Chapt 8
... Homologous chromosomes may carry different versions of genes Separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis can lead to genetic differences between gametes. – Homologous chromosomes may have different versions of a gene at the same locus. – One version was inherited from the maternal parent ...
... Homologous chromosomes may carry different versions of genes Separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis can lead to genetic differences between gametes. – Homologous chromosomes may have different versions of a gene at the same locus. – One version was inherited from the maternal parent ...
Article Old but Not (So) Degenerated—Slow
... differences in gene dose that arise during sex chromosome evolution has apparently found different ways of solution in different organisms (Disteche 2012). This is of some particular interest because recent data suggest that Ohno’s hypothesis (that X-linked expression of both sexes would equalize au ...
... differences in gene dose that arise during sex chromosome evolution has apparently found different ways of solution in different organisms (Disteche 2012). This is of some particular interest because recent data suggest that Ohno’s hypothesis (that X-linked expression of both sexes would equalize au ...
At the Forefront in PGD
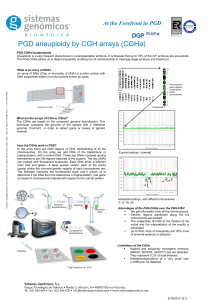
... Fundamentals of combined chromosomal PGD Couples with one member carrying a balanced chromosomal rearrangement (translocation or inversion) have an increased risk of generating abnormal embryos as a result of segregation of the balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many case ...
... Fundamentals of combined chromosomal PGD Couples with one member carrying a balanced chromosomal rearrangement (translocation or inversion) have an increased risk of generating abnormal embryos as a result of segregation of the balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many case ...
STIM1 monoclonal antibody (M01), clone 5A2
... full-length recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. ...
... full-length recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. ...
Introduction - Cedar Crest College
... Many protein-coding genes in eukaryotes are single-copy DNA sequences. Unlike most prokaryotes, however, eukaryotes have genes with noncoding internal sequences. Eukaryotes also form gene families with structurally and functionally related cousins in the genome. ...
... Many protein-coding genes in eukaryotes are single-copy DNA sequences. Unlike most prokaryotes, however, eukaryotes have genes with noncoding internal sequences. Eukaryotes also form gene families with structurally and functionally related cousins in the genome. ...
Y genetic variation and phenotypic diversity in health and disease
... Blood pressure is a risk factor associated with cardiovascular disease, and rodent models of hypertension have identified ChrY as a contributor to hypertension in males. A rat model was used to investigate the genetic mechanism driving spontaneous hypertension in SHR (S) rats compared to the normote ...
... Blood pressure is a risk factor associated with cardiovascular disease, and rodent models of hypertension have identified ChrY as a contributor to hypertension in males. A rat model was used to investigate the genetic mechanism driving spontaneous hypertension in SHR (S) rats compared to the normote ...
Fundamentals of human genetic
... one effect on the phenotype. • Such allele is said to be pleiotropic. • Pleiotropic relationships occur because in examine the characteristics of organisms; we are studying the consequences of the action of products made by genes. • Pleiotropy occurs in genetic diseases that affect a single protein ...
... one effect on the phenotype. • Such allele is said to be pleiotropic. • Pleiotropic relationships occur because in examine the characteristics of organisms; we are studying the consequences of the action of products made by genes. • Pleiotropy occurs in genetic diseases that affect a single protein ...
bioch11b - Otterville R
... III-1 has 12 kids with an unaffected wife 8 sons - 1 affected 4 daughters - 2 affected Does he have reason to be concerned about paternity? ...
... III-1 has 12 kids with an unaffected wife 8 sons - 1 affected 4 daughters - 2 affected Does he have reason to be concerned about paternity? ...
Chapter 11 Genetics
... A. Genes - units of information (Biochem info) 1. Locus - each gene has position on its chromosome 2. Alleles - differing molecular forms of a gene a. Alleles are denoted as: ‘a’, ‘b’, ...... ect.... b. Homozygous - both alleles are the same c. Heterozygous - both alleles are different d. Dominant - ...
... A. Genes - units of information (Biochem info) 1. Locus - each gene has position on its chromosome 2. Alleles - differing molecular forms of a gene a. Alleles are denoted as: ‘a’, ‘b’, ...... ect.... b. Homozygous - both alleles are the same c. Heterozygous - both alleles are different d. Dominant - ...
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled
... is highly compacted and transcriptionally inactive – Random inactivation of either the maternal or paternal chromosome – Occurs early in embryonic development and all cellular descendants have the same inactivated chromosome – Inactivated X chromosome is called a Barr body ...
... is highly compacted and transcriptionally inactive – Random inactivation of either the maternal or paternal chromosome – Occurs early in embryonic development and all cellular descendants have the same inactivated chromosome – Inactivated X chromosome is called a Barr body ...
Gene Regulation
... is highly compacted and transcriptionally inactive – Random inactivation of either the maternal or paternal chromosome ...
