Father of Modern Genetics
... phenotype that is of normal intelligence and upon the onset of puberty exhibits unusually long arms, sparse body hair, undeveloped testes and enlarged breasts ...
... phenotype that is of normal intelligence and upon the onset of puberty exhibits unusually long arms, sparse body hair, undeveloped testes and enlarged breasts ...
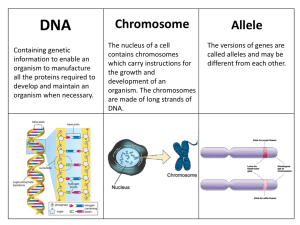
DNA, Genes and Chromosomes
... It appears in all living organisms How big is human DNA? Estimates vary from between 1.5 and 3 m long Other organisms have DNA with shorter or longer strands ...
... It appears in all living organisms How big is human DNA? Estimates vary from between 1.5 and 3 m long Other organisms have DNA with shorter or longer strands ...
bio 15 midterm exam 2 qa 141112
... b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids e. Salt 3. Which is the correct term for compounds that do mix with water? a. phospholipids b. hydrophobic c. hydrophilic d. protein e. hydrogen bonded 4. Which of the following do nucleic acids and proteins have in common? a. They are both made of amino acids. b. Their ...
... b. DNA c. Proteins d. Lipids e. Salt 3. Which is the correct term for compounds that do mix with water? a. phospholipids b. hydrophobic c. hydrophilic d. protein e. hydrogen bonded 4. Which of the following do nucleic acids and proteins have in common? a. They are both made of amino acids. b. Their ...
a-bugno.vp:CorelVentura 7.0
... ZOO-FISH may be due to the fact that this technique shows homology of larger segments without providing any information about the organization of smaller units like genes, so small rearrangements may go undetected. Presumably, an inversion occurred during karyotype evolution of the arctic fox reloca ...
... ZOO-FISH may be due to the fact that this technique shows homology of larger segments without providing any information about the organization of smaller units like genes, so small rearrangements may go undetected. Presumably, an inversion occurred during karyotype evolution of the arctic fox reloca ...
Mendelian Genetics
... and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. As a basis for understanding this concept: » BI2. d. Students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and female gametes (fertilization). » BI2. e. Students know why app ...
... and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. As a basis for understanding this concept: » BI2. d. Students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and female gametes (fertilization). » BI2. e. Students know why app ...
chapter twelve INHERITANCE PATTERNS AND HUMAN GENETICS
... DNA in chromosomes contain information to make proteins. Geneticists use their knowledge of DNA and the way chromosomes behave to study how traits are inherited and expressed. ...
... DNA in chromosomes contain information to make proteins. Geneticists use their knowledge of DNA and the way chromosomes behave to study how traits are inherited and expressed. ...
Hereditary diseases of a man
... 1) Spontaneous (natural) mutations and induced (artificial) mutations. Spontaneous mutations happen in the nature without intervention of the person. The person receives artificial mutations purposefully. 2) Dominant mutations and recessive mutations. Dominant mutation is phenotypically shown in tha ...
... 1) Spontaneous (natural) mutations and induced (artificial) mutations. Spontaneous mutations happen in the nature without intervention of the person. The person receives artificial mutations purposefully. 2) Dominant mutations and recessive mutations. Dominant mutation is phenotypically shown in tha ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems Chromosomes, Karyotyping and Sex Linkage
... 3. In preparing cells for karyotyping, colchicine is added to stimulate cell division stop cell division at metaphase, since this is the only time chromosomes become visible. 4. Nondisjunction of all chromosome pairs in meiosis could result in polyploidy, but polyploid individuals cannot survive. 5. ...
... 3. In preparing cells for karyotyping, colchicine is added to stimulate cell division stop cell division at metaphase, since this is the only time chromosomes become visible. 4. Nondisjunction of all chromosome pairs in meiosis could result in polyploidy, but polyploid individuals cannot survive. 5. ...
Other big difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic
... • If one of these cells mutated so it was resistant, how many resistant cells in 7 more hours? ...
... • If one of these cells mutated so it was resistant, how many resistant cells in 7 more hours? ...
Pre – AP Biology
... (Brown, blue, green eye color. These are three different versions or DNA sequences of a single gene, but they all are making the eye color.) Each trait needs two alleles. One from each parent to be made or “expressed”. Dominant alleles are given capital letters. (These are like books or recipe cards ...
... (Brown, blue, green eye color. These are three different versions or DNA sequences of a single gene, but they all are making the eye color.) Each trait needs two alleles. One from each parent to be made or “expressed”. Dominant alleles are given capital letters. (These are like books or recipe cards ...
lecture4(GS351)
... Expressing a regulatory gene in the wrong place can have disastrous consequences!!! Example: Antennapedia gene in fruit flies Antennapedia gene is normally only transcribed in the thorax; legs are made. ...
