NAME KIT # ______ Karyotyping Lab 1. a. Normally, how many
... b. Is the sex of each baby readily obvious? _________ Occasionally, complications exist which make it difficult to determine the sex of a baby. What do you think these complications might be, and how could they occur? Explain your answer. ...
... b. Is the sex of each baby readily obvious? _________ Occasionally, complications exist which make it difficult to determine the sex of a baby. What do you think these complications might be, and how could they occur? Explain your answer. ...
Karyotyping Lab:
... b. Is the sex of each baby readily obvious? _________ Occasionally, complications exist which make it difficult to determine the sex of a baby. What do you think these complications might be, and how could they occur? Explain your answer. ...
... b. Is the sex of each baby readily obvious? _________ Occasionally, complications exist which make it difficult to determine the sex of a baby. What do you think these complications might be, and how could they occur? Explain your answer. ...
Essential Bio 4.1
... part of the discussions in class. After class, go back and review them. Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. Avoid printing this if possible. ...
... part of the discussions in class. After class, go back and review them. Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. Avoid printing this if possible. ...
Gene disruption-Why?
... Lexicon Features • 270,000 lines affecting >20,000 transcribed regions (50% of total genes?) • Mutagenesis is carried out in ES cells-thus can generate mutant mice ...
... Lexicon Features • 270,000 lines affecting >20,000 transcribed regions (50% of total genes?) • Mutagenesis is carried out in ES cells-thus can generate mutant mice ...
The frequency of crossing over appears to be governed largely by
... called the map unit to talk about distances in this way. Map units are not physical units in that they do not always represent a single, fixed length of DNA. They are relative measures, as “C is farther from A than is B.” Sordaria fimicola is an ascomycete fungus that can be used to demonstrate the ...
... called the map unit to talk about distances in this way. Map units are not physical units in that they do not always represent a single, fixed length of DNA. They are relative measures, as “C is farther from A than is B.” Sordaria fimicola is an ascomycete fungus that can be used to demonstrate the ...
GENETICS A
... alleles, one from each parent. 3. If the 2 alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele is fully expressed in the organism’s appearance; the recessive allele has no noticeable effect on the ...
... alleles, one from each parent. 3. If the 2 alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele is fully expressed in the organism’s appearance; the recessive allele has no noticeable effect on the ...
your name (first and last)
... Sexual reproduction occurs when new individual is formed through union of two sex cells (gametes). ...
... Sexual reproduction occurs when new individual is formed through union of two sex cells (gametes). ...
PART – I (General Agriculture) Please Note: printed in this set.
... formula can be used to predict the phenotypic classes in F2, where 'n' represents number of segregating genes? n a) 2 b) 3n c) 4n n+1 d) 2 117. In a diploid rice plant, the number of chromosome in the endosperm cell would be a) 12 b) 24 c) 36 d) 48 118. The amino acid having only one genetic code (c ...
... formula can be used to predict the phenotypic classes in F2, where 'n' represents number of segregating genes? n a) 2 b) 3n c) 4n n+1 d) 2 117. In a diploid rice plant, the number of chromosome in the endosperm cell would be a) 12 b) 24 c) 36 d) 48 118. The amino acid having only one genetic code (c ...
THT - TESD home
... D. genetic material is exchanged between chromosomes during this process. 24. A cat’s coloring is mostly determined by genes on their X chromosomes, which contain alleles for colors, such as black, orange, gray and cream. The allele for white fur is located on a different gene. Calico cats, by defin ...
... D. genetic material is exchanged between chromosomes during this process. 24. A cat’s coloring is mostly determined by genes on their X chromosomes, which contain alleles for colors, such as black, orange, gray and cream. The allele for white fur is located on a different gene. Calico cats, by defin ...
Meiosis and Mendel`s Law of Segregation
... Gametes (sperm and eggs) are produced from germ cells (the progenitors of sperm and eggs) through the process of meiosis. Meiosis is the process in which a diploid germ cell, diploid meaning that the cell has two sets of chromosomes – one from each parent, first replicates its DNA and then undergoes ...
... Gametes (sperm and eggs) are produced from germ cells (the progenitors of sperm and eggs) through the process of meiosis. Meiosis is the process in which a diploid germ cell, diploid meaning that the cell has two sets of chromosomes – one from each parent, first replicates its DNA and then undergoes ...
MEIOSIS Notes
... Why do we have meiosis? - to generate haploid gametes - to make new combinations of genes -How? random (independent) assortment ...
... Why do we have meiosis? - to generate haploid gametes - to make new combinations of genes -How? random (independent) assortment ...
sex chromosomes
... that a specific allele will have the same effect regardless of whether it was inherited from the mother or father. • However, for some traits in mammals, it does depend on which parent passed along the alleles for those traits. – The genes involved may or may not lie on the X chromosome. – Involves ...
... that a specific allele will have the same effect regardless of whether it was inherited from the mother or father. • However, for some traits in mammals, it does depend on which parent passed along the alleles for those traits. – The genes involved may or may not lie on the X chromosome. – Involves ...
Snurfle Meiosis Name: Date: Click on Snurfle Meiosis App Click on
... For recessive traits to show in the phenotype the snurfle will need copies of the gene. means an organism has 2 copies of the same allele in its genotype (GG, gg) means an organism has 2 different alleles in its genotype (Gg, Tt, Rr) Click on The Chromosome Quandary and follow the directions Cli ...
... For recessive traits to show in the phenotype the snurfle will need copies of the gene. means an organism has 2 copies of the same allele in its genotype (GG, gg) means an organism has 2 different alleles in its genotype (Gg, Tt, Rr) Click on The Chromosome Quandary and follow the directions Cli ...
