3. Explain the basic thrust of signal-detection theory. 5. Discuss the
... initial intensity of a stimulus, but also on other sensory and decision processes as well. One factor that is particularly important here is the criterion you set for how certain you must feel before you react (what are the gains from being correct and what are the losses from being incorrect). What ...
... initial intensity of a stimulus, but also on other sensory and decision processes as well. One factor that is particularly important here is the criterion you set for how certain you must feel before you react (what are the gains from being correct and what are the losses from being incorrect). What ...
Development of emotional facial recognition in late
... The ability to interpret emotions in facial expressions is crucial for social functioning across the lifespan. Facial expression recognition develops rapidly during infancy and improves with age during the preschool years. However, the developmental trajectory from late childhood to adulthood is les ...
... The ability to interpret emotions in facial expressions is crucial for social functioning across the lifespan. Facial expression recognition develops rapidly during infancy and improves with age during the preschool years. However, the developmental trajectory from late childhood to adulthood is les ...
Review 2 - Texas A&M University
... Figure 5.3 The principle behind the inverse projection problem. The small square stimulus creates a square image on the retina. However, this image could also have been created by the other two shapes and many other stimuli. This is why we say that the image on the retina is ambiguous. ...
... Figure 5.3 The principle behind the inverse projection problem. The small square stimulus creates a square image on the retina. However, this image could also have been created by the other two shapes and many other stimuli. This is why we say that the image on the retina is ambiguous. ...
Syllabus P140C (68530) Cognitive Science
... Information Processing • Information processing models resemble processing in computers – made cognitive psychology popular • Idea is that information is processed in a number of stages • The major goal of information processing research is to – identify those processes – identify how information i ...
... Information Processing • Information processing models resemble processing in computers – made cognitive psychology popular • Idea is that information is processed in a number of stages • The major goal of information processing research is to – identify those processes – identify how information i ...
Summer
... that begins after just a few milliseconds of being presented with emotional stimuli – differed in ...
... that begins after just a few milliseconds of being presented with emotional stimuli – differed in ...
Models of bodily expression perception
... this traditional view we are miles away from a naturalistic perspective on emotions as adaptive actions as Darwin views them. ...
... this traditional view we are miles away from a naturalistic perspective on emotions as adaptive actions as Darwin views them. ...
... inspired by the biological disposition of animals and mimics biomechanisms. From the beginning of the 1990s, the NN technology attracted the attention of a large part of the scientific community. Since then, the technology has been advancing rapidly, and its applications are expanding in different a ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 51.1 Normal and pathological brain
... and structures—here synchronized action potentials in neocortical pyramidal neurons—sufficient for a specific conscious percept or memory. From Koch (2004). FIGURE 51.4 A fraction of aminute in the life of a typical IT cellwhile amonkey experiences binocular rivalry. The upper row indicates the visu ...
... and structures—here synchronized action potentials in neocortical pyramidal neurons—sufficient for a specific conscious percept or memory. From Koch (2004). FIGURE 51.4 A fraction of aminute in the life of a typical IT cellwhile amonkey experiences binocular rivalry. The upper row indicates the visu ...
Sensation and Perception
... Sensory processes are also known as low-level or peripheral processes Perceptual processes are also known as high-level or central processes ...
... Sensory processes are also known as low-level or peripheral processes Perceptual processes are also known as high-level or central processes ...
Biological Basis of Emotions - California Training Institute
... intelligence, subjectivity, sense of time and space, memory, mobility, and other less specific functions. Reptilian Brain: The primitive (reptilian) brain is responsible for self preservation. It is there that the mechanisms of aggression and repetitive behavior ...
... intelligence, subjectivity, sense of time and space, memory, mobility, and other less specific functions. Reptilian Brain: The primitive (reptilian) brain is responsible for self preservation. It is there that the mechanisms of aggression and repetitive behavior ...
Sensation and Perception - Shannon Deets Counseling
... Basilar Membrane-resting place of the organ of Corti Organ of Corti- contains receptor cells for the sense of hearing Auditory Nerve- bundle of axons from the hair cells in the inner ear that run to the brain ...
... Basilar Membrane-resting place of the organ of Corti Organ of Corti- contains receptor cells for the sense of hearing Auditory Nerve- bundle of axons from the hair cells in the inner ear that run to the brain ...
THE LIMBIC SYSTEM
... The amygdala is involved in signaling the cortex of motivationally significant stimuli such as those related to reward and fear in addition to social functions such as mating. The amygdala is the limbic structure that assigns the sensory information an emotional interpretation and instructs the bod ...
