomes. • The environment we grow up in ...
University of Debrecen - DEA
... The cell is the fundamental unit of life. Cells are isolated from the surrounding environment by a semipermeable membrane. That means that the cell is an open, dynamic structure, with exchanging materials and communicating with its environments. All cells have similar properties and containing sever ...
... The cell is the fundamental unit of life. Cells are isolated from the surrounding environment by a semipermeable membrane. That means that the cell is an open, dynamic structure, with exchanging materials and communicating with its environments. All cells have similar properties and containing sever ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.