Dominantаннаallele that is always shown in the phenotype, never
... gene, will be hidden by the other 3. Phenotype physical display or expression of trait 4. Genotype actual makeup of genes (TT, Tt, etc.) 5. Homozygous both alleles are same (TT, tt) 6. Heterozygous 2 different alleles (Tt) 7. Chromosomes extremely long molecule of DNA, humans have 2 ...
... gene, will be hidden by the other 3. Phenotype physical display or expression of trait 4. Genotype actual makeup of genes (TT, Tt, etc.) 5. Homozygous both alleles are same (TT, tt) 6. Heterozygous 2 different alleles (Tt) 7. Chromosomes extremely long molecule of DNA, humans have 2 ...
Gene – Sequence of DNA that codes for a particular protein or trait
... protein or trait. Ex. Gene for pea plant flower color Allele – Different form of a particular gene Ex. P = purple, p = white Locus (loci) – the physical location of a gene on a chromosome Ex. Closer/farther from the centromere (colored bands on the chromosomes above) ...
... protein or trait. Ex. Gene for pea plant flower color Allele – Different form of a particular gene Ex. P = purple, p = white Locus (loci) – the physical location of a gene on a chromosome Ex. Closer/farther from the centromere (colored bands on the chromosomes above) ...
I Will Divide
... Oh, no, but I, I will divide! Oh, through the stages of mitosis, I know my genes will stay alive I've made two new daughter cells, and they’ve got all my DNA I will divide! I will divide! Hey, hey! The first stage is prophase, the nucleus falls apart The DNA forms chromosomes, there’s no more hiding ...
... Oh, no, but I, I will divide! Oh, through the stages of mitosis, I know my genes will stay alive I've made two new daughter cells, and they’ve got all my DNA I will divide! I will divide! Hey, hey! The first stage is prophase, the nucleus falls apart The DNA forms chromosomes, there’s no more hiding ...
The Fly Genome
... 180 million base pairs 120 Mbp has been sequenced The sequenced portion is euchromatin thought to be richer in gene sequences than the remaining heterochromatin Drosophila has a haploid number of 4: 3 autosomes plus 1 sex chromosome Polytene chromosomes can be easily observed in the salivary glands ...
... 180 million base pairs 120 Mbp has been sequenced The sequenced portion is euchromatin thought to be richer in gene sequences than the remaining heterochromatin Drosophila has a haploid number of 4: 3 autosomes plus 1 sex chromosome Polytene chromosomes can be easily observed in the salivary glands ...
Meiosis - cloudfront.net
... Cytokinesis I - ___________ new cells are formed. Each cell has only ________ of each gene and is _____________________ from the mother cell. Prophase II - _____________________________ dissolves. _____________ replicates Metaphase II - _______________________________________ line up in the center o ...
... Cytokinesis I - ___________ new cells are formed. Each cell has only ________ of each gene and is _____________________ from the mother cell. Prophase II - _____________________________ dissolves. _____________ replicates Metaphase II - _______________________________________ line up in the center o ...
Unit 5 - Notes
... 6. The letters (ex. RR) that represent the traits are referred to as the a) phenotype b) genotype 7. An organism that has two different alleles, or letters, such as Rr is: a) homozygous b) heterozygous 8. 7. An organism that has two of the same alleles, or letters, such as RR is: a) homozygous b) h ...
... 6. The letters (ex. RR) that represent the traits are referred to as the a) phenotype b) genotype 7. An organism that has two different alleles, or letters, such as Rr is: a) homozygous b) heterozygous 8. 7. An organism that has two of the same alleles, or letters, such as RR is: a) homozygous b) h ...
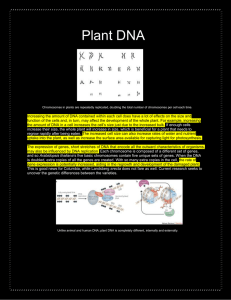
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
the definitions of the following terms
... The law of segregation and the law of independent assortment The stages of the cell cycle in the correct order and what happens in each That the new cells produced as a result of a mitotic division are identical to the parental cells That the new cells produced as a result of a meiotic divis ...
... The law of segregation and the law of independent assortment The stages of the cell cycle in the correct order and what happens in each That the new cells produced as a result of a mitotic division are identical to the parental cells That the new cells produced as a result of a meiotic divis ...
the definitions of the following terms:
... The law of segregation and the law of independent assortment The stages of the cell cycle in the correct order and what happens in each That the new cells produced as a result of a mitotic division are identical to the parental cells That the new cells produced as a result of a meiotic divis ...
... The law of segregation and the law of independent assortment The stages of the cell cycle in the correct order and what happens in each That the new cells produced as a result of a mitotic division are identical to the parental cells That the new cells produced as a result of a meiotic divis ...
Section Objectives
... Mutations in body cells/autosomes • A cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not be passed on to offspring. • Damage to a gene may impair the function of the cell. Some mutations of DNA in body cells affect genes that control cell division. This can result in the cells growing and dividing rapi ...
... Mutations in body cells/autosomes • A cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not be passed on to offspring. • Damage to a gene may impair the function of the cell. Some mutations of DNA in body cells affect genes that control cell division. This can result in the cells growing and dividing rapi ...