Document
... same DNA, but only certain genes are ‘turned on’ at a time – Ex) the genes that determine hair color are only turned on in our hair follicles, and the genes that determine our height are only ‘turned on’ in our bone and muscle ...
... same DNA, but only certain genes are ‘turned on’ at a time – Ex) the genes that determine hair color are only turned on in our hair follicles, and the genes that determine our height are only ‘turned on’ in our bone and muscle ...
Recitation Section 16 Recombination and Pedigrees
... hemophilia B . Hemophilia A is due to a lack of one clotting factor, and hemophilia B is due to a lack of a different clotting factor. These two clotting factors are encoded by two different genes, located at different positions on the X chromosome. Note that no individual shown in this pedigree is ...
... hemophilia B . Hemophilia A is due to a lack of one clotting factor, and hemophilia B is due to a lack of a different clotting factor. These two clotting factors are encoded by two different genes, located at different positions on the X chromosome. Note that no individual shown in this pedigree is ...
Protocol S1
... Equation (S1) gives the expected number of generations until two beneficial mutations arepresent together in the same individual. Consequently, 31 g generations must pass, on average, until an individual would arise that had lost 32 chromosomes by mutation, if each mutation were to occur indepen ...
... Equation (S1) gives the expected number of generations until two beneficial mutations arepresent together in the same individual. Consequently, 31 g generations must pass, on average, until an individual would arise that had lost 32 chromosomes by mutation, if each mutation were to occur indepen ...
Unit 3 Test
... contained in the parent cell. That fact tells us that a. Spindle fibers form when the nuclear envelop breaks. b. Chromosomes form from chromatin in the nucleus. c. The chromosome number doubled during mitosis. d. Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes at their centromeres. What is the process in which ...
... contained in the parent cell. That fact tells us that a. Spindle fibers form when the nuclear envelop breaks. b. Chromosomes form from chromatin in the nucleus. c. The chromosome number doubled during mitosis. d. Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes at their centromeres. What is the process in which ...
3-24-16 Genetics and Heredity 12.3
... Genes & Heredity • When genes are passed on by reproduction, the offspring will have traits based on those genes • Asexual reproduction makes an exact genetic copy of the original organism (+ random mistakes) • Sexual reproduction can end up with a mix of 2 genes for the same thing, so it’s more co ...
... Genes & Heredity • When genes are passed on by reproduction, the offspring will have traits based on those genes • Asexual reproduction makes an exact genetic copy of the original organism (+ random mistakes) • Sexual reproduction can end up with a mix of 2 genes for the same thing, so it’s more co ...
Genetic Diseases
... man who is colorblind. What percentage of their sons will be color blind? Will any of their daughters be colorblind? b- A woman who inherited the gene for hemophilia from her mother has children with a man who does not have hemophilia. Using a Punnet square show all the possible genotypes of their c ...
... man who is colorblind. What percentage of their sons will be color blind? Will any of their daughters be colorblind? b- A woman who inherited the gene for hemophilia from her mother has children with a man who does not have hemophilia. Using a Punnet square show all the possible genotypes of their c ...
Chromosomal theory of inheritance
... • III-5 and III-6 are both heterozygous i.e. Aa. • What is the genotype of the gametes produced by an Aa individual? ...
... • III-5 and III-6 are both heterozygous i.e. Aa. • What is the genotype of the gametes produced by an Aa individual? ...
Heredity
... In vitro Fertilization – egg is extracted and egg and sperm are combined in the lab. The fertilized egg is then inserted into the mother’s uterus Ovum Transfer – donated egg plus in vitro fertilization Surrogate Mother – fertilized egg is inserted into surrogate or artificial insemination proc ...
... In vitro Fertilization – egg is extracted and egg and sperm are combined in the lab. The fertilized egg is then inserted into the mother’s uterus Ovum Transfer – donated egg plus in vitro fertilization Surrogate Mother – fertilized egg is inserted into surrogate or artificial insemination proc ...
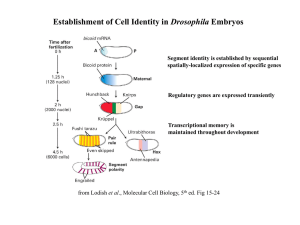
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
... Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
Generation 1
... actually be of opposite sexes, but one must play the role of mother (double X chromosome) and the other must play the role of father (XY chromosome). The chromosomes will be separated according to Mendel’s law of independent assortment. The genetic codes that are passed on to the babies will be reco ...
... actually be of opposite sexes, but one must play the role of mother (double X chromosome) and the other must play the role of father (XY chromosome). The chromosomes will be separated according to Mendel’s law of independent assortment. The genetic codes that are passed on to the babies will be reco ...
PHYSICS/ CHEM
... 11) If your two chromosomes have different alleles for a gene, does your body use the dominant or the recessive gene? ____________________________________________________________________ 12) Does “F” stand for a dominant or a recessive allele? _______________________________________ 13) If I tell yo ...
... 11) If your two chromosomes have different alleles for a gene, does your body use the dominant or the recessive gene? ____________________________________________________________________ 12) Does “F” stand for a dominant or a recessive allele? _______________________________________ 13) If I tell yo ...
Cell Processes: CRCT Review Notes
... • In mitosis, chromosomes are copied once, and then the nucleus divides once. In meiosis, chromosomes are copied once, and then the nucleus divides twice. • The process of meiosis produces sex cells, which have half the number of chromosomes. These two halves combine during reproduction. • In humans ...
... • In mitosis, chromosomes are copied once, and then the nucleus divides once. In meiosis, chromosomes are copied once, and then the nucleus divides twice. • The process of meiosis produces sex cells, which have half the number of chromosomes. These two halves combine during reproduction. • In humans ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.