... Expressing a regulatory gene in the wrong place can have disastrous consequences!!! Example: Antennapedia gene in fruit flies Antennapedia gene is normally only transcribed in the thorax; legs are made. ...
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
... 2 different alleles this is called heterozygous and the cell always uses the ...
... 2 different alleles this is called heterozygous and the cell always uses the ...
Full Text - Harvard University
... the S. pombe/S. kambucha hybrid must receive all three killer genes by random segregation to be fully sheltered from all three poisons (Figure 1). To add to the complication, two of the killer genes interact: the killer gene on chromosome 2 is stronger when there is also a killer gene on chromosome ...
... the S. pombe/S. kambucha hybrid must receive all three killer genes by random segregation to be fully sheltered from all three poisons (Figure 1). To add to the complication, two of the killer genes interact: the killer gene on chromosome 2 is stronger when there is also a killer gene on chromosome ...
Mutation Notes
... ►What would happen if a single base were lost from a DNA strand? ►A mutation in which a single base is added or deleted from DNA is called a frameshift mutation because it shifts the reading of codons by one base. As a result, every codon after the deleted base would ...
... ►What would happen if a single base were lost from a DNA strand? ►A mutation in which a single base is added or deleted from DNA is called a frameshift mutation because it shifts the reading of codons by one base. As a result, every codon after the deleted base would ...
PPT File
... • The behavior of chromosomes during meiosis and fertilization is responsible for most of the variation that arises in each generation • Three mechanisms contribute to genetic variation – Independent assortment of chromosomes – Crossing over – Random fertilization ...
... • The behavior of chromosomes during meiosis and fertilization is responsible for most of the variation that arises in each generation • Three mechanisms contribute to genetic variation – Independent assortment of chromosomes – Crossing over – Random fertilization ...
Cyber-genetic Neo-Plasticism:
... A procedure that gives more chances of survival to those can cope with the environment. Good individuals has more chance to pass on their characteristics. All individuals tend to be better when time passes. ...
... A procedure that gives more chances of survival to those can cope with the environment. Good individuals has more chance to pass on their characteristics. All individuals tend to be better when time passes. ...
X-linked Genes
... ◦ People who have hemophilia are missing the protein to clot blood ◦ They can bleed to death by minor cut. ...
... ◦ People who have hemophilia are missing the protein to clot blood ◦ They can bleed to death by minor cut. ...
BPS 555
... telomere can result in fusion with another broken chromosome or can be degraded. •Establish chromosome positioning •Ensure complete replication. The end replication problem is solved by telomerase, an RNA-protein enzyme. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase - RNA-dependent DNA polymerase - carries ...
... telomere can result in fusion with another broken chromosome or can be degraded. •Establish chromosome positioning •Ensure complete replication. The end replication problem is solved by telomerase, an RNA-protein enzyme. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase - RNA-dependent DNA polymerase - carries ...
Heredity and Evolution - E
... For example- Hands of human beings and wings of birds. Analogous organs- Organs which have different basic structure and origin but have similar function are called analogous organs. For example(1) wing of bat and wing of bird. (2) wing of birds and wing of insect. ...
... For example- Hands of human beings and wings of birds. Analogous organs- Organs which have different basic structure and origin but have similar function are called analogous organs. For example(1) wing of bat and wing of bird. (2) wing of birds and wing of insect. ...
Overview of Basic Genetic Concepts and Terminology
... In a recent build of the human genome, annotation data are available for approximately 32,000 genes with around 18,000 confirmed genes. ...
... In a recent build of the human genome, annotation data are available for approximately 32,000 genes with around 18,000 confirmed genes. ...
hereditary diseases of a man - Ставропольская Государственная
... to have differentiated between heritable and environmental variations. However, the term mutation is now used in a rather strict sense to cover only those changes, which alter the chemical structure of the gene at the molecular level. These are commonly called gene mutations or point mutations. In p ...
... to have differentiated between heritable and environmental variations. However, the term mutation is now used in a rather strict sense to cover only those changes, which alter the chemical structure of the gene at the molecular level. These are commonly called gene mutations or point mutations. In p ...
File - Coleman Honors Biology
... One gene results in many phenotypic effects. Genes are carried on autosomes (chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes). Simple dominance and recessive inheritance showing complete dominance in both homozygous dominant and heterozygous genotypes. A gene at one location alters the phenotypic expressio ...
... One gene results in many phenotypic effects. Genes are carried on autosomes (chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes). Simple dominance and recessive inheritance showing complete dominance in both homozygous dominant and heterozygous genotypes. A gene at one location alters the phenotypic expressio ...
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.