DNA info
... Genes are the basic structural and functional unit of heredity. Together they form chromosomes which are made up of DNA, histones, and other support proteins. Therefore genes are found on DNA. All of the hereditary material could be called ‘instructions for making a living thing’! A gene is a specif ...
... Genes are the basic structural and functional unit of heredity. Together they form chromosomes which are made up of DNA, histones, and other support proteins. Therefore genes are found on DNA. All of the hereditary material could be called ‘instructions for making a living thing’! A gene is a specif ...
Types of chromosome abnormalities
... 45,XY,der(13;14)(q10;q10): A male with a balanced Roberstonian translocation of chromosomes 13 and 14. Karyotype shows that one normal 13 and one normal 14 are missing and replaced with a derivative chromosome 46,XY,t(11;22)(q23;q22): A male with a balanced reciprocal translocation between chromosom ...
... 45,XY,der(13;14)(q10;q10): A male with a balanced Roberstonian translocation of chromosomes 13 and 14. Karyotype shows that one normal 13 and one normal 14 are missing and replaced with a derivative chromosome 46,XY,t(11;22)(q23;q22): A male with a balanced reciprocal translocation between chromosom ...
Unit 5 Review
... Name one thing that DNA provides templates for Name two of the three important roles of cell division True or false: Binary Fission produces two genetically unique cells Name the process by which single-celled eukaryotic organisms produce genetically identical copies of themselves How many daughter ...
... Name one thing that DNA provides templates for Name two of the three important roles of cell division True or false: Binary Fission produces two genetically unique cells Name the process by which single-celled eukaryotic organisms produce genetically identical copies of themselves How many daughter ...
File - Enders Science Page
... Goal • Review your understanding of the phases of the cell cycle. What to Do Write the name of the stage of the cell cycle that corresponds to each event described below. 1. Centromeres divide. ________________ 2. Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. ________________ 3. Nuclear membranes fo ...
... Goal • Review your understanding of the phases of the cell cycle. What to Do Write the name of the stage of the cell cycle that corresponds to each event described below. 1. Centromeres divide. ________________ 2. Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. ________________ 3. Nuclear membranes fo ...
Biology Final Review Sheet
... DNA & RNA are considered to be what type of organic molecule? What are the 3 components of a nucleotide (the monomer unit of a nucleic acid)? Where is DNA located in eukaryotic cells? Watson & ...
... DNA & RNA are considered to be what type of organic molecule? What are the 3 components of a nucleotide (the monomer unit of a nucleic acid)? Where is DNA located in eukaryotic cells? Watson & ...
Meiosis Poster Project - Mercer Island School District
... o Remember to make sister chromatids identical (same gene form). o Use pieces of clay to represent the centromeres. o Show the 2 possible ways that the 2 pairs of chromosomes can line up during independent assortment and label these two possibilities as option 1 and option 2. o Display the 4 possibl ...
... o Remember to make sister chromatids identical (same gene form). o Use pieces of clay to represent the centromeres. o Show the 2 possible ways that the 2 pairs of chromosomes can line up during independent assortment and label these two possibilities as option 1 and option 2. o Display the 4 possibl ...
BioSc 231 Exam 4 2008
... underwent meiosis, the prophase chromosome configuration was examined. If the guess about the suspected parent is correct, what would the chromosome configuration look like? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... underwent meiosis, the prophase chromosome configuration was examined. If the guess about the suspected parent is correct, what would the chromosome configuration look like? A. B. C. D. E. ...
Document
... 2ND QUARTER STUDY GUIDE Name_____________________________________Date_______________________Period____________________ ...
... 2ND QUARTER STUDY GUIDE Name_____________________________________Date_______________________Period____________________ ...
Mammalian X Chromosome Inactivation
... Triploid oysters are of economic value. In general, polyploid mammals are not viable. ...
... Triploid oysters are of economic value. In general, polyploid mammals are not viable. ...
080701Genes and chromosomes
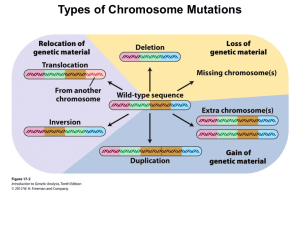
... spontaneous miscarriage and, of these, 50% have a chromosome anomaly (Turnpenny and Ellard, 2007). If a zygote forms from a chromosomally abnormal egg or sperm cell, and survives, the chromosome error can perpetuate each time the cells divide. Thus, as the embryo grows, the added or missing genetic ...
... spontaneous miscarriage and, of these, 50% have a chromosome anomaly (Turnpenny and Ellard, 2007). If a zygote forms from a chromosomally abnormal egg or sperm cell, and survives, the chromosome error can perpetuate each time the cells divide. Thus, as the embryo grows, the added or missing genetic ...
What are chromosomes?
... inverted or opposite manner. Since there is no loss nor gain of chromosomal material, inversion carriers are normal Paracentric: does not include the centromere pericentric:inverted segment contains the centromere In meiosis, the normal chromosome and the inverted chromosome will form a loop to allo ...
... inverted or opposite manner. Since there is no loss nor gain of chromosomal material, inversion carriers are normal Paracentric: does not include the centromere pericentric:inverted segment contains the centromere In meiosis, the normal chromosome and the inverted chromosome will form a loop to allo ...
Multiple Choice Questions – Answers
... cells. Mitotic division results in daughter cells containing a full number of genes as the parent cell they came from. 5. The type of cell division that occurs in the gamete cells is known as: A Cytosis B Meiosis [True] C Osmosis D Mitosis The correct answer is B. Meiosis is the cell division proces ...
