Cells - Newton County Schools
... •(A) is the dominant trait. • (a) is the recessive trait. • There is a 100% probability that the offspring will be heterozygous. • The offspring will only carry the recessive trait, but not show it. • This is one of Mendel’s Laws of Genetics. (Law of Dominance) • The Genotype of the offspring ...
... •(A) is the dominant trait. • (a) is the recessive trait. • There is a 100% probability that the offspring will be heterozygous. • The offspring will only carry the recessive trait, but not show it. • This is one of Mendel’s Laws of Genetics. (Law of Dominance) • The Genotype of the offspring ...
1. The molecular “machines” (those components that do things) of
... carry some genes that have nothing to do with sex. d. were unknown to Mendel. e. all of these 85. Which of the following designates a normal human female? a. XXY b. XY c. XX d. XYY e. XO 86. In his experiments with Drosophila melanogaster, Morgan demonstrated that a. fertilized eggs have two sets of ...
... carry some genes that have nothing to do with sex. d. were unknown to Mendel. e. all of these 85. Which of the following designates a normal human female? a. XXY b. XY c. XX d. XYY e. XO 86. In his experiments with Drosophila melanogaster, Morgan demonstrated that a. fertilized eggs have two sets of ...
Tour of the Basics Web Quest
... 17. Does the second baby in the What is Heredity? animation inherit the exact same chromosomes as the first? Do both babies have a complete set? ...
... 17. Does the second baby in the What is Heredity? animation inherit the exact same chromosomes as the first? Do both babies have a complete set? ...
Introduction
... not inherited but are due to the effects of temperature, moisture, food, light or other environmental factors on the development of the organisms are called environmental variations. For example, the differences between a well-nourished and malnourished person. The heredity and variations have a sig ...
... not inherited but are due to the effects of temperature, moisture, food, light or other environmental factors on the development of the organisms are called environmental variations. For example, the differences between a well-nourished and malnourished person. The heredity and variations have a sig ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... unbalanced translocations of 11 and 22 are cleft palate, heart defects, ear anomalies, and male genital defects. ...
... unbalanced translocations of 11 and 22 are cleft palate, heart defects, ear anomalies, and male genital defects. ...
Making Reebops: a model for meiosis
... to show one of the ways in which meiosis is responsible for the tremendous variation in offspring in any species that reproduces sexually ...
... to show one of the ways in which meiosis is responsible for the tremendous variation in offspring in any species that reproduces sexually ...
First Semester Biology Study Guide
... Researchers report that genetically modified (GM) grains fed to test mice have no negative impact on health. In two trials, the offspring of mice fed GM grain for three weeks showed a similar survival rate as the offspring of mice that were fed non-GM grain. The trials have been called as a victory ...
... Researchers report that genetically modified (GM) grains fed to test mice have no negative impact on health. In two trials, the offspring of mice fed GM grain for three weeks showed a similar survival rate as the offspring of mice that were fed non-GM grain. The trials have been called as a victory ...
FISH
... imaging software, can distinguish all 23 chromosomes by chromosome specific colors. This type of analysis can be used to detect abnormalities that affect multiple chromosomes as is sometimes found in cancer cells or immortalized cell lines. ...
... imaging software, can distinguish all 23 chromosomes by chromosome specific colors. This type of analysis can be used to detect abnormalities that affect multiple chromosomes as is sometimes found in cancer cells or immortalized cell lines. ...
Ch. 14 The Human Genome
... cells “adjust” to having an extra X if males can survive with just one? ...
... cells “adjust” to having an extra X if males can survive with just one? ...
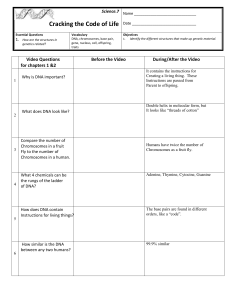
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
... Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
Chapter 24
... Incomplete dominance is a condition in which the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between that of either homozygote. In other words, neither of the alleles of the gene is completely dominant over any other allele. This can be seen in sickle cell disease. In codominance, the different alleles a ...