Guide to 2nd Drosophila discussion
... Paper for discussion: Hartl TA, Smith HF, Bosco G. (2008) Chromosome alignment and transvection are antagonized by condensin II. Science 322(5906):1384-7 Although this paper is not heavy on genetic techniques, it will expose you to some interesting aspects of biology with very strong Drosophila gene ...
... Paper for discussion: Hartl TA, Smith HF, Bosco G. (2008) Chromosome alignment and transvection are antagonized by condensin II. Science 322(5906):1384-7 Although this paper is not heavy on genetic techniques, it will expose you to some interesting aspects of biology with very strong Drosophila gene ...
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Quiz 6B
... diploid cell forms haploid cells (gametes) •a dividing process during which the # of chromosomes is cut by 1/2 in each resulting cell •also called reduction division ...
... diploid cell forms haploid cells (gametes) •a dividing process during which the # of chromosomes is cut by 1/2 in each resulting cell •also called reduction division ...
DNA Assignment
... b) During prophase 1 of meiosis, chromosomes form pairs called:______________________________ c) Meiosis I ends with __________________________, there are ______________ daughter cells. d) d) How many cells are there at the end of meiosis 2? ____________ ...
... b) During prophase 1 of meiosis, chromosomes form pairs called:______________________________ c) Meiosis I ends with __________________________, there are ______________ daughter cells. d) d) How many cells are there at the end of meiosis 2? ____________ ...
Chapter 7
... a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type. b. Students know only certain cells in a multicellular organism undergo meiosis. c. Stude ...
... a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type. b. Students know only certain cells in a multicellular organism undergo meiosis. c. Stude ...
PowerPoint
... • Only those trisomies involving the smallest or heterochromatic chromosomes are able to survive at all ...
... • Only those trisomies involving the smallest or heterochromatic chromosomes are able to survive at all ...
Ch. 10.5 Sex-Linked Traits
... • Males need just 1 recessive allele ( they have only 1 X chromosome) Xr Y to have white eyes. ...
... • Males need just 1 recessive allele ( they have only 1 X chromosome) Xr Y to have white eyes. ...
Name - Humble ISD
... chromosomes separate in __________________, the sex chromosomes separate also. The resulting egg cell can only contain an _______ chromosome, while the sperm cell produced has a ______% chance of containing a _______ and a ______% chance of containing an _______. Therefore, the __________ determines ...
... chromosomes separate in __________________, the sex chromosomes separate also. The resulting egg cell can only contain an _______ chromosome, while the sperm cell produced has a ______% chance of containing a _______ and a ______% chance of containing an _______. Therefore, the __________ determines ...
Principles of Biology Lake Tahoe Community College
... 1. fruit flies 2. wild type 2. behavior of gene w/ behavior of chromosomes 3. gene for eye color found on sex chromosome II. Linked genes A. near each other on same chromosome, tend to be inherited together 1. Linked genes – chromosomal basis a. X linked b. Y linked 2. X inactivation in female mamma ...
... 1. fruit flies 2. wild type 2. behavior of gene w/ behavior of chromosomes 3. gene for eye color found on sex chromosome II. Linked genes A. near each other on same chromosome, tend to be inherited together 1. Linked genes – chromosomal basis a. X linked b. Y linked 2. X inactivation in female mamma ...
Sex Determination and Sex Chromosomes
... o Wrasses also can change sex When the male in a group dies or leaves, one of the females changes to a male o In clown fish, just the opposite occurs In C. elegans, things are even stranger Sex determination Sexual reproduction usually consists of the alternation of haploid and diploid cells C ...
... o Wrasses also can change sex When the male in a group dies or leaves, one of the females changes to a male o In clown fish, just the opposite occurs In C. elegans, things are even stranger Sex determination Sexual reproduction usually consists of the alternation of haploid and diploid cells C ...
CH 3 GENETICS - TEST – GIFT GUIDE HINTS due
... Bb rabbit would be Black not white, and a Nn snake would be Normal not albino. The only way it could be recessive (white or albino) is either bb or nn. Capital = upper case letters represent the dominant allele (B or N or P, etc.) Chromosome = a tightly coiled (packaged up) molecule of DNA. Humans h ...
... Bb rabbit would be Black not white, and a Nn snake would be Normal not albino. The only way it could be recessive (white or albino) is either bb or nn. Capital = upper case letters represent the dominant allele (B or N or P, etc.) Chromosome = a tightly coiled (packaged up) molecule of DNA. Humans h ...
What are dominant genes?
... father’s genetic information was passed in sperm cells, your mother’s through her egg cells. These genetic instructions are located in the nucleus of every cell, stored within chromosomes. The chromosomes are made up of genes; a gene is a section of a chromosome, that codes for a specific trait. Hen ...
... father’s genetic information was passed in sperm cells, your mother’s through her egg cells. These genetic instructions are located in the nucleus of every cell, stored within chromosomes. The chromosomes are made up of genes; a gene is a section of a chromosome, that codes for a specific trait. Hen ...
Which of the following organisms are autotrophs? algae
... spends most of its time in mitosis cytokinesis interphase cleavage ...
... spends most of its time in mitosis cytokinesis interphase cleavage ...
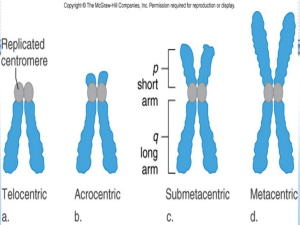
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.