... cells. Mitotic division results in daughter cells containing a full number of genes as the parent cell they came from. 5. The type of cell division that occurs in the gamete cells is known as: A Cytosis B Meiosis [True] C Osmosis D Mitosis The correct answer is B. Meiosis is the cell division proces ...
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false
... ____ 15. The fact that species today look different from their ancestors can be described as descent with modification. _________________________ ____ 16. According to Charles Darwin, members of a species must share limited resources. _________________________ ____ 17. A polygenic trait is controlle ...
... ____ 15. The fact that species today look different from their ancestors can be described as descent with modification. _________________________ ____ 16. According to Charles Darwin, members of a species must share limited resources. _________________________ ____ 17. A polygenic trait is controlle ...
Meiosis - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
... A) two cells with 46 chromosomes in each. B) two cells with 23 chromosomes in each. C) four cells with 23 chromosomes in each. D) four cells with 46 chromosomes in each. ...
... A) two cells with 46 chromosomes in each. B) two cells with 23 chromosomes in each. C) four cells with 23 chromosomes in each. D) four cells with 46 chromosomes in each. ...
Hypothesis: Variations in the rate of DNA replication determine the
... The existence of two identical chromosomes within the same cell in which genes and higher order structures compete for limited resources is a symmetrybreaking situation previously proposed to lead to differentiation. Recent experiments are consistent with an intimate relationship between metabolism ...
... The existence of two identical chromosomes within the same cell in which genes and higher order structures compete for limited resources is a symmetrybreaking situation previously proposed to lead to differentiation. Recent experiments are consistent with an intimate relationship between metabolism ...
genetics - MrsGorukhomework
... Polygenic inheritance –Characteristics caused by a combine effect of more than one gene. Phenotype varies in graduation. Most human characteristics are polygenetic. Eg. Skin colour, body height, muscle development, hair colour, eye colour. (examine eyes with lens, will see more than 2 separate colou ...
... Polygenic inheritance –Characteristics caused by a combine effect of more than one gene. Phenotype varies in graduation. Most human characteristics are polygenetic. Eg. Skin colour, body height, muscle development, hair colour, eye colour. (examine eyes with lens, will see more than 2 separate colou ...
What are chromosomes?
... All people resemble their parents in some ways. They have similar traits. …And it is no accident. Many traits are passed on from parents to offspring. We say they are inherited. How are they inherited? The answer is found in the cell nucleus. Each kind of organism has a specific number of chromosome ...
... All people resemble their parents in some ways. They have similar traits. …And it is no accident. Many traits are passed on from parents to offspring. We say they are inherited. How are they inherited? The answer is found in the cell nucleus. Each kind of organism has a specific number of chromosome ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... Questions 1-2 pertain to the following. Fertile varieties of the Golana melon are known that contain 14, 28, 42, 56, and 70 chromosomes, respectively. A variety that contains 21 chromosomes exists, but can only be propagated through cuttings. 1. The monoploid number for these Golana melon species is ...
... Questions 1-2 pertain to the following. Fertile varieties of the Golana melon are known that contain 14, 28, 42, 56, and 70 chromosomes, respectively. A variety that contains 21 chromosomes exists, but can only be propagated through cuttings. 1. The monoploid number for these Golana melon species is ...
Genetic Disease
... 12) Twin studies show that pairs of identical (monozygotic) twins, with their identical genes, have a higher-than-average chance of sharing the same orientation compared to pairs of randomly selected individuals; the average (or "background") rate of the trait in any given population is just under 8 ...
... 12) Twin studies show that pairs of identical (monozygotic) twins, with their identical genes, have a higher-than-average chance of sharing the same orientation compared to pairs of randomly selected individuals; the average (or "background") rate of the trait in any given population is just under 8 ...
Cytogenetic and molecular cytogenetic analysis in clinical genetics
... imaging software, can distinguish all 23 chromosomes by chromosome specific colors. This type of analysis can be used to detect abnormalities that affect multiple chromosomes as is sometimes found in cancer cells or immortalized cell lines. ...
... imaging software, can distinguish all 23 chromosomes by chromosome specific colors. This type of analysis can be used to detect abnormalities that affect multiple chromosomes as is sometimes found in cancer cells or immortalized cell lines. ...
Human Inheritance
... Inherited human genetic disorders are the result of gene mutations; that is, _a change in the DNA sequence of the gene____. B. Types of Inherited Genetic Disorders 1. Sex-Linked Disorders – Mutated gene is on the _X__ chromosome. 2. Autosomal Genetic Disorders – Gene mutation is on any chromosome ot ...
... Inherited human genetic disorders are the result of gene mutations; that is, _a change in the DNA sequence of the gene____. B. Types of Inherited Genetic Disorders 1. Sex-Linked Disorders – Mutated gene is on the _X__ chromosome. 2. Autosomal Genetic Disorders – Gene mutation is on any chromosome ot ...
teacher version
... divided into genes. A gene is a sequence of DNA that contains information to perform a cellular function. There are over 30,000 genes in the human genome, and a copy of the entire genome is present in the nucleus of every cell of the body (with a few exceptions—such as red blood cells and platelets) ...
... divided into genes. A gene is a sequence of DNA that contains information to perform a cellular function. There are over 30,000 genes in the human genome, and a copy of the entire genome is present in the nucleus of every cell of the body (with a few exceptions—such as red blood cells and platelets) ...
Inheritance – Summary
... 4. One result of a chromosome mutation in humans is Down’s syndrome. Describe this condition and how it is caused. Down’s Syndrome _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ...
... 4. One result of a chromosome mutation in humans is Down’s syndrome. Describe this condition and how it is caused. Down’s Syndrome _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ...
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.