MouseMine: Mouse Gene Lists (and a whole lot more)
... – Use the list of genes you find using MouseMine as input into the SNP query form @ MGI to see if there are any SNPs in these genes between the strains used to map the phenotype MGI: www.informatics.jax.org MouseMine: www.mousemine.org ...
... – Use the list of genes you find using MouseMine as input into the SNP query form @ MGI to see if there are any SNPs in these genes between the strains used to map the phenotype MGI: www.informatics.jax.org MouseMine: www.mousemine.org ...
Name
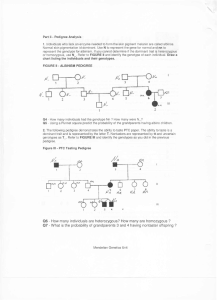
... 15. In the P generation, a dog homozygous dominant for straight fur (FF) is crossed with a dog homozygous recessive for curly fur (F’F’). The results of the F1 generation were 8 puppies with wavy fur. What type of inheritance pattern does this represent? _________________________ If two dogs with c ...
... 15. In the P generation, a dog homozygous dominant for straight fur (FF) is crossed with a dog homozygous recessive for curly fur (F’F’). The results of the F1 generation were 8 puppies with wavy fur. What type of inheritance pattern does this represent? _________________________ If two dogs with c ...
pedigree_worksheet_1-16
... Sex-linked dominant: Gene is located on the X-chromosome. Need only one dominant allele to have the disorder/trait (A_). All daughters of an affected male will be affected since the father has only the defective allele to give. Sex-linked recessive: Gene is located on the X-chromosome. Need two copi ...
... Sex-linked dominant: Gene is located on the X-chromosome. Need only one dominant allele to have the disorder/trait (A_). All daughters of an affected male will be affected since the father has only the defective allele to give. Sex-linked recessive: Gene is located on the X-chromosome. Need two copi ...
X r Y
... progeny, the distances between alleles are determined and a map created. – The distance between black-body and purpleeye alleles is 6 map units. – The distance between purple-eye and vestigial wing alleles is 12.5 map units. – The distance between black-body and vestigial wing alleles is 18.5 map un ...
... progeny, the distances between alleles are determined and a map created. – The distance between black-body and purpleeye alleles is 6 map units. – The distance between purple-eye and vestigial wing alleles is 12.5 map units. – The distance between black-body and vestigial wing alleles is 18.5 map un ...
Full Text PDF - Jaypee Journals
... or deletions in the Y chromosome (Yq11). It is important to note that numerous mouse knock out models that display as spermatogenic phenotype, including sperm cell arrest, has contributed little of clinical relevance to the large number of men with idiopathic infertility. The possible role of severa ...
... or deletions in the Y chromosome (Yq11). It is important to note that numerous mouse knock out models that display as spermatogenic phenotype, including sperm cell arrest, has contributed little of clinical relevance to the large number of men with idiopathic infertility. The possible role of severa ...
all chromosomes recombine in meiosis F2 plants
... Finding a gene based on phenotype • 1. 100’s of DNA markers mapped onto each chromosome – high density linkage map. • 2. identify markers linked to trait of interest by recombination analysis • 3. Narrow region down to a manageable length of DNA – for cloning and sequence comparison • 4. Compare mu ...
... Finding a gene based on phenotype • 1. 100’s of DNA markers mapped onto each chromosome – high density linkage map. • 2. identify markers linked to trait of interest by recombination analysis • 3. Narrow region down to a manageable length of DNA – for cloning and sequence comparison • 4. Compare mu ...
Albino gene
... If the sperm of a normal colored male pigeon has an albino gene and the ova it fertilizes has an albino gene than the offspring will be albino. ...
... If the sperm of a normal colored male pigeon has an albino gene and the ova it fertilizes has an albino gene than the offspring will be albino. ...
Testcross - dihybrid x recessive homozygous
... A female fruit fly heterozygous for the genes y (yellow body), w (white eyes), and ec (echinus eyes) located on the X chrom is mated to a yellow, white, echinus male. The phenotypes of ...
... A female fruit fly heterozygous for the genes y (yellow body), w (white eyes), and ec (echinus eyes) located on the X chrom is mated to a yellow, white, echinus male. The phenotypes of ...
Albino Rec Gene Powerpoint
... If the sperm of a normal colored male pigeon has an albino gene and the ova it fertilizes has an albino gene than the offspring will be albino. ...
... If the sperm of a normal colored male pigeon has an albino gene and the ova it fertilizes has an albino gene than the offspring will be albino. ...
A microarray gene expression data classification using hybrid back
... algorithm is mainly composed of three operators: reproduction, crossover, and mutation. As a first step of GA, an initial population of individuals is generated at random or heuristically. The individuals in the genetic space are called chromosome. The chromosome is a collection of genes where genes ...
... algorithm is mainly composed of three operators: reproduction, crossover, and mutation. As a first step of GA, an initial population of individuals is generated at random or heuristically. The individuals in the genetic space are called chromosome. The chromosome is a collection of genes where genes ...