... Incomplete dominance is a condition in which the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between that of either homozygote. In other words, neither of the alleles of the gene is completely dominant over any other allele. This can be seen in sickle cell disease. In codominance, the different alleles a ...
Chapter 24
... over any other allele. This can be seen in sickle cell disease. In codominance, the different alleles are both expressed. This can be seen in ABO blood types. The most drastic upset in chromosome number is an entire extra set, a condition called polyploidy. This results from formation of a diploid ( ...
... over any other allele. This can be seen in sickle cell disease. In codominance, the different alleles are both expressed. This can be seen in ABO blood types. The most drastic upset in chromosome number is an entire extra set, a condition called polyploidy. This results from formation of a diploid ( ...
Reproduction of Organisms
... Mitosis—cell reproduction in which two identical cells are made from one cell All living things start life as a single cell All body growth and repair beyond this first cell happens through a process called mitosis. Chromosomes (contain genes made of DNA) are duplicated for each new cell Thi ...
... Mitosis—cell reproduction in which two identical cells are made from one cell All living things start life as a single cell All body growth and repair beyond this first cell happens through a process called mitosis. Chromosomes (contain genes made of DNA) are duplicated for each new cell Thi ...
Lesson 15d Meiosis PPT - Educational Excellence
... with sister chromatids remaining together. • Telophase 1: Two daughter cells are formed with each daughter containing only one chromosome of the homologous pair. ...
... with sister chromatids remaining together. • Telophase 1: Two daughter cells are formed with each daughter containing only one chromosome of the homologous pair. ...
File
... 18. Explain the steps that occur during meiosis. Drawing out the stages help to show your understanding 19. Explain the differences between Meiosis I and Mitosis ...
... 18. Explain the steps that occur during meiosis. Drawing out the stages help to show your understanding 19. Explain the differences between Meiosis I and Mitosis ...
Sex chromosomes - Perry Local Schools
... Sex chromosomes – determine the sex of an organism • Sex chromosomes, X and Y, determine gender in mammals. • May also carry genes for other characteristics • 2 sex chromosomes • Normal Females XX • Normal males XY Autosomes – all of the other chromosomes •44 autosomes •Two sets of each autosome •Re ...
... Sex chromosomes – determine the sex of an organism • Sex chromosomes, X and Y, determine gender in mammals. • May also carry genes for other characteristics • 2 sex chromosomes • Normal Females XX • Normal males XY Autosomes – all of the other chromosomes •44 autosomes •Two sets of each autosome •Re ...
document
... • Recombination frequencies are not always additive: 9% (b-cn) + 9.5% (cn-vg) ≠ 17% (b-vg). • Second crossing over can “cancel out” the first • Genes father apart are more likely to experience multiple crossing over events ...
... • Recombination frequencies are not always additive: 9% (b-cn) + 9.5% (cn-vg) ≠ 17% (b-vg). • Second crossing over can “cancel out” the first • Genes father apart are more likely to experience multiple crossing over events ...
Dragon Meiosis
... simulate the process of crossing-over that occurs during prophase I. Select one sister chromatid from each of the homologous chromosomes in pair one and cut them in half. Now take each piece and tape it to the piece from the opposite chromatid. Reassemble the chromatids into the homologous chromosom ...
... simulate the process of crossing-over that occurs during prophase I. Select one sister chromatid from each of the homologous chromosomes in pair one and cut them in half. Now take each piece and tape it to the piece from the opposite chromatid. Reassemble the chromatids into the homologous chromosom ...
Human Heredity
... The female is a sex linked carrier for “red glowing nose”…but her phenotype is black nose….and she is ...
... The female is a sex linked carrier for “red glowing nose”…but her phenotype is black nose….and she is ...
Genetics Exercises PDF
... m1/m1 homozygotes show a particular phenotype. m2/m2 homozygotes show the same phenotype. Are m1 and m2 mutations in the same gene or in different genes? ...
... m1/m1 homozygotes show a particular phenotype. m2/m2 homozygotes show the same phenotype. Are m1 and m2 mutations in the same gene or in different genes? ...
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.