![SCI.9-12.B-2.6 - [Indicator] - Summarize the characteristics of the cell](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000150435_1-912fe69b2f4dbf751a0e7f8b49905e2e-300x300.png)
SCI.9-12.B-2.6 - [Indicator] - Summarize the characteristics of the cell
... In plant cells, the cell wall begins to form first. Then the cell membrane divides. ...
... In plant cells, the cell wall begins to form first. Then the cell membrane divides. ...
MUTATIONS - Valhalla High School
... protein that does not work correctly • In some rare cases, it may have a positive effect • Can be passed on to offspring ...
... protein that does not work correctly • In some rare cases, it may have a positive effect • Can be passed on to offspring ...
MS-LS3-2 Evidence Statements
... result in different amounts of genetic variation in offspring relative to their parents, including that: i. In asexual reproduction: 1. Offspring have a single source of genetic information, and their chromosomes are complete copies of each single parent pair of chromosomes. 2. Offspring chromosomes ...
... result in different amounts of genetic variation in offspring relative to their parents, including that: i. In asexual reproduction: 1. Offspring have a single source of genetic information, and their chromosomes are complete copies of each single parent pair of chromosomes. 2. Offspring chromosomes ...
Know More About Genetic Disease
... 6. What are Chromosomes? Chromosomes are the genetic material within a cell nucleus. Except some specialized cells like red blood cells and gametes, every cell in our body carries 23 pairs of chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs are known as autosomes and show no sex difference. The remaining pair are know ...
... 6. What are Chromosomes? Chromosomes are the genetic material within a cell nucleus. Except some specialized cells like red blood cells and gametes, every cell in our body carries 23 pairs of chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs are known as autosomes and show no sex difference. The remaining pair are know ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide: Mendel and Heredity Section 1 – Origins of
... does NOT clot properly; a serious injury may cause them to bleed to death. 7. Human males inherit the recessive allele for colorblindness and hemophilia from their __________________, who gives them their X sex chromosome. Females don’t usually inherit these diseases because they inherit two X sex c ...
... does NOT clot properly; a serious injury may cause them to bleed to death. 7. Human males inherit the recessive allele for colorblindness and hemophilia from their __________________, who gives them their X sex chromosome. Females don’t usually inherit these diseases because they inherit two X sex c ...
Genetic Baby Activity Teacher Guide
... This is a picture of a human karyotype, which represents all the chromosomes in the each human cell. 12. How many chromosomes are in each human cell? ...
... This is a picture of a human karyotype, which represents all the chromosomes in the each human cell. 12. How many chromosomes are in each human cell? ...
Unit 08 Notes - Pierce College
... these 46 chromosomes consist of doubled (replicated) DNA molecules, so there are 92 DNA molecules total. Each DNA molecule has supercoiled into chromatids, so there are 92 chromatids, held together by kinetochores as 46 chromosomes. The daughter cells also contain 46 chromosomes, only these chromoso ...
... these 46 chromosomes consist of doubled (replicated) DNA molecules, so there are 92 DNA molecules total. Each DNA molecule has supercoiled into chromatids, so there are 92 chromatids, held together by kinetochores as 46 chromosomes. The daughter cells also contain 46 chromosomes, only these chromoso ...
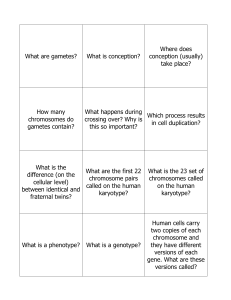
CH 3 Review Game Cards
... What is the What are the first 22 difference (on the chromosome pairs cellular level) called on the human between identical and karyotype? fraternal twins? ...
... What is the What are the first 22 difference (on the chromosome pairs cellular level) called on the human between identical and karyotype? fraternal twins? ...
Warm-up - Foothill Technology High School
... have either Will the F1 grey always have wings aand grey body and flies normal wingshave OR small a black body with will black always wing sizes? small wings, like their parents ...
... have either Will the F1 grey always have wings aand grey body and flies normal wingshave OR small a black body with will black always wing sizes? small wings, like their parents ...
Beyond Mendel
... have either Will the F1 grey always have wings aand grey body and flies normal wingshave OR small a black body with will black always wing sizes? small wings, like their parents ...
... have either Will the F1 grey always have wings aand grey body and flies normal wingshave OR small a black body with will black always wing sizes? small wings, like their parents ...
Chapter 10: Genes and Chromosomes
... • In order to make the enzymes, RNA polymerase must move along the genes on the chromosomes, producing mRNA in the process • Before the RNA polymerase can get to the desired genes, it must first attach to the promoter region near the genes • One the RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter, it can mo ...
... • In order to make the enzymes, RNA polymerase must move along the genes on the chromosomes, producing mRNA in the process • Before the RNA polymerase can get to the desired genes, it must first attach to the promoter region near the genes • One the RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter, it can mo ...
OCR GCSE (9-1) Biology Lesson Element Mitosis and Meiosis
... The activity is about mitosis and meiosis in animal cells. This activity is designed to access higher order thinking, analysing and creating skills. Learners should know that nucleus of a cell contains genetic information. They should be aware what a gene, chromosome and DNA are. They should also ha ...