Genome Research 13, 8 - Tel
... frame, by an angle equal to the corresponding central value. In protein coding regions, this rotation is assumed to closely align all vectors in the complex plane, thereby amplifying the magnitude of the vector sum. In noncoding regions, this operation does not significantly change this magnitude. C ...
... frame, by an angle equal to the corresponding central value. In protein coding regions, this rotation is assumed to closely align all vectors in the complex plane, thereby amplifying the magnitude of the vector sum. In noncoding regions, this operation does not significantly change this magnitude. C ...
Patterns of Heredity
... Occurs because other genes besides the alleles for sex are also located on the sex chromosomes. recessive to the normal are ___________ condition and the Y chromosomes appear to lack genes for these traits. ...
... Occurs because other genes besides the alleles for sex are also located on the sex chromosomes. recessive to the normal are ___________ condition and the Y chromosomes appear to lack genes for these traits. ...
4 TtGg
... The X chromosome contains additional genetic information that the Y chromosome does not have, therefore a male child actually inherits more genetic information from his ________ mother than his father (a very tiny amount). ...
... The X chromosome contains additional genetic information that the Y chromosome does not have, therefore a male child actually inherits more genetic information from his ________ mother than his father (a very tiny amount). ...
Transcription
... O Can control Z only when on same chromosome !!! -> cis acting control I is trans acting factor Proteins are synthesized in two stages: 1. DNA is transcribed in mRNA 2. mRNA is translated into protein This model explains behavior of lac system ...
... O Can control Z only when on same chromosome !!! -> cis acting control I is trans acting factor Proteins are synthesized in two stages: 1. DNA is transcribed in mRNA 2. mRNA is translated into protein This model explains behavior of lac system ...
ppt
... Both encode proteins aka “polycystin I & II” PKD1 gene is adjacent to gene of Tuberous sclerosis (TSC2), associated with cyst formation (angiomyolipoma) Genotype/phenotype correlation with PKD1 & 2 “unclear” – immense size, complexity, allelic heterogeneity ...
... Both encode proteins aka “polycystin I & II” PKD1 gene is adjacent to gene of Tuberous sclerosis (TSC2), associated with cyst formation (angiomyolipoma) Genotype/phenotype correlation with PKD1 & 2 “unclear” – immense size, complexity, allelic heterogeneity ...
nuclear structure (2): the nucleolus
... (1) The promoter is located at the upper left hand end of the genes. (2) The black “dots” on the DNA (at the bottom of each “branch”) are the RNA polymerase molecules. (3) The “branches” are the nascent 45S rRNA molecules. (4) At various locations along each “branch” (each nascent 45S rRNA molecule) ...
... (1) The promoter is located at the upper left hand end of the genes. (2) The black “dots” on the DNA (at the bottom of each “branch”) are the RNA polymerase molecules. (3) The “branches” are the nascent 45S rRNA molecules. (4) At various locations along each “branch” (each nascent 45S rRNA molecule) ...
Extraordinary Sequence Divergence at Tsga8, an X
... 2001; Khil et al. 2004; Dean et al. 2008). However, these patterns are largely restricted to genomic contrasts between mouse and rat and it is unclear to what extent this represents the action of positive natural selection (as opposed to relaxation of constraint). Moreover, mouse and rat diverged ;1 ...
... 2001; Khil et al. 2004; Dean et al. 2008). However, these patterns are largely restricted to genomic contrasts between mouse and rat and it is unclear to what extent this represents the action of positive natural selection (as opposed to relaxation of constraint). Moreover, mouse and rat diverged ;1 ...
Introduction to Microarray Analysis (Section D1)
... Microarrays work by exploiting the ability of a given mRNA molecule (target) to bind specifically to, or hybridize to, the DNA template (probe) from which it originated. This mechanism acts as both an "on/off" switch to control which genes are expressed in a cell as well as a "volume control" that i ...
... Microarrays work by exploiting the ability of a given mRNA molecule (target) to bind specifically to, or hybridize to, the DNA template (probe) from which it originated. This mechanism acts as both an "on/off" switch to control which genes are expressed in a cell as well as a "volume control" that i ...
Genes can be switched on and off by the protein CTCF
... The complex development of mammals requires that the majority of all genes can be switched off at any given time. Cell and tissue-specific inactivation is a characteristic feature of many developmentally regulated genes. Inactivation and reactivation of genes is often associated with chemical modifi ...
... The complex development of mammals requires that the majority of all genes can be switched off at any given time. Cell and tissue-specific inactivation is a characteristic feature of many developmentally regulated genes. Inactivation and reactivation of genes is often associated with chemical modifi ...
Meiosis
... A Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis - animation • Mitosis conserves the number of chromosome sets, producing cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell • Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes sets from two (diploid) to one (haploid), producing cells that differ genetically from eac ...
... A Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis - animation • Mitosis conserves the number of chromosome sets, producing cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell • Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes sets from two (diploid) to one (haploid), producing cells that differ genetically from eac ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.