... is highly compacted and transcriptionally inactive – Random inactivation of either the maternal or paternal chromosome ...
chp 4 Notes
... • Ex: coat color in rodents – natural coat color in wild rodents is a greyish color (produced by alternating bands of black and yellow – agouti pattern) – Aids in camouflage – Found in mice, squirrels, etc – Other colorations exist, but are recessive to agouti » (A/– agouti; a/a nonagouti) ...
... • Ex: coat color in rodents – natural coat color in wild rodents is a greyish color (produced by alternating bands of black and yellow – agouti pattern) – Aids in camouflage – Found in mice, squirrels, etc – Other colorations exist, but are recessive to agouti » (A/– agouti; a/a nonagouti) ...
1.We wish to locate these four genes on the chromosomes. We don`t
... 6. Suppose a number of adenine-requiring mutants were isolated from a newly isolated fungi and the mutations have been classified into complementation groups. Each gene is thought to code for an enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway for adenine, so each mutation causes a block at a different step. All t ...
... 6. Suppose a number of adenine-requiring mutants were isolated from a newly isolated fungi and the mutations have been classified into complementation groups. Each gene is thought to code for an enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway for adenine, so each mutation causes a block at a different step. All t ...
Genetics Terms You`ve Gotta Know
... You get one allele from your mom and one from your dad. If you get the same alleles from your mom and dad, you are homozygous for that trait. If your mom gave you a different allele than your dad, you are heterozygous for that trait ...
... You get one allele from your mom and one from your dad. If you get the same alleles from your mom and dad, you are homozygous for that trait. If your mom gave you a different allele than your dad, you are heterozygous for that trait ...
Molecular Evolution of the Avian CHD1 Genes on the Z
... Li 1997). Second, while autosomal genes spend an equal amount of time in the male as in the female germline, sex-linked genes show a bias with respect to their transmission through the two sexes. The mammalian X chromosome, for example, is two-thirds of the time in the female germline. Moreover, gen ...
... Li 1997). Second, while autosomal genes spend an equal amount of time in the male as in the female germline, sex-linked genes show a bias with respect to their transmission through the two sexes. The mammalian X chromosome, for example, is two-thirds of the time in the female germline. Moreover, gen ...
Chapter 8 Mendel & Heredity
... Example Sex-linked disorders: #3. Hemophilia is a blood clotting disorder that is sex-linked recessive disorder (found on the X chromosome). Demonstrate a cross between a mom who is a carrier for the disorder and a dad who does not have hemophilia. a) What percent of the offspring will have hemoph ...
... Example Sex-linked disorders: #3. Hemophilia is a blood clotting disorder that is sex-linked recessive disorder (found on the X chromosome). Demonstrate a cross between a mom who is a carrier for the disorder and a dad who does not have hemophilia. a) What percent of the offspring will have hemoph ...
GeneticsforNursesinObstetricDisciplines
... • Mendelian diseases like osteogenesis imperfecta have distinctive family patterns • The pattern of affected relatives is caused by transmission of single genes, each with a unique position (locus) on the chromosome. • The paired chromosomes 1-22 and XX in females imply paired genes except for X an ...
... • Mendelian diseases like osteogenesis imperfecta have distinctive family patterns • The pattern of affected relatives is caused by transmission of single genes, each with a unique position (locus) on the chromosome. • The paired chromosomes 1-22 and XX in females imply paired genes except for X an ...
G Standard 7 - ALCOSbiologyPowerPoints
... Genotype- the genetic make-up of an organism that is determined by a single trait, set of traits, or an entire complex of traits. Heterozygous-having dissimilar pairs of genes for any given hereditary characteristic. Homozygous-having identical pairs of genes for any given pair of hereditary charact ...
... Genotype- the genetic make-up of an organism that is determined by a single trait, set of traits, or an entire complex of traits. Heterozygous-having dissimilar pairs of genes for any given hereditary characteristic. Homozygous-having identical pairs of genes for any given pair of hereditary charact ...
No Slide Title
... chromosome. Their ‘linkage distance’ can be determined by seeing how frequently they segregate together. Consider two linked genes in a heterozygous individual: ...
... chromosome. Their ‘linkage distance’ can be determined by seeing how frequently they segregate together. Consider two linked genes in a heterozygous individual: ...
mendel intro
... wound strand of DNA. Contains thousands of genes. Gene: A segment of a chromosome that codes for a protein. Gamete: A haploid sex cell (sperm and egg). Trait: The physical characteristic you get from the proteins made by one or more genes. ...
... wound strand of DNA. Contains thousands of genes. Gene: A segment of a chromosome that codes for a protein. Gamete: A haploid sex cell (sperm and egg). Trait: The physical characteristic you get from the proteins made by one or more genes. ...
Non-Mendelian Inheritance Question 1 Red flower color is
... Question 1 A gene that encodes an enzyme required for ribose synthesis is found on the X chromosome. Females that are heterozygous for the wild-type and defective mutant allele of this gene will show: E. 50% of their cells will lack enzymatic activity, the other 50% will be active. F. None of their ...
... Question 1 A gene that encodes an enzyme required for ribose synthesis is found on the X chromosome. Females that are heterozygous for the wild-type and defective mutant allele of this gene will show: E. 50% of their cells will lack enzymatic activity, the other 50% will be active. F. None of their ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.