Chapter 3 human development
... chromosome contains a gene called SRY that directs a developing fetus to make male organs. The X chromosome doesn’t have this thus female organs will be made. V. Define spontaneous abortion. a. Also called miscarriage. Is when the naturally occurring termination of a pregnancy before the fetus is fu ...
... chromosome contains a gene called SRY that directs a developing fetus to make male organs. The X chromosome doesn’t have this thus female organs will be made. V. Define spontaneous abortion. a. Also called miscarriage. Is when the naturally occurring termination of a pregnancy before the fetus is fu ...
Punnett Squares Sex-linked lab
... chromosome in comparison to the large number on the X chromosome. ...
... chromosome in comparison to the large number on the X chromosome. ...
Ch 14-2 DR
... 2. About how much of the DNA in your chromosomes are genes?______________________________ 3. How many base pairs does a single gene contain? _____________________ How many in the largest human genome?________________ 4. Chromosome 22 is one of the ____________________human autosomes, and contains __ ...
... 2. About how much of the DNA in your chromosomes are genes?______________________________ 3. How many base pairs does a single gene contain? _____________________ How many in the largest human genome?________________ 4. Chromosome 22 is one of the ____________________human autosomes, and contains __ ...
Biology Mitosis / Meiosis 2012 – 2013 #3
... B. Duplication = part of the chromosome breaks off and attaches to its homologous chromosome C. Inversion = part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards D. Translocation = part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a Non-homologous chromosome ...
... B. Duplication = part of the chromosome breaks off and attaches to its homologous chromosome C. Inversion = part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards D. Translocation = part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a Non-homologous chromosome ...
Homework #2
... A species has 2n = 20 chromosomes. How many chromosomes will be found per cell in each of the following mutants? a. b. c. d. e. ...
... A species has 2n = 20 chromosomes. How many chromosomes will be found per cell in each of the following mutants? a. b. c. d. e. ...
Piecing Together an Identity
... • Since cells in a male contain a single X chromosome and cells in a female contain two X chromosomes, females contain twice as many copies of the genes on the X chromosome per cell as do males. To equalize the dosage of X chromosome genes between the two sexes, one of the two X chromosomes in each ...
... • Since cells in a male contain a single X chromosome and cells in a female contain two X chromosomes, females contain twice as many copies of the genes on the X chromosome per cell as do males. To equalize the dosage of X chromosome genes between the two sexes, one of the two X chromosomes in each ...
Genekids - CICO TEAM
... you may have inherited factors that put you at risk. Inherited risk factors are passed down from parent to child by way of genes. All humans have the same genes, but different people have different versions of these genes. Sometimes genetic differences cause disease. In rare cases, changing a single ...
... you may have inherited factors that put you at risk. Inherited risk factors are passed down from parent to child by way of genes. All humans have the same genes, but different people have different versions of these genes. Sometimes genetic differences cause disease. In rare cases, changing a single ...
Ch 3 Sec3
... • Meiosis II– The chromosome with their 2 chromatids move to the center of the cell – Centromeres split and chromatids separate, single chromosome move to opposite ends of the cell ...
... • Meiosis II– The chromosome with their 2 chromatids move to the center of the cell – Centromeres split and chromatids separate, single chromosome move to opposite ends of the cell ...
CP Biology
... We know that males have XY sex chromosomes, and they seem to function just fine, so they must be able to survive with only 1 X chromosome. Females, however, have XX as sex chromosomes, two of them! So, do we really need two, or do females have an extra? The answer was discovered in 1961 by Mary Lyon ...
... We know that males have XY sex chromosomes, and they seem to function just fine, so they must be able to survive with only 1 X chromosome. Females, however, have XX as sex chromosomes, two of them! So, do we really need two, or do females have an extra? The answer was discovered in 1961 by Mary Lyon ...
Unit 3- Section 2
... Most of the code is useless Useful code=genes Genes code for proteins b. EX: Melanin a. ...
... Most of the code is useless Useful code=genes Genes code for proteins b. EX: Melanin a. ...
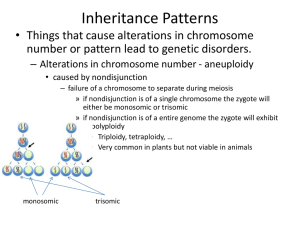
nondisjunction
... theory of heredity. The red-eyed male is XRY and the vermillion-eyed female is XrXr. Females in the F1 must receive XR from the male and Xr from the female. How could a vermillion-eyed female XrXr result? Yet the condition occurred and must be accounted for in terms of sex chromosomes and sex-linked ...