... The amygdala is involved in signaling the cortex of motivationally significant stimuli such as those related to reward and fear in addition to social functions such as mating. The amygdala is the limbic structure that assigns the sensory information an emotional interpretation and instructs the bod ...
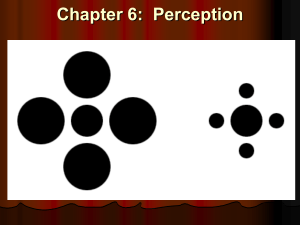
Chapter 6: Perception
... Who is closer: Snoopy or Woodstock? Woodstock How do you know? Woodstock blocks part of Snoopy. In other words, INTERPOSITION. ...
... Who is closer: Snoopy or Woodstock? Woodstock How do you know? Woodstock blocks part of Snoopy. In other words, INTERPOSITION. ...
Emotion, Memory and the Brain - sdsu
... shock (center). After several such pairings, the rat’s blood pressure rises at the same time that the animal holds still for an extended period when it hears the sound. The rat has been fearconditioned (right): sound alone achieves the same physiological changes as did sound and shock together. ...
... shock (center). After several such pairings, the rat’s blood pressure rises at the same time that the animal holds still for an extended period when it hears the sound. The rat has been fearconditioned (right): sound alone achieves the same physiological changes as did sound and shock together. ...
Sensation & Perception
... the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to the optic nerve (bundle of neurons that take informati ...
... the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to the optic nerve (bundle of neurons that take informati ...
Modules 16-21: Sensation and Perception
... 3) Deliver neural information to the brain ● Psychophysics- the study of relationship between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as their intensity, and our psychological experience of them ● Absolute threshold- the minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the tim ...
... 3) Deliver neural information to the brain ● Psychophysics- the study of relationship between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as their intensity, and our psychological experience of them ● Absolute threshold- the minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the tim ...
A unifying view of the basis of social cognition
... Towards a unifying neural hypothesis of the basis of social cognition • A bridge between ourselves and others • The understanding of basic aspects of social cognition depends on activation of neural structures normally involved in our own personally experienced actions or emotions. • Network of act ...
... Towards a unifying neural hypothesis of the basis of social cognition • A bridge between ourselves and others • The understanding of basic aspects of social cognition depends on activation of neural structures normally involved in our own personally experienced actions or emotions. • Network of act ...
Unit 4 - Learning and Cognitive Processes
... of humans and other animals. Investigate the role of biology and learning in motivation and emotion Describe the theories of motivation, such as expectancy value, cognitive dissonance, arousal, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, and drive reduction. Discuss cultural factors in emotions and motivations Des ...
... of humans and other animals. Investigate the role of biology and learning in motivation and emotion Describe the theories of motivation, such as expectancy value, cognitive dissonance, arousal, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, and drive reduction. Discuss cultural factors in emotions and motivations Des ...
Chapters Five and Six – Sensation and Perception
... Activity – Critical thinking and thresholds Understanding transduction Vision Anatomy of the eye Activity – locating the blind spot Activity – Examining peripheral vision Theories of color vision o Explain the difference between the YoungHelmholtz Trichromatic theory and the Opponent Proce ...
... Activity – Critical thinking and thresholds Understanding transduction Vision Anatomy of the eye Activity – locating the blind spot Activity – Examining peripheral vision Theories of color vision o Explain the difference between the YoungHelmholtz Trichromatic theory and the Opponent Proce ...
Slide 1
... -The James-Lange theory of emotion states that we experience our emotions by becoming aware of our physiological responses to emotion-arousing stimuli. Physical changes cause mental stresses. -Cannon- Bard theory of emotion says that an emotion-arousing stimulus simultaneously triggers physiologica ...
... -The James-Lange theory of emotion states that we experience our emotions by becoming aware of our physiological responses to emotion-arousing stimuli. Physical changes cause mental stresses. -Cannon- Bard theory of emotion says that an emotion-arousing stimulus simultaneously triggers physiologica ...
Between universal and local: Towards an evolutionary anthropology
... Paul Ekman developed an evolutionary research approach based on the study of the link between a small number of basic emotions and their resulting facial expressions. From his studies on the Fore ethnic group of New Guinea, Ekman became convinced of the mutual ability between them and people of West ...
... Paul Ekman developed an evolutionary research approach based on the study of the link between a small number of basic emotions and their resulting facial expressions. From his studies on the Fore ethnic group of New Guinea, Ekman became convinced of the mutual ability between them and people of West ...