... The activity is about mitosis and meiosis in animal cells. This activity is designed to access higher order thinking, analysing and creating skills. Learners should know that nucleus of a cell contains genetic information. They should be aware what a gene, chromosome and DNA are. They should also ha ...
Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
... chromosome 21, called a balanced translocation. The parent may be unaware that he or she is a carrier of this balanced translocation, since it does not affect his or her health. However, this parent can pass the unbalanced translocation to his or her child. Routine chromosome analysis and fluorescen ...
... chromosome 21, called a balanced translocation. The parent may be unaware that he or she is a carrier of this balanced translocation, since it does not affect his or her health. However, this parent can pass the unbalanced translocation to his or her child. Routine chromosome analysis and fluorescen ...
(r ). - isb
... NON-HOST RESISTANCE – plant could not by any means support the propagation of an otherwise pathogenic microbe. (unsuitable conditions for survival and propagation of most of fungi and bacteria). Plants are completely immune to infection. HOST-RESISTANCE - plant could support the propagation of ...
... NON-HOST RESISTANCE – plant could not by any means support the propagation of an otherwise pathogenic microbe. (unsuitable conditions for survival and propagation of most of fungi and bacteria). Plants are completely immune to infection. HOST-RESISTANCE - plant could support the propagation of ...
Scientific-method
... Cell theory is the theory that ALL living things have come from one place. An organelle is a cell part designed for a specific function. Plasma membrane is the thin outer layer of the cell that regulates things from entering and leaving the cell. Nucleus is an atom that is located inside the nucleou ...
... Cell theory is the theory that ALL living things have come from one place. An organelle is a cell part designed for a specific function. Plasma membrane is the thin outer layer of the cell that regulates things from entering and leaving the cell. Nucleus is an atom that is located inside the nucleou ...
(lectures 26
... the Finding Nemo fish). (h) Self-sterility. In plants, have a particular multi-allele locus for which you can mate if the two individuals do not have any allele in common, or if the female plant tissue does not share any allele with the pollen that fertilizes it. This leads to many alleles at roughl ...
... the Finding Nemo fish). (h) Self-sterility. In plants, have a particular multi-allele locus for which you can mate if the two individuals do not have any allele in common, or if the female plant tissue does not share any allele with the pollen that fertilizes it. This leads to many alleles at roughl ...
So you say you want extra credit…
... 1. Allele — alternative forms of a gene for each variation of a trait of an organism co-dominant alleles-Two different alleles at a locus are responsible for different phenotypes, and both alleles affect the phenotype of the heterozygote. For example, consider the situation where there are three all ...
... 1. Allele — alternative forms of a gene for each variation of a trait of an organism co-dominant alleles-Two different alleles at a locus are responsible for different phenotypes, and both alleles affect the phenotype of the heterozygote. For example, consider the situation where there are three all ...
BSC 2010C SAMPLE TEST 3
... At the completion of meiosis, the daughter cells will consist of genetic information that is (14)_______ and has (15)-________ chromosome number as the parent cell. a. b. c. d. ...
... At the completion of meiosis, the daughter cells will consist of genetic information that is (14)_______ and has (15)-________ chromosome number as the parent cell. a. b. c. d. ...
AP Biology Notes: Recombinants Thomas Hunt Morgan from
... which provided convincing evidence that Mendel's inheritable factors are located on chromosomesMorgan selected the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, as the experimental organism because these flies: *Are easily cultured in the laboratory * Are prolific breeders *Have a short generation time ...
... which provided convincing evidence that Mendel's inheritable factors are located on chromosomesMorgan selected the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, as the experimental organism because these flies: *Are easily cultured in the laboratory * Are prolific breeders *Have a short generation time ...
genes
... (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). • The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. • The recombination frequency between cn and vg is ...
... (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). • The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. • The recombination frequency between cn and vg is ...
Beyond Mendel
... have either Will the F1 grey always have wings aand grey body and flies normal wingshave OR small a black body with will black always wing sizes? small wings, like their parents ...
... have either Will the F1 grey always have wings aand grey body and flies normal wingshave OR small a black body with will black always wing sizes? small wings, like their parents ...
Genetic Algorithms
... Evaluate the individual fitnesses of the offspring (set best) Replace worst ranked part of population with offspring ...
... Evaluate the individual fitnesses of the offspring (set best) Replace worst ranked part of population with offspring ...
Chromosomal Anomalies
... of the vertebrae (bones) of the spinal column without apparent damage to the spinal cord. 2. Meningocele: The meninges, or protective covering around the spinal cord, has pushed out through the opening in the vertebrae in a sac called the "meningocele." However, the spinal cord remains intact. This ...
... of the vertebrae (bones) of the spinal column without apparent damage to the spinal cord. 2. Meningocele: The meninges, or protective covering around the spinal cord, has pushed out through the opening in the vertebrae in a sac called the "meningocele." However, the spinal cord remains intact. This ...
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.