... theory of heredity. The red-eyed male is XRY and the vermillion-eyed female is XrXr. Females in the F1 must receive XR from the male and Xr from the female. How could a vermillion-eyed female XrXr result? Yet the condition occurred and must be accounted for in terms of sex chromosomes and sex-linked ...
Drosophila handout
... cloned DNA can be accomplished by in situ hybridization, and polytene maps can be correlated with genetic maps based on recombination by testing for complementation between mutant alleles and cytologically visible deletions. A summary of such correlated information is available on Flybase and links ...
... cloned DNA can be accomplished by in situ hybridization, and polytene maps can be correlated with genetic maps based on recombination by testing for complementation between mutant alleles and cytologically visible deletions. A summary of such correlated information is available on Flybase and links ...
Inheritance of Sex and Sex-Linked or Influenced Traits
... Fathers pass mutated allele to all ___________ Mothers pass mutated allele to _______________ ...
... Fathers pass mutated allele to all ___________ Mothers pass mutated allele to _______________ ...
Sex Linked Traits
... Sex Linked Traits • When X and Y chromosomes meet at fertilization, each sex-linked gene on the X chromosome (whether recessive or dominant) becomes expressed in the phenotype. • This is because the Y chromosome does not possess alleles of any of these genes and cannot offer dominance to them. ...
... Sex Linked Traits • When X and Y chromosomes meet at fertilization, each sex-linked gene on the X chromosome (whether recessive or dominant) becomes expressed in the phenotype. • This is because the Y chromosome does not possess alleles of any of these genes and cannot offer dominance to them. ...
BY 123 SI Session #9 Chapter 15 Siby123.yolasite.com Terms to
... b. The genes assort independently even though the chromosomes they are on travel to the metaphase plate together c. Their alleles segregate in anaphase I, and each gamete receives a single allele for all of these genes d. Dihybrid crosses with these genes produce more than 50% recombinant offspring ...
... b. The genes assort independently even though the chromosomes they are on travel to the metaphase plate together c. Their alleles segregate in anaphase I, and each gamete receives a single allele for all of these genes d. Dihybrid crosses with these genes produce more than 50% recombinant offspring ...
Note Review Sex-Linked Traits
... human, sperm and eggs carry 23 chromosomes (one from each pair of chromosomes). In addition to 22 other chromosomes (autosomes)... •Egg cells carry one X chromosome. •Sperm cells can carry either an X or a Y chromosome. With that in mind, which parent determines the sex of the child? _______________ ...
... human, sperm and eggs carry 23 chromosomes (one from each pair of chromosomes). In addition to 22 other chromosomes (autosomes)... •Egg cells carry one X chromosome. •Sperm cells can carry either an X or a Y chromosome. With that in mind, which parent determines the sex of the child? _______________ ...
Genes on Chromosomes - Capital High School
... (USA) have identified some 78 genes on the chromosome, instead of the 40 or so it was thought to contain. ...
... (USA) have identified some 78 genes on the chromosome, instead of the 40 or so it was thought to contain. ...
What is the difference between Autotrophs and heterotrophs?
... b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g. gene located on the X or Y chromosome ...
... b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g. gene located on the X or Y chromosome ...
when a woman is color blind ______.
... single gene. appear to be caused by an autosomal-dominant gene appear to have some sex linkage since men suffer NBDs more often than women ...
... single gene. appear to be caused by an autosomal-dominant gene appear to have some sex linkage since men suffer NBDs more often than women ...
answers to review questions chapter 6
... to one sex. A sex-limited trait affects a structure or function distinct to one sex. A sexinfluenced trait is inherited as a recessive in one sex and dominant in the other. 9. Coat color in cats is X-linked. In females, one X chromosome in each cell is inactivated, and the pattern of a calico cat's ...
... to one sex. A sex-limited trait affects a structure or function distinct to one sex. A sexinfluenced trait is inherited as a recessive in one sex and dominant in the other. 9. Coat color in cats is X-linked. In females, one X chromosome in each cell is inactivated, and the pattern of a calico cat's ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.